Introduction
Rhinitis is an inflammation of the nose. Its characterized by runny nose, itching, sneezing and nasal congestion. It is divided into acute and chronic rhinitis. Acute rhinitis when the symptom less than 1 month. Examples are infective rhinitis like influenza or sensitive nose when expose to perfumes or chemical. Chronic rhinitis if the symptoms persists for more than six weeks. Chronic rhinitis can be further divided into allergic and non-allergic rhinitis.

House Dust mite
- Allergic rhinitis: can divided to two type; seasonal and perennial. The easonal usually associated with pollen and common in European country like hay fever. It seldom occur in Malaysia.
- Perennial Allergic rhinitis: It is an allergic response to moulds, house dust mites, animal dander, foods, etc act as allergen. The allergen combine with antibody at mast cells. The mast cells release histamines which cause dilation of blood vessels, redness of skin and swollen membranes. When this occurs in the nose, the symptoms of allergic rhinitis are manifested.
- Non allergic rhinitis cause by imbalance between sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve activity name as Vasomotor rhinitis. It aggravated by changes in temperature and stress, felling sad or happy.
- Medications can cause rhinitis or worsen it in people with allergies. Prolonged use of nasal decongestants can worsen rhinitis. Some blood pressure medications such as beta blockers and vasodilators can cause rhinitis.
- Hormonal changes in pregnancy cause “Rhinitis in Pregnancy”. The expecting mother will recover once the baby is delivered.
Sign & Symptom
Symptoms of Rhinitis include sneezing, rhinorrhea(runny nose), nasal congestion, and itching of the nose, palate and ears: eye irritation, itching and headaches.
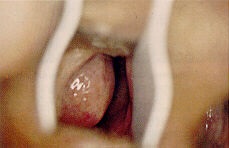
Inferior Turbinate
Complications
In severe and persistent non-allergic rhinitis, complication that may develop such as:
- Nasal polyps. These are soft benign growths that develop on the lining of nose or sinuses due to chronic inflammation. Small polyps may not cause problems, but larger ones block the airflow through nose, making it difficult to breathe.
- Chronic sinusitis. Prolonged rhinitis may increase chances of developing sinusitis (an infection or inflammation of the membrane that lines the sinuses). Sinusitis causes pain, tenderness and swelling around the eyes, cheeks, nose or forehead, foul smelly, greenish nasal discharge. The infection can spread to the eye and brain and can cause death.
- Middle ear infections. Increased fluid and nasal congestion may lead to middle ear infections causing deaf.
Treatment
Avoidance:
Try to avoid allergen that you can identify. Clean area with dust or the area that you commonly expose to get rhinitis such as room area, bed, pillow, carpet or curtain. Fan and air conditioner also should clean from dust. Avoid pets and food that cause rhinitis.
Medical
- Fever mainly due to viruses. Antipyritic can prescribe fo this problem. Antibiotic only prescribe when infection due to bacteria.
- Anti-histamines: It provides good relief for mild to moderate symptoms.
- Newer antihistamines that are long-acting and less likely to cause drowsiness have been found to be useful.
- Decongestants: It is helpful in reducing symptoms such as nasal congestion.
- Corticosteroids: Usually in the form of nasal spray to reduce nasal block.
Surgical
Rhinitis that are due to structural problem like enlarge turbinate, nasal polyps, enlarged adenoids and deviated septum can be corrected with surgery.
Prevention
- Avoidance of allergens is the best treatment in allergic and vasomotor rhinitis
- Try to avoid pets, carpets and keep house clean from dust.
- Please do not smoke and choose a non-smoking environment. Complete avoidance of environmental allergens may be impossible but it can be minimised to prevent from another attack of rhinitis.
Rehabilitation
Preventive is better then cure. No definitive cure for allergic rhinitis except avoidance and healthy life style.
| Last reviewed | : | 20 June 2014 |
| Writer | : | Dr. A. Khalek Abd Rahman |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Fuziah Paimin |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Hj. Abd. Razak Hj. Ahmad |







