Introduction
The hand is a very complex part of human body with multiple joints, different types of ligaments, tendons and nerves.Hand is an essential organ in all our daily activities and with continuous use there is a high risk of injury occurring in our hands.
Definition of hand function
Hand function involves the hand performing meaningful movements such as reaching for object,holding,releasing object and manipulation of objects in performing purposeful tasks.
Grip can be divided into power grips and precision grips. Types of power grips are cylindrical grip,sphiral grip and hook grip.Examples are pulling a rope, holding a large ball ,opening a bottle or carrying a suitcase.Meanwhile types of precision grip are pincer grip and lateral pinch.Examples are turning a key, holding a pen or turning pages in a book and holding a plate
All these grips will become meaningless if the hand has no ability to release the grip. All grips require muscle strength,sensation ,coordination and stability of the whole arm.
Types of hand injuries
Hand injuries can be caused by the excessive use of hands, degenerative problems and accidents. Hand injury most commonly occur during:
- Sports and recreational activities
- Work-related tasks
- Accidental falls
- Road accidents
The common types of injuries that can occur as a result of an accident are:
- Fractures
- Sprains
- Injuries to the nerve
- Injuries to the tendon
- Joint dislocation
Overuse injuries occur when too much stress is placed on a joint or other tissue, often by overdoing an activity or repeating the same activity. Overuse injuries include the following :
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. The symptoms include tingling, numbness, weakness or pain to the fingers and hand.
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. It is painful condition affecting the tendons on the thumb of the side of your wrist.
- Osteoarthritis of the hand can cause patients to experience painful sensations in the joints of the fingers. Joint may become swollen, deformed, stiff and this will impair hand function.
Impact of Hand Injury
Post hand injury, patients often experience problems in hand function. Patient will have trouble doing daily activities, working, enjoying hobbies, perform religious rituals and social activities.
The common problems encountered after a hand injury are:
- Swelling
- Inflammation
- Joint stiffness
- Pain
- Limited joint movement
- Poor sensation
- Hyper/hypo sensitivity
- Deformity
- Weakness
Home exercises Tips
Hand functional problems can be resolved by performing correct exercise. The benefit of home exercise is to:
- Reduce pain
- Avoid joint stiffness
- Increase joint mobility
- Reduces hyper/hypo sensitivity
- Avoid the occurrence of deformity
- Increase the strength of your hand
- Control swelling
Examples of home exercise are as follows:
1. Exercise to encourage Grasp and release
 |
 |
- Place an elastic ball on the palm, and grasp/squeeze the ball tight like making a fist. Then release/straighten your fingers and stretch out your hand. Repeat the activity several times
2. Exercise to encourage Finger abduction and adduction
 |
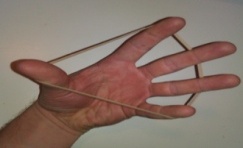 |
- Straighten your thumb and fingers. Abduct/Spread the fingers apart and then adduct/bring them together. Place a rubber band around your fingers when they’re in the adduct/closed position and then abduct/spread them apart, pressing against the band
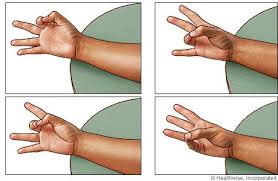
3. Exercise to encourage Finger pinch grip
 |
 |
 |
- Use your thumb and index finger to pinch. To strengthen your pinch, use your thumb, index finger, and third finger to pinch a clothes peg
4. Exercise to encourage wrist Joint movement
 |
 |
- Place your hand on the plastic jar .Roll back and forth to exercise the wrist joint
- Twist the cap of the container left to right to exercise the wrist joint
5. Exercise to encourage thumb movement

- To exercise the thumbs press the pump cap up and down
6. Exercise to encourage hand Manipulation
 |
 |
 |
- Pick the coins using thumb and index/first finger one by one, then insert the coins into the coins box
- Take 3 cords and then cross-rope it like making hair plaits
7. Exercise to improve hand Sensation
 |
 |
- Take a cotton swab or a towel and gently rub the area that is hypersensitive or
- Put the beans or rice into the container, then stir the beans or rice with the hand
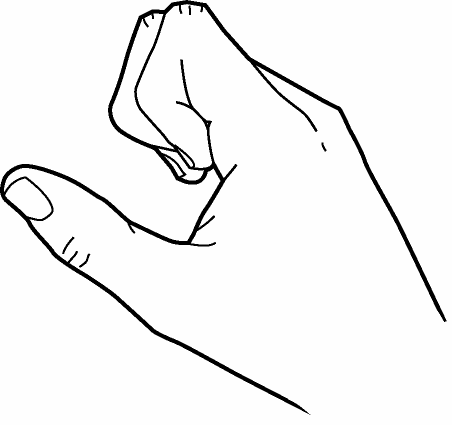
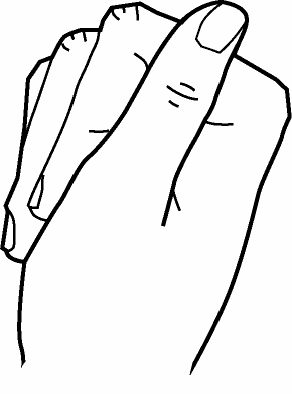
8. Exercise to encourage Tendon gliding
- These exercises allow each tendon to reach its greatest range of movement. They also reduce hand swelling
- Start with your fingers straight every time you do these exercise
- Then bending only at the wrist and at the knuckles. Relax and repeat.
