Introduction
In common cases, people are confused with hyperopia and presbyopia. Both can cause difficulty in reading and fine work. Presbyopia and hyperopia are actually two different eye problems.
Any objects will be clear if the image formed on the retina. There are three components of the eye that helps to see clearly:
- The power of the cornea-outer part of the eye
- The power of the lens
- The length of the eye
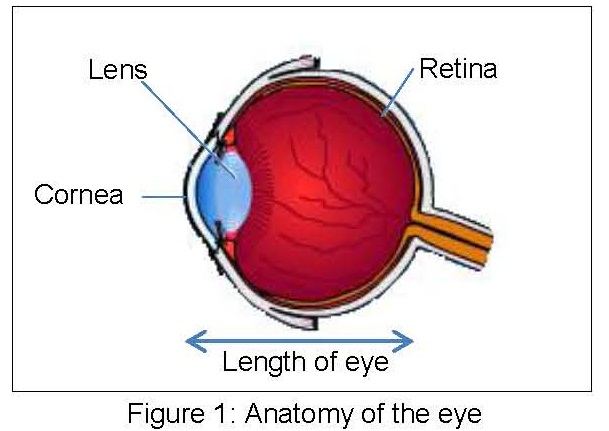
If one or more components are outside of normal values, the eye will be out of focus for distance vision, near vision, or both.
Hyperopia, also known as farsightedness, is a condition wherepeople are able to see distant objects clearly but objects up close seem blurry. Hyperopia can occur at any age, and it is often there after birth.
Presbyopia is a condition where people see blurred when looking at close objects even with glasses. The condition usually starts around age 40 and progresses through age 60.
Causes
Hyperopia occurs when image of the object focus behind the retina as shown below.
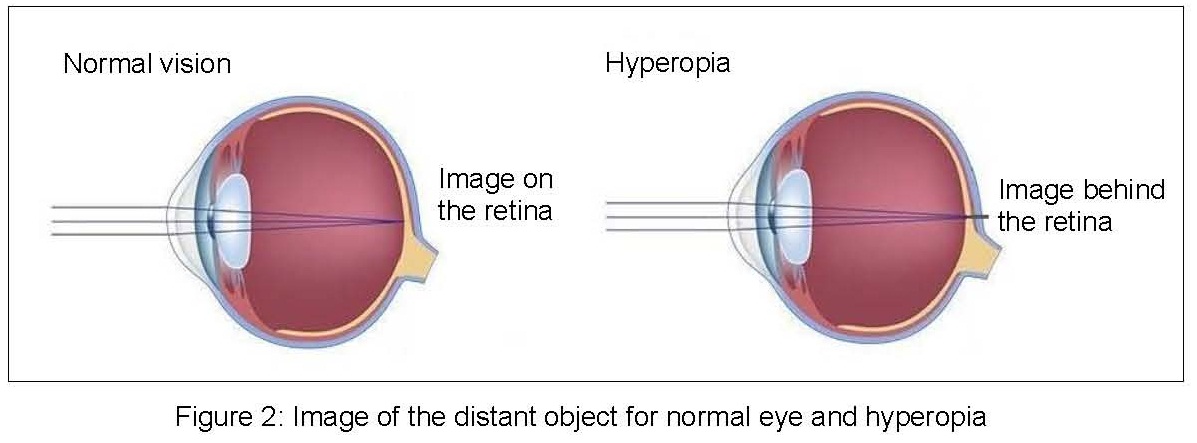
This is caused by:
- The cornea is less powerful than normal
- The lens is less powerful than normal
- The eyeball is shorter than normal
Presbyopia is a natural aging process. The eye is not able to focus light directly onto the retina due to hardening and inflexible of the lens.
