Introduction
Organ or tissue donation is a noble practice. It is not new in Malaysia as it is a treatment method that has been accepted in our country. The number of patients who need organ transplants is increasing from year to year, but the number of pledgers who want to donate after death is low. In 1999, the Organ Donor Card was launched as an indication of a person’s registration as an organ donor. Until now, it is estimated that over 126 000 donors have been recorded in the National Transplant Resource Centre. This number is very low compared to the population of approximately 27 million people in this country. The National Transplant Resource Centre was established not only to increase the number of organ donors, but also to raise public awareness, and to provide information about the importance of organ donation.
Definition Of Organ / Tissue
Organ / tissue donation is the process of donating organs or tissues of the body for the purpose of transplantation into others in need because of failure or damage to an organ or tissues of the recipient. After transplantation, the recipient can go on and lead a better quality of life.
Organ & Tissues Which Can Be Donated In Malaysia Are:
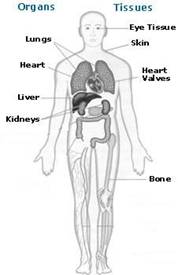
Organs:
Tissues:
|
 |
Types Of Donors:
Living Donor Living donor can only donate one kidney or part of the liver and bone marrow only. Donation during life is divided into two types:
- Donations that have family ties (Living Related)
- Donation of out of family ties ( Non -living Related )
Donation during life has low risk and is limited to those related by blood or who have emotional ties such as husband and wife. This regulation is important to prevent organ trading. A living donor can only donate one kidney or part of the liver. Cadaveric donor Cadaveric donor is a donor who has died. Cadaveric donations are encouraged and given priority in this country. It does not pose any risk to the donors. Cadaveric donors are divided into two types:
-
- Brain Death Only brain dead donors can donate organs and tissues such as heart, lung, liver kidney, eye (cornea), bone and skin. Brain-dead donors are donors who die at the hospital. Brain death is a condition where there is no circulation of blood and oxygen to the brain thus ending all functions that support life such as breathing and heartbeat. This may be due to brain injuries that cause brain swelling or severe bleeding in the head, spontaneous bleeding due to rupture of blood vessels or high blood pressure, severe stroke, brain cancer and so on. A person who is brain dead will not display any reaction; the breathing stops and with the help of a machine (ventilator) the heart will work for a while. However, other organs will be damaged and eventually the heart will stop by itself even with the support of the machine. Confirmation of death will be performed by two doctors who are qualified, in two separate trials. These doctors are not related to the recruitment and organ transplantation assignments. Confirmation/verification tests are performed according to the protocol adopted worldwide. Once brain death is confirmed, certification will be issued and the ventilator machine will be stopped. In organ donation, the ventilator machine will be stopped at the operating theatre before an organ is harvested.
- ii) Declaration of death when heart stops beating It is considered a normal death when a person is confirmed dead due to the heart having stopped beating. Donors who have died in this manner can donate tissues like eyes (cornea), bone, skin and heart valves. However those who die at home may just donate the cornea . The family should contact the nearest government hospital for tissue procurement.
Harvesting And Transplantation Of Organs And Tissues
Definition of transplantation Transplantation means to transfer an organ or tissue that is still functioning from one person to another who has organ failure or tissue damage, so that the recipient can continue leading a normal life. It is a proven method of treatment and is the best and effective way to save lives of patients suffering from end-stage organ failure. Upon confirmation of death by the hospital, the family will be given the opportunity to think about organ donation. At the same time, blood screening will be done to ensure the organs and tissues are free of infectious diseases and are still functioning for the purpose of transplantation. Surgery to remove the organs and tissues will be undertaken after a written consent from the next of kin is obtained. Only organs and tissues which are viable will be taken. The process of removal by surgery or harvesting can take between 2 to 8 hours depending on the number of organs and tissues available. It is carried out in operating theatres by surgeons under sterile conditions. Surgery is done with care and respect so as to avoid any damage to the body.
-
- Organ TransplantationThe organ transplantation surgery is done immediately after the harvesting process is carried out. Organs obtained from brain-dead donors should be transplanted immediately to ensure that the organ is still functioning and viable. Therefore, the donor (brain dead patient) will be remained on a support machine (ventilator) until he reach the operating theatre where the organ will be removed.Once the organ is removed from the donor, the transplant surgery must be carried out within the following time frame:Heart : 4 to 6 Hours Lung : 4 to 6 hours Liver : 8 to 12 hours Kidney : 24 hours
- Tissue TransplantationBesides organ transplant, other body tissues can also be used in transplantation such as cornea, skin, bone and heart valves.
