Imagine looking at yourself in the mirror with no front teeth. Are you confident enough to appear in public with missing front teeth? Gaps at the back of our mouth may not have the same implication to our appearance. It might just cause some difficulty in chewing instead. What are the options available in replacing missing teeth? Let us first discuss the common causes of tooth loss.
 |
 |
|
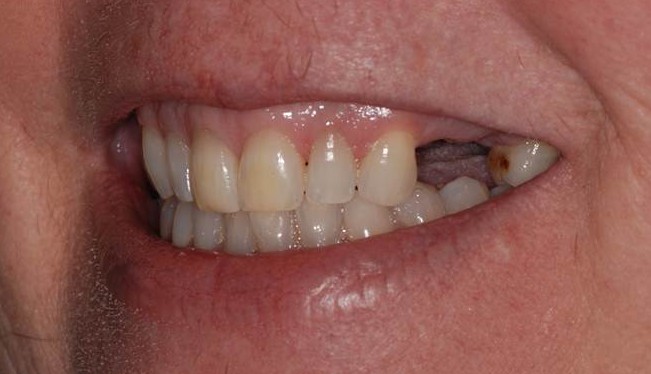
Figure 1 : Gaps due to missing teeth can affect aesthetics and / or function.
Image courtesy of www.dental-excellence.org |
|
What are the reasons of tooth loss?
Tooth loss can occur for a variety of reasons such as trauma, dental diseases (eg. caries or uncontrolled periodontal disease) or mechanical failure (eg. cracked or broken tooth). Sometimes, missing teeth are due to developmental disorder such as congenital absence of teeth.
What are the options for missing tooth replacements?
Currently, the options available in tooth replacements are either fixed or removable prosthesis. Fixed prosthesis can be tooth supported or implant supported bridge. This article will only further discuss on tooth supported dental bridge.
What is a dental bridge?
It is a fixed dental prosthesis used to replace one or more missing teeth by permanently joining an artificial tooth to adjacent teeth or dental implants. In the more developed countries, dental implants tend to be the first treatment option in replacing missing teeth (bridges exclusively supported by osseointegrated implants). Nevertheless, the conventional natural tooth supported dental bridges are still widely carried out all over the world as it is the more affordable option.
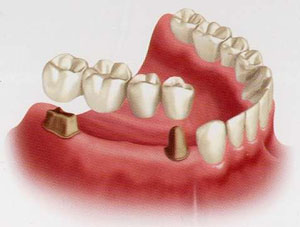
Figure 2 : Dental bridge replacing two missing teeth.
Image courtesy of www.geelongdental.com
Figure 3 : Example of a 3-unit bridge.
Image courtesy of common.wikimedia.org
What are the basic components of a dental bridge?
- Retainer
The bridge retainers are usually two dental crowns that are cemented on the teeth adjacent to the missing tooth area to support the bridgework. The two anchoring teeth are called abutment teeth.
- Pontic
The artificial tooth replacement occupying the missing tooth space is known as pontic. It can be single or multiple, depending on the number of missing teeth and clinical situation. Pontics are rigidly connected to the bridge retainers.
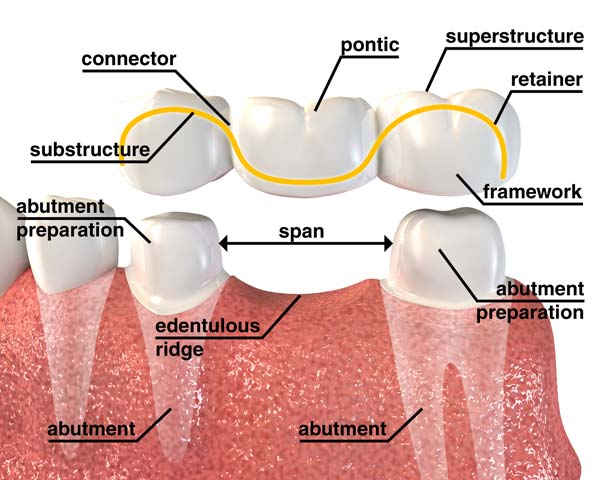
Figure 4 : Basic components of a bridge.
Image courtesy of successing.com
Can anybody have a bridge? What are the considerations in patient selection?
A few important general considerations have to be fulfilled by patients. A good oral hygiene, absence of active periodontal disease and positive attitude towards dentistry are a must. Patients with poor oral hygiene are contraindicated for any fixed prosthesis as it will not only result in recurrent caries of the abutment teeth but it may also cause periodontal breakdown. Poor oral hygiene usually indicates negative attitude towards dentistry. This type of patients will usually be advised to visit the dental hygienist regularly over a period of time to see if the oral hygiene improves before being re-evaluated.
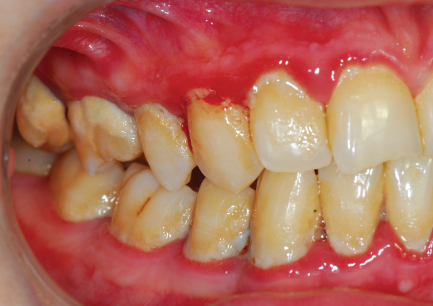
Figure 5 : Poor oral hygiene.
Image courtesy of www.pocketdentistry.com
Must all missing teeth be replaced?
Aesthetics is the most important factor to consider in tooth replacement. However, not all missing teeth have to be replaced. It depends on the location of the toothless gap in the mouth. If the gap is visible, it may severely affect ones appearance and function. Missing front teeth may also affect normal speech and pronunciation. In this case, a replacement is definitely needed. If the gaps are not visible, daily function not affected and occlusion is stable, perhaps there is no need to replace the missing tooth. Prevention of complications after a tooth loss is also a valid reason to plan for a restoration. The risks involve and clinical presentation has to be assessed as it may differ from one person to another. A shorten dental arch should also be considered in some clinical situation.
