Introduction
Every married women want to be pregnant. Pregnancy is the period of time when a fetus develops inside a woman’s uterus ends with the birth of the infant. Pregnancies typically involve a variety of clinical laboratory tests. The tests provide useful information from the time pregnancy is first considered through the initial days of the newborn’s life.
All pregnancy tests measures a hormone in the body called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). HCG is a hormone produced during pregnancy. This hormone is produced by the placenta as soon as implantation happens, about one week after fertilization and ovulation. hCG levels continue to rise after implantation until about 10-12 weeks gestation, at which point the hCG level will stabilize or drop.
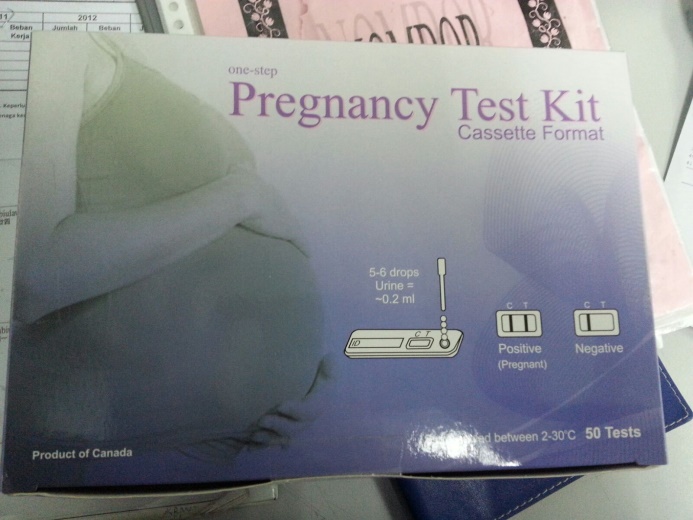
Pregnancy tests detect the amount of hCG in the blood or urine and a pregnancy test becomes positive when there are sufficient levels of hCG. Blood hCG testing is much more sensitive than urine hCG testing, therefore a blood hCG test can detect pregnancy several days before a urine pregnancy test. There are two common types of hCG tests. A qualitative hCG measures whether the hCG hormone is present, for example urine pregnancy test. A quantitative hCG test (or beta hCG) measures the amount of hCG actually present in the blood. One of the commonly performed test in the laboratory to confirm pregnancy is urine pregnancy test (UPT) (See Figure 4).
Sample Requirement
Common practice in medical laboratory, the samples will be collected as below:

Figure 1: Sterile urine plain cup
Urine Pregnancy Test
- Type of sample : Urine
- Type of container: Sterile urine plain cup
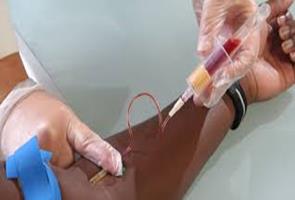
Figure 2: Blood collection for pregnancy testing
Blood test for pregnancy
- Type of sample: Blood
- Type of container: Plain Tube
Procedure
Urine tests can be performed in two different ways and these can be performed at home or in a clinic. Usually, the common practice in the lab, the urine should be collected in a sterile container and will be analysed by the lab staff. The procedure is dipping a stick into the urine, or putting urine into a special container with an eyedropper. Another option involves placing a stick into your urine stream and catching your urine in midstream.
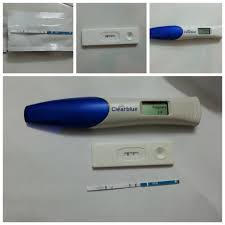
The result can be obtained by looking for a change in color, a line, or a symbol (like a plus or minus). The newer digital pregnancy test offered by Clearblue Easy makes reading your results simple: the window will either show the words “not pregnant” or “pregnant”. (See Figure 3)
The blood test is done by drawing a single tube of blood and sending it to a laboratory. (See Figure 5 and 6). The result for blood test can be obtained after a few hours to more than a day depends on the policy of the clinics or laboratories.
Sensitivity (cut off value)
If the hCG level of less than 5 mIU/mL is considered negative for pregnancy, and anything above 25 mIU/mL is considered positive for pregnancy. Since these tests can detect as little as 25 mIU/mL hCG in a urine specimen, the test can be performed as early as 7-10 days after conception. Because of its convenience, this test is frequently used in clinics and laboratories and can even be performed by patients at home. For blood test, pregnancy indicated by a blood hCG of >10 IU/L.
Interferences
Many factors can interfere with the test results in UPT and cause false-positives, this means you’re not pregnant but the test says you are, this including the presence of serum human anti-mouse antibodies (HAMA) and diseases associated with the excretion of hCG into the urine (e.g., colon or cervical cancer). False-positive urine hCG results have also been reported in patients with nephrotic range proteinuria and those with tubo-ovarian abscess. Analytical causes of false-positive or false-negative urine hCG tests include human or technical errors in the performance and/or interpretation of the test results.
Limitation
Every the tests have their limitation. Below are the limitation of urine pregnancy test are :
- This urine test is a qualitative test, therefore, neither the quantitative value nor the rate of increase in hCG can be determined by this test.
- False negative results may occur when the levels of hCG are below the sensitivity level of the test.
