Painful red eye usually indicates severe eye problem that need immediate medical attention, as some conditions may cause permanent blindness if treatment is delayed.
Common and important causes of painful red eye include corneal ulcer, acute glaucoma and uveitis.
1. Corneal ulcer
The cornea is the central, outermost layer of the eye. It is the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye and helps to focus light onto the retina. Corneal infection occurs when bacteria gain entry into the cornea through a scratch or breakdown in the corneal surface. Contact lens user has high risk of getting corneal ulcer if instructions on contact lens care not strictly followed.
Photograph of left eye
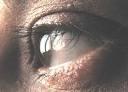
Cornea
Photograph of eye with contact lens
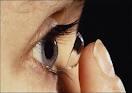
Contact lens(Prolonged use and poor hygiene can cause ulcer)
Photograph showing red eye due to corneal ulcer
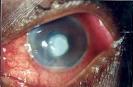
Corneal ulcer
Sign and symptoms of corneal ulcer (infective keratitis) include:
- Severe eye pain
- Redness
- Tearing
- Foreign body sensation
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Blurring of vision
In some contact lens users, the cornea may become somewhat insensitive to pain, and only symptoms of redness and irritation may appear.
A corneal ulcer is a serious, vision threatening problem. Some bacteria can be extremely aggressive, and the cornea can actually perforate (leading to endophthalmitis, or infection within the eyeball). Therefore, corneal ulcer needs urgent medical attention.
2. Acute Glaucoma
This type of glaucoma is considered as an ocular emergency. Acute glaucoma occurs following acute rise in eyeball pressure due to problem in drainage of fluid from inner part to outer part of eyeball. As a result the eyeball became hard and it caused intense pain.
Photograph of eye with acute glaucoma
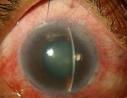
Red eye with hazy cornea and semi dilated pupil
Sign and symptoms of acute glaucoma:
- Sudden onset of pain
- Blurring of vision
- Seeing haloes (colourful ring around light)
- Red eye
- Headache
- Nausea or even vomiting
It is important for the patient with acute glaucoma to be managed by eye doctor in order to abort the attack. Delayed in treatment will leads to permanent loss of vision.
3. Uveitis
Uveitis refers to a group of ocular inflammatory diseases that affect inner lining of the eyeball such as the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Some cases of uveitis is of unknown cause while others may be related to systemic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic infection and even malignancy. One or both eyes can be affected. Uveitis is not contagious (spreading to other people).
Photograph of eye with uveitis
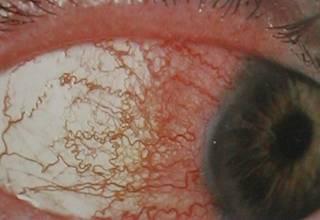
Redness localised around the cornea
Signs and symptoms of uveitis:
- Eye pain
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Blurring of vision
- Eye redness (usually a “flush” of redness in a ring around the cornea)
- Sometimes floaters (seeing something floating in front of affected eye).
Eye doctor can diagnose uveitis through proper examination with special instrument such as slit lamp. This condition needs appropriate treatment and follow up. Cases of recurrent uveitis and bilateral involvement may indicate systemic diseases. In this case, it is important to investigate (by doing few blood tests and X-ray) to determine the disease so as appropriate treatment is given. Delay and improper in treatment may cause complication such as cataract and glaucoma.
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Joseph Vijaya Alagaratnam |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Rosniza bt. Ab. Razak |