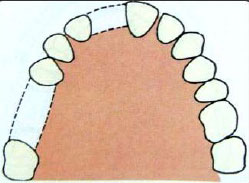
Figure 6 : Location of missing teeth.
Image courtesy of slidesharecdn.com
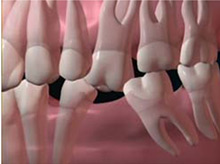
Figure 7 : The possible complications of tooth loss.
Image courtesy of dr.zenaidycastro.com
What are the specific indications for missing teeth replacement with a dental bridge?
- Psychological
Some patients are unable to tolerate a removable prosthesis as they feel that it is not ‘part of their body’. Wearing a denture is perceived as a sign of disability and associated with ageing. More so, dentures have to be removed before going to sleep as it has a detrimental effect if worn overnight. For married couples, they may not want their partners to see them in a horrid toothless state. Fitting a dental bridge will greatly benefit these patients.
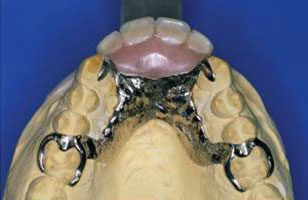
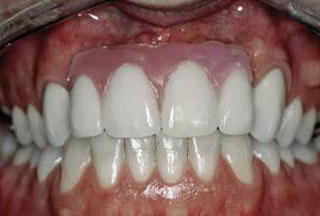 Figure 8 : Removable prosthesis to replace missing front teeth.
Figure 8 : Removable prosthesis to replace missing front teeth.
Image courtesy of www.intranet.tdmu.edu - Systemic disease
Patients who had history of sudden bouts of fits or unconsciousness as in epilepsy are contraindicated from having any form of removable appliances. This is due to the high risk of fracture or even inhalation of the appliance with life threatening complications.
What are the contra-indications for having a dental bridge?
- Inability to cooperate – spastic, mental disorder
- Limitations of mouth opening
- Too young or too old
- High caries rate
- Uncontrolled periodontal disease
- Doubtful prognosis of the abutment teeth
- Factors affecting the strength of bridge retainers such as unfavourable abutment crown height, size and shape; unfavourable crown: root ratio; weak dentine (eg. dentinogenesis imperfecta
- Length of span – too long a span will overload the abutment teeth
- Unfavourable tilting or rotation of teeth
- Inadequate available space for restoration
- Lack of manual dexterity to carry out daily hygiene maintenance
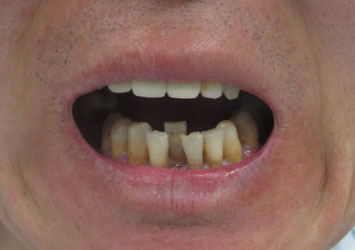
Figure 9 : Limitation of mouth opening renders it impossible to prepare for posterior teeth.
Image courtesy of www.synapse.koreamed.org
What are the advantages of dental bridges?
- Fixed prosthesis – dental bridges are permanently cemented to the abutment teeth. Periodic removal for cleaning is not required.
- Rapid adaptation – dental bridges are small and lightweight compared to removable prosthesis. After cementation, the prosthesis is usually immediately accepted as part of the natural dentition.
- Excellent chewing comfort. No worries on any potential embarrassing incidents in public.
- Very good aesthetics are possible to achieve with high strength full porcelain material
- Dental bridge is easier and quicker to get (within 3 visits)
- Good life span and prognosis with proper maintenance and home care.
- Less expensive compared to dental implants
What are the disadvantages of dental bridges?
- A substantial amount of tooth structure will be permanently removed in bridge preparation. This may include sound tooth structure. There is also an increased chance to develop pulpal complication which will need endodontic intervention before or after definitive cementation of the bridge. Therefore, implant prosthesis has a bigger advantage that no teeth are involve in the construction. This is especially important, when both future abutment teeth are perfectly sound. However, a more conservative design to conserve tooth structure is still possible by having a metal collar all around the abutment teeth and metal chewing surface.
- Increased sensitivity may be experienced after tooth preparation. It will usually subside after a few days provided that a proper temporary restoration has been constructed and cemented.
- A special method of cleaning with a ‘Superfloss’ is mandatory to ensure longevity and good outcome. This has to be carried out daily to clean the under surfaces of the bridge. A good manual dexterity is needed to perform this. Failure to keep the under surfaces clean will result in accumulation of food debris which may lead to decay of the abutment teeth and periodontal disease.
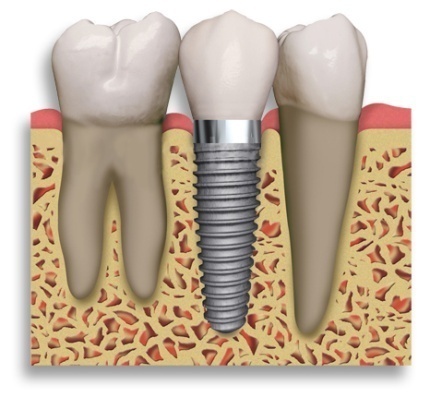
Figure 10 : Replacement of a missing tooth with dental implant.
Image courtesy of samdental.org
Reference
- Roberts D.H. (1973) Fixed bridge prostheses (John Wright & Sons Ltd.), Bristol. Great Britain.
| Last Reviewed | : | 19 June 2015 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Nur Laila Sofia bt. Ahmad |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Nik Fareedah bt. Mustafa |