- This urine test provides a presumptive diagnosis for pregnancy. A confirmed pregnancy diagnosis should only be made by a physician after all clinical and laboratory findings have been evaluated.
Reliability of tests
Urine tests or home pregnancy tests are around 97% accurate when done correctly. However, if done incorrectly or taken too early, the result can be inaccurate. If you get a negative result and still have symptoms of pregnancy (missed period, nausea, breast tenderness and fatigue), wait a week and take another test or contact your doctor so you can have a blood test done. Blood tests are even more accurate than urine tests.
Conclusion
These tests is done to determine if you are pregnant, diagnose abnormal conditions that can raise hCG levels and to watch the development of the pregnancy during the first 2 months (for quantitative test only). HCG level rises rapidly during the first trimester of pregnancy and then slightly declines.
In early diagnosis of pregnancy, hCG is detectable in maternal blood seven to nine days after conception and in urine one to two days after that,with its concentration doubling thereafter every 48 hours. Maximum hCG is reached at approximately week 10 of gestation and subsequently declines (although it remains detectable in the urine throughout pregnancy. Qualitative testing of urine for hCG is used routinely for diagnosis of pregnancy and is reliable from at least 10 days after a missed menstrual period. It should only be followed up using laboratory blood testing if there is believed to be is an issue with the pregnancy, for example if there is vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain or if a gestational sac is not visible on ultrasound. Problems related to an abnormally rising hCG level include miscarriage and ectopic (tubal) pregnancy. First trimester screening is a combination of fetal ultrasound and maternal blood testing performed during the first trimester of pregnancy. This screening process can help to determine the risk of the fetus having certain birth defects.
|
Figure 3: Clearblue Urine Pregnancy Test (digital- can be done at home) |
Figure 4: One-step Pregnancy Test Kit Cassette |
|||
|
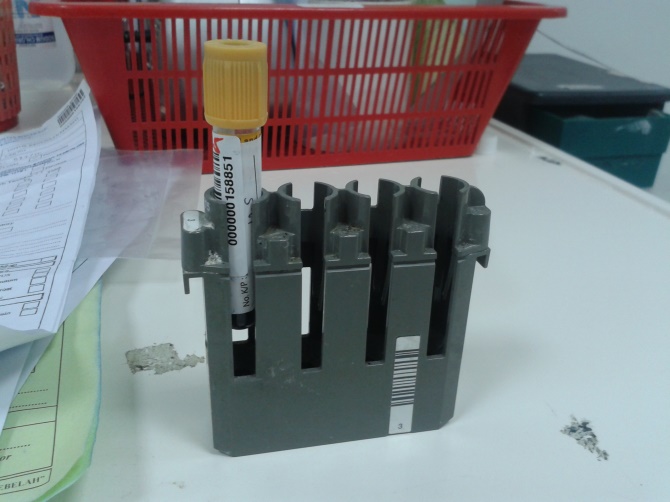
Figure 5: Example of blood sample (Serum) for hCG analysis in laboratory |
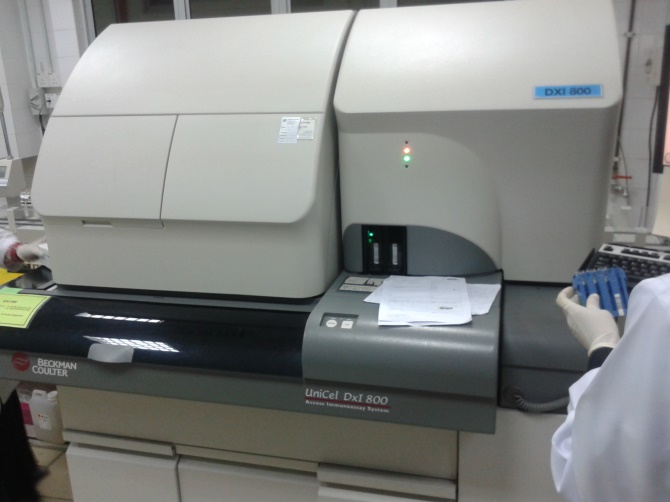
Figure 6: Example of analyser use in the lab to analyse blood sample |
|||
Pregnancy blood test analysis in medical laboratories (photo courtesy of chemical pathology laboratory HRPZ II , Kota Bharu)
References
- STM/SR/023 (2015). Urine Pregnancy Test (Rapid). Pathology Department Hospital Raja Perempuan Zainab II, Kota Bharu, Kelantan.
- Package Insert: hCG One Step Pregnancy Test Kit (Cassette Format)
- http://www.clearblueeasy.com/clearblue-easy-digital-pregnancy-test.php
- http://www.babymed.com/hcg-level-in-early-pregnancy
- americanpregnancy.org/getting-pregnant/understanding-pregnancy-tests/
- www.nlm.nih.govmedlineplus/ency/article/003232.htm
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc3289784/
- http://www.acb.org.uk/docs/default-source/amalc/hcg.pdf
| Last Reviewed | : | 22 May 2016 |
| Writer | : | Nur Hazlinda bt. Khalidi |
| Accreditor | : | Rofidah bt. Abu Bakar |