Introduction
Tetanus is a disease caused by neurotoxin producing bacteria called Clostridium tetani. This bacteria are found everywhere in the environment, particularly in the soil of warm and moist areas. The bacteria can get into the body through broken skin, usually through injuries from contaminated objects such as nail and needle. Tetanus is different from other vaccine-preventable diseases because it does not spread from person to person.
When introduced into the body, the bacteria will produce neurotoxin which attacks the human nervous system and causing the following symptoms:
- Headache
- Jaw cramping
- Sudden, involuntary muscle tightening (sometimes the spasms affect muscles that help with breathing, which can lead to breathing problems)
- Painful muscle stiffness all over the body
- Swallowing difficulty
- Fever and sweating
- High blood pressure and fast heart rate
- Seizures
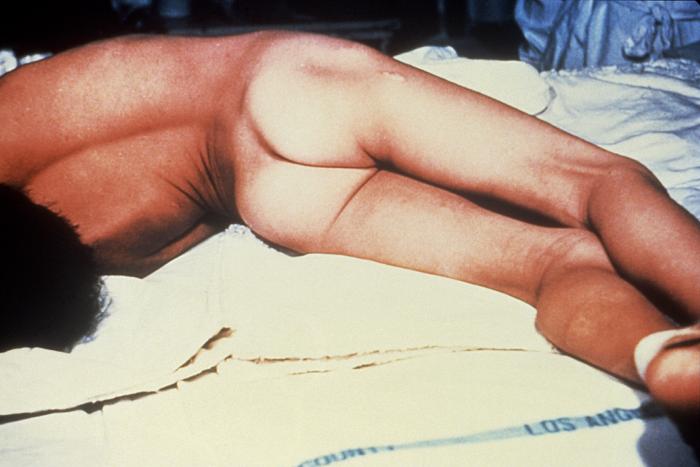
Diagram : Painful muscle stiffness all over the body due to Tetanus
Source: CDC United States of America
Tetanus could be fatal due to breathing difficulty if the treatment is delayed. The treatment of tetanus includes administration of human tetanus immunoglobulin (antitoxin), wound care and drugs such as antibiotics and drugs to control muscle spasms. Depending on how severe the infection is, a machine to help you breathe may be required. A tetanus vaccine should be given once recovered as recovery from clinical tetanus does not result in protection against the disease in the future. Preventive measures should be taken to prevent tetanus infection. Being fully immunized is the best tool to prevent tetanus.
Indication
Administration of tetanus vaccine is to prevent tetanus infection.
Target groups
Tetanus vaccines are recommended for all people as tetanus could infect anyone regardless of age, gender and race.
At present under National Immunization Programme by Ministry of Health Malaysia, the tetanus vaccine is targeted to children and pregnant women. All children shall receive 3 primary doses of tetanus vaccine at the age of 2 months, 3 months and 5 months respectively while a booster dose will be given at the age of 18 months. Another 2 booster doses of tetanus will be given again at the age of 7 years and 15 years old.
Tetanus vaccine is given to pregnant women in order to prevent neonatal tetanus due to unclean instruments used to cut the umbilical cord.
Everyone needs protection from tetanus. If you have not had a booster shot in 10 years or more, you should receive a tetanus shot.
Side effects (Common/Rare)
Tetanus vaccine is composed of toxin of Clostridium tetani which has been detoxified and adjuvant is added to a vaccine to increase the body’s immune response.
Tetanus toxoid used alone or in combinations is considered safe. Tetanus toxoid causes minor local reactions such as pain and redness and occasionally nodules and, very rarely, sterile abscesses (1–10 per million doses administered). A sterile abscess is a localized swelling filled with fluid without organism growth.
Mild systemic reactions including fever, aches and malaise might occur following tetanus vaccine injections. Severe generalized adverse events such as anaphylactic reactions (a serious allergic reactions) and brachial neuritis (a type of severe neurological illness) are extremely rare, 1–6 and 5–10 per million administered doses, respectively.
According to the database of the National Drug Safety Monitoring Centre, National Pharmaceutical Control Bureau, majority of the adverse events reported post Tetanus Vaccine immunization are mild in nature and vaccinees recovered from the adverse events.
Current issue regarding ATT
No
References
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Tetanus (Lockjaw) Vaccination http://www.cdc.gov/tetanus
- WHO Vaccine Position Paper on Tetanus 2006
| Last Reviewed | : | 24 June 2015 |
| Writer/Translator | : | Ng Chiew Seng |
| Accreditor | : | Noraisyah bt. Mohd Sani |







