Pencil grip in young children follows developmental age of children and may vary between cultures (Tseng,1998). Children commonly begin by holding the pencil with primitive grip and later the pencil grip will be more mature according to the developmental age of the child (Figure 1).
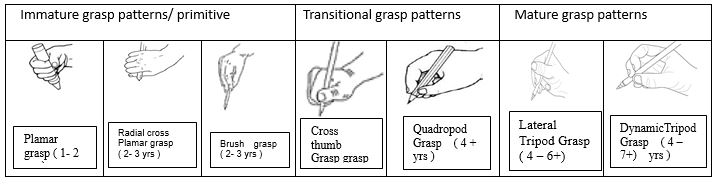
Figure 1
Below are some common difficulties in children to develop good pencil grip.
- Poor muscle tone- problem in fine mootr skill and coordination
- Poor control of shoulder movements for drawing long lines and moving the hand across the page when writing.
- Difficulty sitting erect ease and comfort when engaging in drawing and handwriting tasks.
- Poor basic graphic abilities for creating straight and curved lines. These abilities should be acquired before the child starts to learn to print. A child with good basic graphic abilities is able to pre-plan movements for forming lines without continuous visual guidance.
- Avoidance of tasks that are difficult and require attention and persistence. Learning a new motor skill requires dedicated practice, with attention to getting it right and being able to learn from one’s mistakes.
- Poor handwriting teaching practices, which emphasize tracing letters, over reliance on visual feedback and emphasis on correct letter sizing before child has learned the basic movement patterns for.
Writing Aids and adaptation to help in children with pencil grips
If your child’s poor pencil grip is affecting handwriting and causing pain and fatigue, then just telling your child to “hold the pencil better” is NOT going to help!. The child need writing aids and therapeutic strategies which will help he/she to improve her hand writing skills.
Below are some writing aids and adaptation that might help your child:
- Facilitate Tripod Grasps : Use Stetro grips, and triangular pencils.

- Writing muscle tension and fatigue: Using a wider-barreled pencil/ foam grip

- To gain more mobility of the radial digits: Children may hold a small eraser against their palms with the ulnar digits, allowing for more dynamic movement of the pencil

- Older children with hand hypotonicity: holding the pencil shaft between the web space of the index and middle fingers with thumb opposition may give them a viable pencil grasp.

- To encourage the delicate stability-mobility balance of a functional pencil grasp : use of external supports such as microfoam surgical tape supports, ring splints, and neoprene splints (Benbow, 1995)

- For relaxed and slanted pencil position : Using a rubber band sling

References
- Pre-writing and Hand Writing Skills,Occupational Therapy for Children, fifth edition, Jane Case-Smith,587-610
- Tseng,M.H.(1998).Development of pencil grip position in preschool children. Occupational Therapy Journal of Research, 18, 207-224
- Amundson,S.J.(1995).Evaluation tool of children’s handwriting. Homer, AK:O.T.KIDS
- Benbow,M.(1995).Principle and practices of teaching handwriting. In A. Henderson & C. Pehoski(Eds), Hand function in the child: Foundation for remediation
| Last Reviewed | : | 30 April 2018 |
| Writer/Translator | : | Shahirah binti Md Rashid |
| Accreditor | : | Peremalatha A/P Sundram |







