Introduction
Angiography is a radiological procedure to examine the arteries or veins. Blood vessels cannot be seen in general X-ray examination. Contrast medium will be injected into your blood vessels to visualize the arteries or vein in the area of interest.
 |
 |
|
Picture1: Blood Circulation of the body Source: http://kwikfit4u.com |
Picture2: Blood circulation of the head Source: http://betterphotography.in |
How Can I Get This Examination Done And Where?
- The doctor you are seeing will decide if you need the examination.
- If necessary, the doctor will make a request for the examination using ‘Request Form For Radiological Examination’.
- This examination is available in selected Ministry of Health hospitals.
Types Of Angiography Examination
- There are various types of angiography examination depending on the area of examination such as:
– cerebral/ carotid angiography – to examine blood vessels in the head and neck.
– coronary angiography – to examine blood vessels, valves and chambers of the heart.
– pulmonary angiography – to examine blood vessels in the lungs.
– peripheral angiography – to examine blood vessels of the upper and lower extremities.
– renal angiography – to examine blood vessels of the kidneys.
- Angiography is also used to:
– find the cause of bleeding in the body.
– detect blood clots in the body.
– assess/ view changes to organs of the body due to injury.
- To plan for surgery and repair of of arterial dissections. In some cases a method known as interventional radiology will be used.
- Angioplasty which is a procedure that involves inserting a small balloon or tube called stents through a catheter to open narrowed arteries.
Preparation For Angiography Examination
- You will be admitted into the ward 1 or 2 days before the examination so as to prepare for the procedure which requires close monitoring.
- Please do not bring any jewellery or valuables.
While in the ward
- The site of insertion of the catheter (groin for femoral artery, upper arm for brachial artery) will be shaved.
- Blood pressure will be monitored and blood tests will be done.
- You will not be allowed to eat and drink for 6 – 8 hours before the examination.
- You will need to sign a consent form to undergo the examination.
- The examination will take between 30 minutes to 2 hours depending on the complexity of the case.
Before the examination
- The radiographer will explain the procedure and instructions that will need to be followed.
- The radiographer will check:
– your medical history.
– if you are allergic to any food or medicine..
– if you are on medication.
– your blood test result.
Information obtained will be communicated to the radiologist performing the examination.
During the examination
- You will be brought into the examination room (Picture 3).
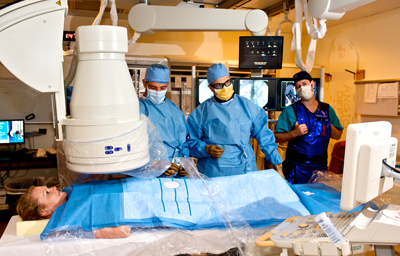 Picture3: Examples of Angiography
Picture3: Examples of Angiography
Source: www.medicine.virginia.edu/clinical/departments/radiology/divisions/angiography/
- You will be asked to lie down on the examination table. Immobilising device will be used prevent movement during the examination.
- You will be conscious throughout the examination.
- The radiologist will insert a thin tube called a catheter in the groin (femoral artery) or the arm (brachial artery) for contrast media injection.
- This procedure is not painful, you may feel a warm sensation or bitterness in the mouth during the injection of contrast media.
- You will be asked to breathe in and hold your breath for a few seconds and a series of X-ray images will be recorded.
- When the examination is completed the catheter will be removed. Slight pressure will be applied at the catheter insertion site to prevent bleeding.
After the examination
- After the examination you will be sent back to the ward for observation.
- You will be allowed to eat and drink after the examination if there is no complication.
Report
- Images acquired during the examination will be viewed by the radiologist who will then report the examination.
| Last Reviewed | : | 2 June 2016 |
| Translator | : | Daud bin Ismail |
| Accreditor | : | Jasintha S. Sangarapillai |







