Introduction
Congenital Talipes Equino Varus’ (CTEV) is also known as Clubfoot. The impairment is common in infants & children. As the result, they have postural problems when one or sometimes both of their feet tend to move inward and upward, especially in non-weight bearing position.
There are two types of clubfoot
- Postural Clubfoot – Due to muscle tightness without the involvement of the surrounding bone and joint
- Structural Clubfoot – Due to bones and joints caused by delayed development. Foot’s range can’t be fully achieved passively.
As the prevalence, cases of Clubfoot commonly occurs in 1000 delivery. The rate shows that boys are two times more crucial to suffer with Clubfoot in comparison with the girls. Family history also been identify to have contribution in that case ratio.
Causing Factors
- Postural clubfoot: Packing Disorder: First child & big sized (more than 4kg) during delivery & lack of lubricant during pregnancy
- Structural clubfoot: Unknown cause. Might be due to genetic influences.
Aim of Physiotherapy Management
- To maintain the optimum alignment of joints
- To improve joint sense and function
- To maintain muscle length for optimal body functions such as walking
- To strengthen the muscles
- To relieve pain (if necessary)
Signs & Symptoms
Clubfoot can be diagnosed during early baby delivery. The signs and symptoms that could occur:
- Inward and upward foot inverted
- Tightness along the calf
- Limited ankle motion (if structural problem)
- Obvious lower leg (ankle) deformity
Complications
- Abnormal walking pattern
- Lower leg pain
- Lower leg uncomfort (if not treated early)
- Difficulty in walking (if not treated early)
Physiotherapy Treatment
- Postural type: This type can be treated effectively by:
-
- Stretching exercise
- Foot base stimulation
- Taping technique
- Soft tissue manipulation
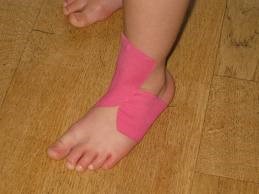 |
| Example: Taping technique |
| Source:http://www.stepscharity.org.uk/CDH/DDH/67246-Physio-weak-muscles-Kinesio-Tape.html |
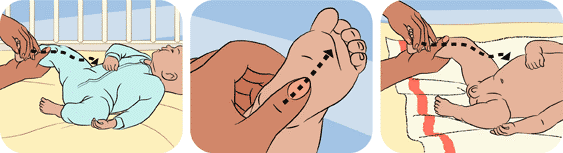 |
| Example: Stretching exercise |
| Source: http://raisingchildren.net.au/articles/baby_massage.html/context/430 |
- Structural type: This type can be managed effectively by:
-
- Serial casting and foot manipulation
- Achilles Tenotomy Surgery for severe case eg Achilles Tenotomy
- Stretching exercise to prevent muscle shortening
- Range of motion exercise to improve/maintain the joint range
- Proprioceptive training to improve the joint sense and ankle joint control
- Strengthening exercise to strengthen the thigh, peroneus and calf
- Foot arch support prescription to improve ankle joint bio mechanic and functions
- Ankle-Foot-Orthosis (AFO) or Ankle support (orthosis) eg Foot-Orthosis (AFO)
Conclusion
The early detection of this problem/condition is very important for:
- Early management can be done to maintain/improve the joint movement and muscle length
- Surgery can be done for the severe case and physiotherapy treatment need to be continued after that
References
- Mary P, Damsin JP, Carlioz H. Correction of equinus in clubfoot: the contribution of arthrography. J Pediatr Orthop 2004;24:312–16.
- Richards BS, Johnston CE, Wilson H. Nonoperative clubfoot treatment using the French physical therapy method. J Pediatr Orthop 2005;25:98–102.
- Souchet P, Bensahel H, Themar-Noel C, Pennecot G, Csukonyi Z. Functional treatment of clubfoot: a new series of 350 idiopathic clubfeet with long-term follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop B 2004;13:189–96.
Source Image
- (2012) Retrieved Jun 1 2015. http://www.dermalinstitute.com/us/news/?m=201202
- Retrieved Jun 1 2015. http://thephysiotherapy.com/clubfoot-or-ctev-congenital-talipes-equinovarus/
- Retrieved Jun 1 2015. http://www.kkh.com.sg/HealthPedia/Pages/ChildhoodIllnessesClubFoot.aspx
- Retrieved Jun 1 2015. http://raisingchildren.net.au/articles/baby_massage.html/context/430
- Retrieved Jun 1 2015. http://www.dermalinstitute.com/us/news/?m=201202
- Retrieved Jun 1 2015. http://www.steps-charity.org.uk/CDH/DDH/67246-Physio-weak-muscles-Kinesio-Tape.html
- Retrieved Jun 1 2015. http://www.kkh.com.sg/HealthPedia/Pages/ChildhoodIllnessesClubFoot.aspx
- Retrieved Jun 1 2015. http://ortotik-prostetik.blogspot.com/2014/04/teknik-perawatan-untuk-kaki-pengkor.html” http://ortotik-prostetik.blogspot.com/2014/04/teknik-perawatan-untuk-kaki-pengkor.html
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer | : | Pauzillah binti Hj Dollah |
| Translator | : | Naqiuddin bin Mohd Johar |
| Accreditor | : | Se To Phui Lin |
| Reviewer | : | Halimah bt. Hashim |