What is Tuberculosis?
- TB is an infection caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is a contagious disease. TB bacteria spread from one person to another by air.
- Children are usually infected after inhaling the bacteria from an adult with TB of the lungs. Not every child becomes sick after being infected by TB bacteria. When TB bacteria multiply in the body and damage body tissue, the child becomes sick and is said to have TB disease.
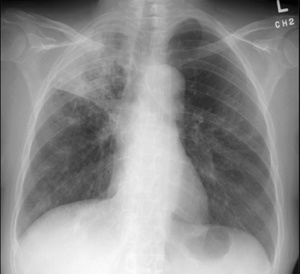
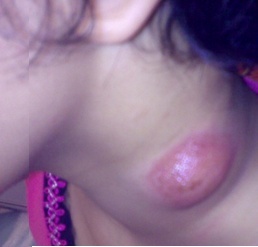
- TB can affect many parts of the body. In children, the common organs infected by TB bacteria are the lungs and lymph nodes. The bacteria can also affect other organs such as the brain, bones and gut; or spread widely in the body causing severe disease.
- The very young children or those with a weakened immune system are at risk of the severe form of TB disease
What are the presenting signs and symptoms?
- TB bacteria usually make a child sick slowly over several months. However, in high risk children, the disease can progress rapidly over a few weeks.
- Not everyone infected by TB bacteria becomes sick. Those who become sick usually suffer from prolonged fever, chronic cough, weight loss, enlargement of the lymph nodes or become inactive.
- When TB affects other organs such as the brain or bones, various symptoms from dysfunction of the affected organs may appear.
- The symptoms are not specific at the early stage of disease. Hence, it is important to suspect TB in an unwell child with a history of contact with an adult with active TB disease
 |
 |
|
TB of the lungs |
Lymph node TB |
How to diagnose TB?
- Diagnosing TB disease in children is more challenging than in adults because of the smaller amount of TB bacteria in children and it is more difficult to collect specimens from children.
- A skin test called Tuberculin test is used to indicate the presence of TB bacteria in the body.
- The common tests used to detect TB disease include X-rays, CT scans, MRI, checking for TB bacteria in the sputum or gastric juice, or microscopic examination of a sample of organs infected by TB bacteria (biopsy).
- The selection of tests depends on the age of the child and the sites of infection.
What is the treatment?
- TB is a treatable and curable disease.
- TB is treated with anti-TB medications. Anti-TB drugs are oral medications. Usually, 3-4 anti-TB drugs are required to treat TB disease. The duration of treatment is usually 6-12 months, depending on the severity and site of infection.
- TB drugs are generally safe for children. The common side effect include:
- Loss of appetite
- Stomach upset
- Nausea and vomiting
- Yellow skin or eyes
- Tingling sensation of the fingers or toes
- Rashes
- Change in eye sight or blurred vision
- Easy bruising
- The caregivers should bring the child to consult the healthcare provider immediately if the child experiences these side effects.
- In Malaysia, treatment of TB disease follows DOT (Direct Observed Therapy) policy. DOT means anti-TB drugs must be taken under direct supervision of a healthcare worker or a reliable individual.
- It is important to complete all the medications as instructed. If the medications are missed or not completed as instructed, some of the TB bacteria will still be alive in the body. These bacteria will become resistant to anti-TB drugs. These drug resistant bacteria may multiply later and become more difficult to treat.
What is the prognosis and outcome?
- The outcome of TB disease after treatment is usually good if the disease is detected early.
- However, the severe form of TB disease may cause permanent damage to the body or death.
What is MDR-TB?
- Multi-drug resistant TB (MDR-TB) is a form of TB caused by TB bacteria that do not respond to the standard anti-TB drugs, such as isoniazid and rifampicin.
- The emergence of MDR-TB is due to inadequate, inappropriate or incorrect use of anti-TB drugs. MDR-TB is harder to treat. The second line anti-TB drugs used to treat MDR-TB are more costly and have more side effects.
Where are the treatment centres in Malaysia?
It is important to seek medical consultation as soon as possible when a child is suspected to have TB or has come in contact with an adult with active TB disease. Most health clinics or hospitals in Malaysia are capable of diagnosing and treating TB disease. Treatment of TB disease in government health centers is free of charge.
Can TB be prevented?
TB can be prevented or controlled by these measures:
- Identify newly infected persons with TB disease early, provide prompt and effective treatment
- Screen those in contact with a person with TB disease and provide treatment to high risk individuals
- BCG (Bacilli Calmette-Guerin) vaccination program
- Improve living standards in the community
| Last Reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Chan Kwai Cheng |
| Accreditor | Dr. Revathy Nallusamy | |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Zainab bt. Kusiar |







