Introduction
- Outdoor activities such as sports, swimming, jungle trekking, mountain climbing and kayaking expose us to the sun for many hours
- Over-exposure in the sun without adequate protection in early life may lead to skin cancers later in life
Risks
Sun exposure may cause:
- Sunburn – can lead to permanent skin damage
- Premature aging – appearance of wrinkles, coarse leathery skin and sunspots
- Skin cancer – as a result of too much sun exposure
- Damage to the eyes by ultraviolet (UV) rays
There are three types of UV rays that can damage our skin:
- UVA rays penetrate deeply into the skin. They may react with some medicine and cosmetics to cause severe sunburn
- UVB rays reach the top layer of the skin and are the primary agent responsible for sunburn
- UVC rays are absorbed almost completely by the atmosphere and hence do not cause skin damage
Signs and symptoms
In mild sunburn:
- There is mild redness and swelling, tenderness and itchiness as well as a hot, dry, tight feeling
- Your muscles may be sore and your skin peels after a couple of days
In severe sunburn:
- There is bright redness, severe swelling and blistering
- You may experience severe pain and an inability to tolerate contact with your clothing
- You may have fever, chills, weakness and should consult a doctor immediately
Redness begins within 2-4 hours of exposure and reaches a peak 24-48 hours later.
Prevention
- Avoid the sun between 10 am and 4 pm when the sun’s rays are strongest
- Use a broad spectrum sunscreen that protects against UVA and UVB rays and has a SPF of at least 15, even on cloudy days
- Stay in the shade as much as possible throughout the day
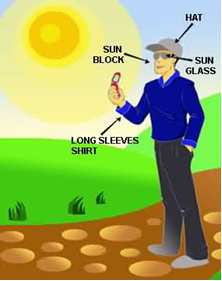
- Use a wide-brimmed hat or sun visor to protect your neck, head and eyes
- Wear tightly woven clothing and sunglasses with UV protection
Precautions
Some medicines, cosmetics and chemicals react with sunlight to cause rashes or severe sunburn. These include:

- Anti-allergy and anti-itch medicines
- Antibiotics
- Mood relaxing medicines
- Anti-diabetic medicines
- Acne treatments (link to Treatment of acne)
- Oral contraceptives
- Some antibacterial agents found in medicated soaps and facial preparations
- Some deodorants or deodorant agents in soaps or perfumes
- Some herbal products, especially those in the citrus, umbilliferae (celery and fennel) and St. John’s Wort families
- Cosmetics that contain alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) also may increase sun sensitivity and susceptibility to sunburn. Look for recommended sunburn alert statement on products that contain AHAs.
Melanin is a natural pigment in the skin that absorbs ultraviolet (UV) rays and causes tanning of the skin
- It offers protection from the sun’s damaging UV rays
- In general, people with fairer skin have less melanin and hence are more sensitive to UV rays
Anyone’s skin can be damaged by the sun, but some people are more at risk,including those who have:
- Pale, fair or sensitive skin which is less melanin and hence more sensitive to UV rays
- A family member who has had skin cancer
- A large number of freckles or moles
- Been treated with skin canceer
- Blonde,red or light brown hair
If you are taking any medicine, ask your pharmacist whether it can cause your skin to become sensitive to UV rays.
Be aware and protect yourself from the sun when using such medicines.
| Last reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Nour Hanah bt. Othman |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Nazhatussima bt. Suhaili |