Treatment Of Donated Tissues
Eye (cornea) This tissue is used to replace a damaged cornea completely. After corneal transplantation, the patient’s eyesight can be restored. The cornea can only be stored for up to 2 weeks. Heart Valve Transplantation of heart valve is to replace a heart valve of patient which is damaged or defective. It can be stored up to 10 years. Bone Bone donation is to help patients with bone cancer. It is also used to replace the bone that is damaged or problematic. In addition, bone is also used in dental treatment. Bones can be stored in bone banks for 5-7 years. Skin Skin is used to accelerate the healing process, especially in patients who suffered burns. Skin can be stored for 2-5 years.
Survival Rate Of Organ Recipients
Liver Transplantation 1 year : 80-85 % 5 years: 70-75 % Heart Transplantation 1 year – 83 % 5 years – 63 % Back to work – 83 % Kidney Transplantation 1 year : 85-90 % 5 years: > 75 % 10 years : 60 % Recipients can return to work and have a normal life.
Human Tissue Act 1974
An act authorizing the use of body parts of a deceased member for medical purposes, medical research and education. Consultation and consent of the next of kin of donors is mandatory before organ and tissue donation.
Religious Views
Generally all religions recognize that organ donation is a noble practice. No religion prevents its followers from performing this noble act. Islam, through the National Fatwa Council in June 1970 has laid down the law that organ donation and transplantation is permitted provided there is no other alternative that can save the life of the patient. It strongly prohibits the act of organ donation for business purposes. Transplantation as a treatment method is allowed if it does not harm the organ recipient or donor (if the donor is still alive). Islam also requires that organ donation is done in good faith with the intention of helping others and for the sake of Allah.
Exceptions To Hospital Charges
Pursuant to section 16 (13) of the Fees ( Medical) Order 1982 , the Secretary of Treasury has agreed to exempt payment of hospital bills for organ donors in government hospitals from the date of admission. This order has taken effect from 29 December 2003, as per letter of the Finance Ministry, KK / BP (S) 09/692/79 Jld.3.sk4/2003(4). For organ and tissue donation in a private hospital, the hospital bills incurred from admission until the death of the patient is the responsibility of the family or their heirs.
Who Is Eligible To Become A Donor?
Anyone can sign up to be an organ and tissue donor except those suffering from infectious diseases such as HIV- AIDS, hepatitis B and C, and syphilis. For those aged less than 18 years, written permission from parents is required. All organ donors are advised to inform their family members about their wish to donate organs after they die. This will help families to give consent for organ and tissue donation after their death.
How To Be An Organ Donor?
Those who wish to donate organs after death can fill out an organ donor registration form available in all government hospitals, District Health Departments, District Health Centres, Transplant Resource Centre at Hospital Raja Permaisuri Bainon, Ipoh, Transplant Resource Centre, Hospital Penang, Transplant Resource Centre Hospital Sultanah Aminah , Johor , or download the form from the website of the National Transplant Resource Centre. National Transplant Resource Centre This department was developed by the Ministry of Health Malaysia under the support and cooperation of Medical Development Division, Ministry of Health Malaysia. The main function is to disseminate a correct information and to raise an awareness regarding organ donation and transplantation among Malaysians. The main objective is to encourage more people to pledge and become donors (cadaveric). It also serves as a central donor registry and keeps a database of all potential donors. The center is working with non-governmental organizations, religious bodies, student associations, corporations and government agencies and the media in disseminating information about organ donation and transplantation programs, through lectures, mobile counters, campaigns, forums, interviews and so on. For more information on organ donation, you can visit the website of the National Transplant Resource Centre at www.dermaorgan.gov.my or call toll free 1-800-88-9080 or email to ntrc@moh.gov.my.
SAMPLE REGISTRATION FORM AND ORGAN DONOR CARD
 |
 |
 |
Photos of activities of the National Transplant Resource Centre
 |
 |
| Lecture on Organ Donation to Mahsa College students | Lecture on Organ Donation at Continuous Nursing Education (CNE) Hospital Kuala Lumpur |
 |
 |
| Information and registration counter set up at Hospital Serdang on the World Kidney Day. | |
 |
 |
| Exhibition and registration counters set up by Hospital Kuala Lumpur at the Putra World Trade Centre | A visit by students of the Science Faculty, University Putra Malaysia to the National Transplant Resource Centre, Hospital Kuala Lumpur |
 |
|
| Official launching of the Media Campaign on Organ Donation 2008/2009 by YBhg Tan Sri Lee Lam Thye, Chaiman of the Public Awareness Action Committee . The chairman also launched the website of the National Transplant Resource Centre | |
| Last Reviewed | : | 14 November 2014 |
| Writer | : | Azizul Khairi Mohd Nor |
| Translator | : | Varuges V.M Abraham |
| Akreditor | : | Dr. Zainal Fitri b. Zakaria |