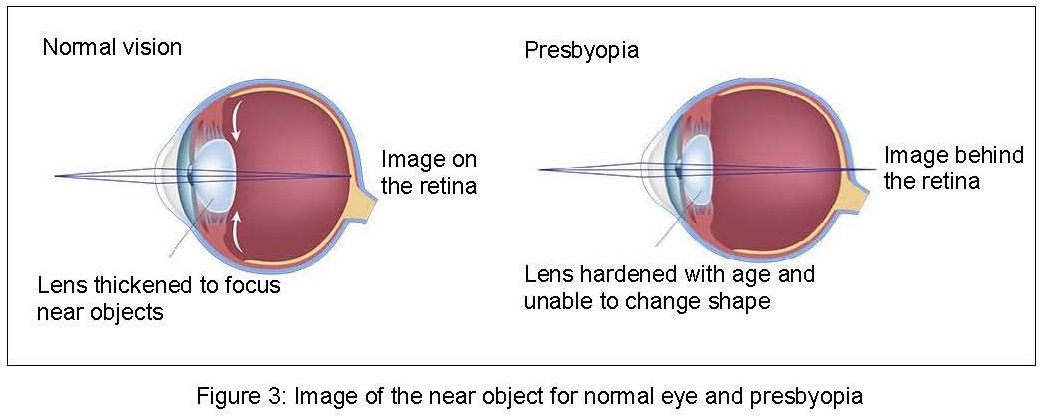
Signs and symptoms
| HYPEROPIA | PRESBYOPIA |
|---|---|
| Blurry vision at near but distant objects are clear. May not notice any problems with their vision, especially when they are young | Blurry vision at near |
| People with significant hyperopia may experience blurry vision at any distances and need to squinting the eyes to see clear | Blurry vision at near |
| Eyestrain and headache when do close work or try to focus on near object. | Eyestrain and headache when do close work or try to focus on near object. |
| Hold reading material at normal distance | Need to hold reading material farther than arm’s distance |
| Able to read in room illumination | Need brighter illumination |
| The symptoms has no significant effects | As age increases, the symptoms get worse |
Complication
Uncorrected hyperopia and presbyopia will cause signs and symptoms as above which lead to other problems such as lack of concentration and decrease work performance.
Untreated hyperopia in children may lead to amblyopia or lazy eye.
Treatment
1. Spectacle
Spectacle are the simplest and safest way to correct hyperopia and presbyopia. Presbyopia can
choose to wear reading glasses, bifocal or multifocal lenses.
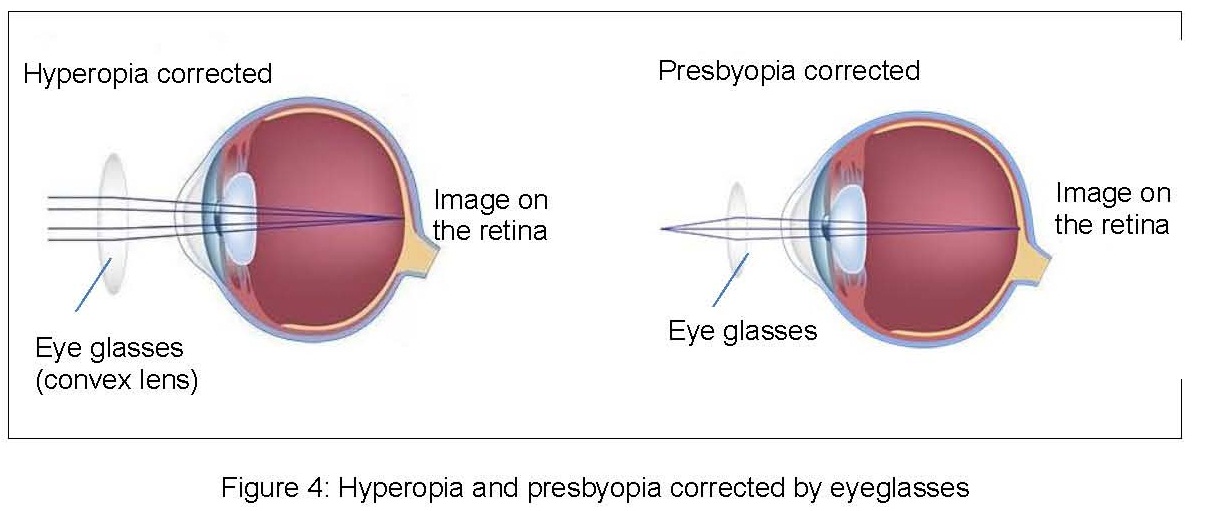
2. Contact lenses
Now, bifocal and multifocal contact lenses are available in market to help presbyopia. Contact lenses provide clearer vision and wider field of vision.However, contact lenses are not suitable for everyone. Get proper eye examination from Optometrist or Ophthalmologist.
3. Refractive surgery
Surgery done by Ophthalmologist in which basically the cornea surface was reshaped.
Reference :
- http://www.blundelloptometry.com/about.htm
- http://holbert.com/eye-disorders/
- http://www.allaboutvision.com/eye-exam/refraction.htm
| Semakan akhir | : | 18 April 2014 |
| Penulis | : | Pn. Siti Hamiza binti Abd. Halim |