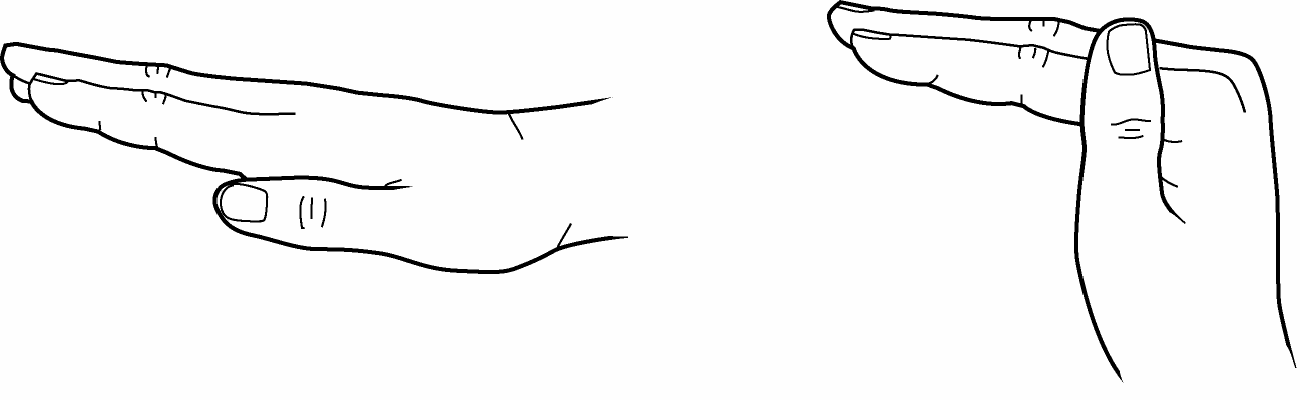

- Make each type of fist shown below, one at a time, with your fingers
 |
 |
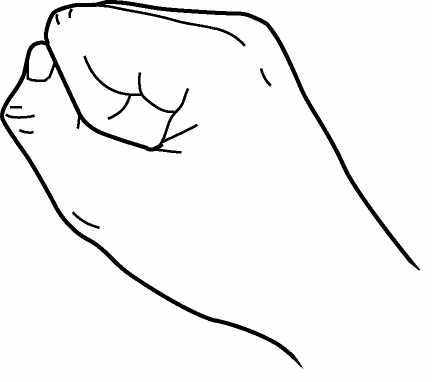 |
| Hook Fist | Straight Fist | Full Fist |
- Curl your thumb into your palm as far as possible, and stretch out as far as possible
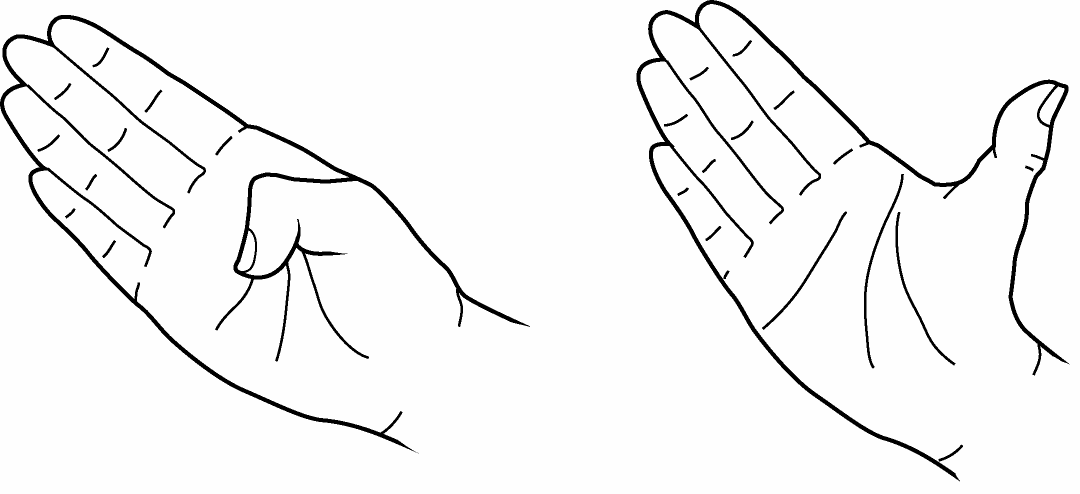
References
- Hand Rehabilitation- a Practical Guide Second Edition, Churchill Livingston
- The Practice of Occupational Therapy- An Introduction To The Treatment Of Physical Dysfunction, Edited by Ann Turner
- Hand and Upper Extremity Rehabilitation- a Practical Guide Third Edition
- http://www.healthlinkbc.ca/healthtopics/content.asp?hwid=handi
| Last Review | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writter | : | Zarina Binti Ghazali |
| Accreditor | : | Ooi Siew Chen |
| Reviewer | : | Tan Foo Lan |







