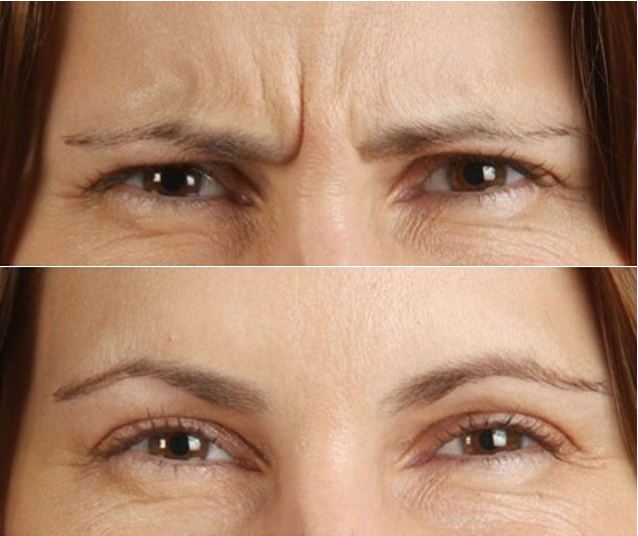
Introduction
Botulinum toxin is an exotoxin that is produced by the bacteria clostridium botulinum. This toxin undergoes various processes before it is used to treat various medical conditions. Botulinum toxin is also widely used in cosmetic surgery. There are two types of botulinum toxin that is type A and type B. Muscle contraction is initiated by the release of a chemical substance called acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. Botulinum toxin acts to block the release of acetylcoline resulting in muscle paralysis. This effect is however temporary and the muscle will regain its function within six to nine months.
Medical Indication
BOTOX/Dysport is produced by botulinum toxin type A. It can be used to treat medical conditions such as muscle spasticity or uncontrolled muscle twitching. In cosmetic surgery, BOTOX/ Dysport is widely used for facial rejuvenation.
| Formula | FDA approved uses |
|---|---|
| BOTOX | – Limb spasticity – Cervical dystonia – Hyperhidrosis – Facial dystonia – Facial rhytides |
| Dysport | – Cervical dystonia – Facial rhytides |
Table 1: Medical uses of BOTOX/Dysport
Application of BOTOX/Dysport
Botox/Dysport must be injected into the muscle to achieve the desired effect. The dose is dependent on the clinical condition. The effect is almost immediate reaching a peak in about six to seven days. Repeated injections may cause muscle atrophy and in cosmetic field this effect is desired to further reduce fine lines on the face.
Side Effects
Injection into the wrong muscle or overdose of injection will cause a wider muscle paralysis. Although the effect is temporary involvement of important muscles such as the eyelids or around the mouth will affect function. These include droopy eyelids, difficulty in talking or eating. Other minor side effects are pain, swelling and bruising.
Reference
- Update on botulinum toxin and dermal ?llers. Zachary J. Berbosa and William J. Liphama,b; Current Opinion in Ophthalmology 2010,21:387–395
- Injectable Agents for Facial Rejuvenation: Botulinum Toxin and Dermal Filling Agents. John T. H. Mandeville, M.D., Ph.D. Peter A. D. Rubin, M.D., F.A.C.S.
| Last reviewed | : | 16 January 2015 |
| Writer/Translator | : | Dr. Salina bt. Ibrahim |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Normala b. Hj Basiron |