Introduction
- Cough is one of the most common presenting symptoms to healthcare professionals.
- It is often distressing to child and parents and affects their quality of life, school and work productivity.
- Healthy and normal kids do cough.
- However, how much cough is normal or expected? Studies have shown that normal children on average cough 10-11 times/day (maximum 34 times/day)
Why do kids cough?
- Cough is a forced expulsive maneuver, usually against a closed glottis, and is associated with a characteristic sound.
- We cough when foreign body is trying to enter our upper airway. We also cough when there are excessive secretions, debris, irritants or phlegm to clear our airway. So, cough is a protective defense mechanism in healthy individuals.
- Nevertheless, cough is also a very common symptom of airway and lung problems.
- You should seek medical attention when the cough become excessive, have breathing difficulty or other symptoms like fever.
The Cough Reflex Pathway
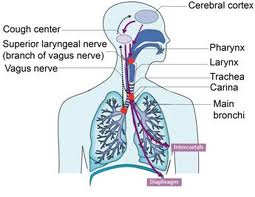
- To understand better why we cough, we should learn about the cough reflex pathway.
- There are cough receptors situated along the upper (nose and throat) and lower airways (windpipe and lungs).
- These cough receptors sense changes in temperature, chemicals and mechanical stresses.
- The signals then go to the cough centres located at brainstem and subsequently modulated by the higher centre in the brain (cerebral cortex)
- From there, the signals will be sent to the upper airway muscles and breathing muscles (intercostals, diaphragm, and abdominal muscles) to produce cough.
- Cough is a forceful contraction of breathing muscles that cause forceful expulsion of air, phlegm/mucous or other foreign body form the airway.
 Source: http://learnpediatrics.com/body-systems/respiratory-system/approach-to-a-child-with-a-cough/
Source: http://learnpediatrics.com/body-systems/respiratory-system/approach-to-a-child-with-a-cough/
Definition of acute cough
- Generally, acute cough is defined if duration of cough is less than 3 weeks.
What are the common causes of acute cough in children?
- There are many causes of acute cough in children. Many are due to infections.
- However, the cough due to infections is usually associated with other symptoms such as runny nose, fever, noisy breathing, fast breathing, etc depending to the cause.
- The most common cause is viral upper respiratory tract infection (URTI or common colds).
- Young children can have viral URTI s 5-8 episodes /year. Patients with URTI in their cough receptors are transiently hypersensitive.
- Other causes of acute cough are as follows (the list is not exhaustive):
- Acute bronchiolitis
- Lung infections (pneumonia)
- Viral croup
- Viral triggered/induced wheeze
- Acute asthma
- Acute pharyngitis
- Acute tonsillitis
- Acute rhinosinusitis
- Heart failure
- Whooping cough (pertussis)
- Foreign body inhalation
What are the danger signs in a child with acute cough?
- As mentioned earlier, most children with acute cough have viral upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) which is usually a mild self limiting illness.
- However, you need to know the danger signs to guide you for early medical consultation.
- The danger signs are as follows:
- Fast breathing
- Chest retractions/in drawing
- High fever
- Lethargy/less active
- Poor feeding
- Bluish discolouration of lips and tongue (cyanosis)
- Impaired conscious level
- Noisy breathing – ‘stridor’ or ‘wheezing’
- Looks ill
 Source: https://junglemagic.in/high-fever
Source: https://junglemagic.in/high-fever
How to manage a coughing kid?
- The most important initial decision is to determine whether the cough is a sign of a serious, potentially life-threatening condition or due to non-serious conditions like URTIs.
- The most appropriate management is to identify the most likely cause of cough and treat accordingly.
- Most parents initially use cough and cold medicines bought at pharmacy or supermarket to relieve acute cough and other symptoms associated with URTIs. They feel that these medicines work for their kids.
- However, many studies failed to demonstrate that cough and cold medicines work.
Cough and Cold medicines
- Most cough medicines are short-acting syrups in four basic categories:
- An antitussive (cough suppressant) – for example, dextromethorphan, or pholcodine.
- An expectorant – for example, guaifenesin, or ipecacuanha.
- An antihistamine – brompheniramine, chlorphenamine, diphenhydramine, doxylamine, promethazine, or triprolidine.
- A decongestant – for example, phenylephrine, pseudoephedrine, ephedrine, oxymetazoline, or xylometazoline.
How do cough medicines work?
- Cough medicines are thought to work in different ways, depending on what the active ingredient is:
- Antitussives – work by reducing the cough reflex to normal levels.
- Expectorants – increase the amount of mucus (fluid) made by the lungs. This would make secretions easier to remove by ciliary transport and/or coughing.
- Antihistamines- reduce histamine release. This reduces congestion and decreases the amount of secretions made by the lungs.
- Decongestants -cause the blood vessels in the lungs and nose to constrict, and this reduces congestion.
What are special considerations?
- These medicines are considered to be safe for the vast majority of adults and older children.
- Some cough medicines can cause drowsiness.
- Generally, cough and cold medicines should NOT be used in children less than 2 years old.
- This is because the risk of a young child having a side-effect to one these preparations is greater than the benefit of the medicine.
- Moreover, these cough and cold medicines can cause serious side effects and potential danger to life.
- There are few case reports that children die because of these medications due to excessive sedation, but it is rare.
- These medications will not cure or shorten the duration of URTIs
- If you choose to use it, please check the drugs facts because some of these medications have multiple active ingredients. These will increase the risk of side effects.
- You should use the measuring cups or spoons that come with the medication to ensure adequate dosing and avoid overdose especially in young children.
- By and large, most studies shown that cough due to URTIs usually resolve by itself within 1 to 3 weeks.
- During URTIs you can give your kids plenty of water, hot soup and beverages to help moist the throat.
- You can offer your kids honey or lemon as home treatment to alleviate the cough. There are no active ingredients, therefore it is safe.

- Very important for parents to avoid their children from tobacco smoke. Studies have shown if both parents are smokers, the children will have 50% increased risk to continue coughing.

References:
- Dicpignigiatis PV et al. Acute cough: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Cough 2009, 5:11
- D Blassio et al. Cough Management: a practical approach.Cough 2011, 7:7
- Chang AB. Cough: Are children really different to adults. Cough 2005, 1:7
- P Munyard, A. Bush. How much coughing is normal? Arch Dis Child. 1996 June; 74(6): 531–534.
- Schroeder K, Fahey T. Over-the-counter medications for acute cough in children and adults in ambulatory settings. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD001831.
- Over-the-counter (OTC) cough and cold products. FDA news release January 17,2008
| Last Reviewed | : | 27 June 2016 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Mariana bt. Daud |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Norzila bt. Mohamed Zainuddin |







