Diabetes and Insulin
Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or unable to use insulin properly (Type 2 Diabetes). Insulin is a hormone made by our pancreas that allows our body to use sugar (glucose) from the food that we consumed. Insulin helps keep our blood sugar level from getting too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia). Hence, for diabetic patients, insulin injection is needed to help control the sugar to avoid hyperglycemia. Therefore, the correct insulin technique is very important to make sure patients receive optimal response from the insulin.
Insulin Technique
The correct sequence for injection technique should be:
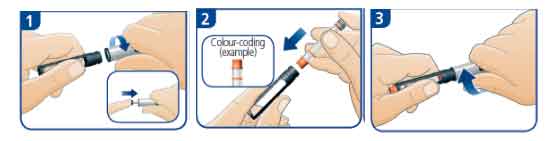
A) Preparing the pen
- Pull off the pen cap and unscrew the pen . If the rod is sticking out, push it all the way back in.
- Insert the insulin cartridge into the cartridge holder, colour-coded cap end first.
- Screw the pen back together and twist it until you feel or hear a click. If the cartridge contains an insulin suspension (cloudy insulin) you must always mix (resuspend) it evenly before use (refer to TIPS).
TIPS:
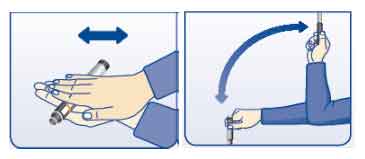
If the cartridge contains a cloudy insulin e.g. Mixtard 30, Insulatard, Insuman Basal, Insuman Comb 30, you must always mix it evenly before EACH use.
To mix, gently roll the pen between your palms 10 times or move the pen up and down 10 times between the 2 positions as shown below:
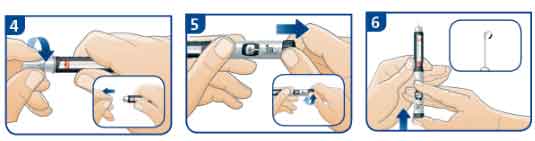
B) Checking the insulin flow (Priming)
- Before injection, always attach a new needle. Remove both the outer and inner needle caps, and dispose of the inner needle cap. Keep the outer needle cap to remove the needle from the pen after injection.
- Pull out the dose button. Turn the dose button to select 2 units.
- Keep the pen upright and tap the cartridge holder gently to raise any air bubbles. Press the dose button all the way in until it clicks and the dial returns to 0. If insulin does not appear at the tip of the needle, repeat steps 4 to 6, until a drop of insulin appears
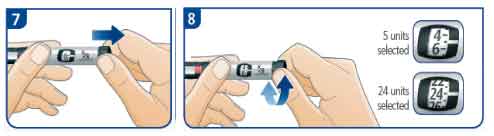
C) Setting your dose
- Pull out the dose button and turn the dial until the white indicator line is level with the required number of units you need to inject.
- Adjust the dose by dialling up or down, if necessary. No insulin will be released until the dose button is pressed.
D) Injecting your dose
- Push the pen gently into your skin, then press the dose button until you feel or hear a click and the dose indicator lines up with 0. Leave the needle under the skin for at least 10 seconds (keeping the button pushed down), and then slowly pull the pen out.
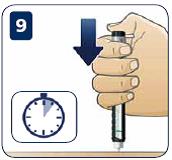
- After you have withdrawn the needle from your skin, put the outer needle cap back on, then remove and dispose of the needle safely. Replace the pen cap after use.
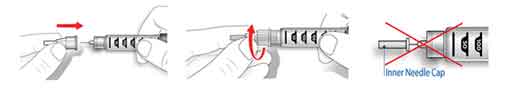
Reusing needles
Reuse of needles can lead to lipohypertrophy which appears as hard lumps at the injection sites. These lumps can affect the way insulin is absorbed, making it more difficult to keep your blood glucose on target. Reusing of needles also increases the risk of infection.
It is recommended needles are used only ONCE.
Sites of injection
There are four main sites of injection: Abdomen, thigh, buttocks and arms. Insulin is absorbed at different rates depending on where you inject:
- Fastest from the abdomen (stomach)
- A little slower from the arms
- Even slower from the legs
- Slowest from the buttocks
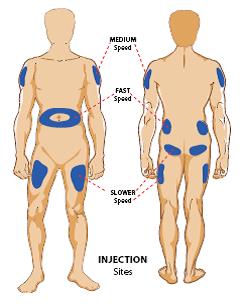
TIPS: The recommendation is to use your abdomen, as insulin is absorbed more consistently there.
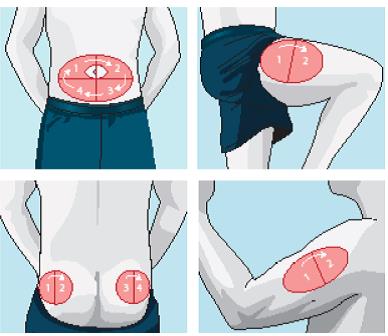
TIPS: Choose a slightly new location for each injection to avoid developing hard lumps (lipohypertrophy). For example, if all injections are given in the abdomen, note of where the last injection was given and move the next one about an inch to one side or the other. Continue to move the injection site until all available sites are covered.
Insulin Storage
- Unused insulin stock must be kept in the fridge (NOT FREEZER).
- The insulin pen with the currently in use cartridge should be kept at room temperature
- Any insulin that is not kept in the fridge will expire after 1 month.
- Insulin pens should not be left in the car or under direct sunlight.
- Never leave the needle with the insulin pen.
Side Effects
Insulin can cause HYPOGLYCEMIA (low blood sugar). Hypoglycemia is defined as blood glucose of less than 4.0 mmol/L. The symptoms include palpitations, tremor, anxiety, cold sweat and hunger. Hypoglycemia can happen if:
- Missed or too little meals after insulin injection
- Too much exercise
- Insulin dose is too high
- Kidney problems
If hypoglycemia happens, take some sugary snack (for example 1 table spoon of honey, ¾ cup of juice, 3 tea spoons of table sugar).
Always remember to bring along some sugary snack with you in case you develop any hypoglycemia symptoms.
References
- Practical Guide to Insulin Therapy in Type 2 diabetes Mellitus. Ministry of Health Malaysia
- Clinical Practice Guideline Maangement of Type 2Diabetes Mellitus 5th Edition 2015.
- http://www.diabeteswellness.net/sites/default/files/Injections.pdf
- Novopen 4 Quick Guide.
| Last Reviewed | : | 15 September 2016 |
| Writer/Translator | : | Candy Lim Li Hui |
| Accreditor | : | Angeline Tan Meng Wah |







