Auditory training is a process of teaching the brain to listen. It is a process of educating people with hearing disabilities to utilize all auditory (hearing) signals they have (Carhart 1960). The aim is to assist them to naturally gain hearing abilities as how normal people have without undergoing any interventions (Erber 1980). Auditory training includes hearing activities which aim to optimize speech perception through hearing. Goldstein (1939) defined it as a development in the ability to distinguish different characteristics of speech sound and non-speech sound.
We use our brain to listen. Although the use of hearing aid and/or cochlear implant may help patients to identify low-pitched sounds, using them only does not give a good listening skill to the patient. The sound received and heard by a patient with hearing aid or cochlear implant is not the same as the one heard by people with normal hearing abilities. This is due to the lack of ability of the brain to perceive sound during the early stages of using the hearing aid and cochlear implant. Thus, patient needs to learn to perceive sounds received (either from the surrounding, from speech, music and etc) and auditory training is required for the brain to accept and understand the stimulus. With continuous stimulation, training allows patient to differentiate, recognize and match sounds.
Auditory training can be performed by parents or caregiver with the guidance and supervision by audiologist and speech-language therapist.
Objectives/Aim
The main objectives of auditory training are:
- To use the residual aided hearing in maximizing use of acoustic signals received for speech perception.
- Aid in adaptation and fulltime use of hearing aid or cochlear implant while awake
- Aid in ensuring that the setting of hearing aid or cochlear implant used by patient is appropriate to the hearing problem faced by patient to help him/her in obtaining the optimum speech language
- To prepare the patient with auditory skill before comprehensive session with speech-language therapist
- To help the parents or caregiver with examples of daily activities and techniques of auditory learning
- To focus on the therapy goal which is to train the patient’s mind to be conscious of the presence of sound stimulus, to give attention and to use/understand the sound stimulus
- To help patient in monitoring own voice and the voice of other speaker in effort to increase the clarity of speech being heard
Individuals In Need of Auditory Training
Auditory training is performed on:
- Children and adults with hearing problem, regardless of the level and type of hearing problem, whom uses hearing aid and/or cochlear implant, at one ear or both ears
- Individuals with normal hearing but have problem in processing auditory sound
Process Involved
After making sure that the patient is using a hearing aid and/or cochlear implant which is consistently functioning well, parents need to provide an environment which allows the children to be exposed to optimum auditory stimuli.
Pre-speech Training
Pre-speech training is a basic training performed to make it easier for the children to learn listening. Pre-speech skill include the copying skill, matching objects or pictures, take turns, give attention and eye-contact.
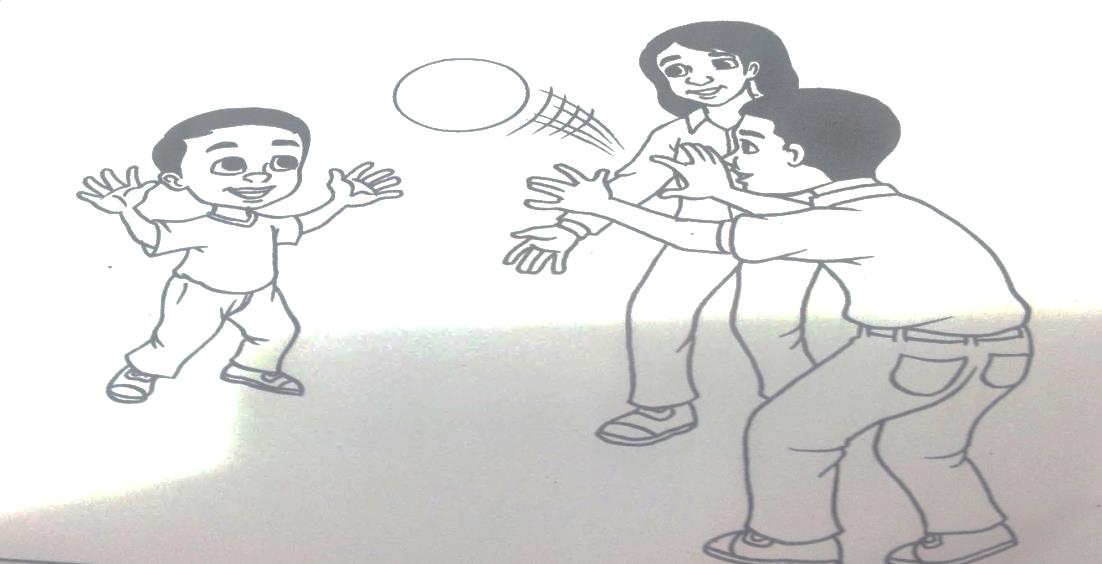
Activities done are for example every morning after the child wakes up from sleep and has put on the hearing device, sit in front of the child and says “ good morning” and talk as much as possible to the child with various facial expressions and appropriate body gestures. Besides that are ball throw-and-catch activity in couple or in group and matching objects and pictures.
|
|
|
Activity of throwing ball |
Listening Skill Training
Listening skill consist of four stages which is detedtion, discrimination, identification and comprehension (Erber 1984). Hierarchy of listening skill development is applied in auditory training activities which are :
|
Auditory Skill |
Example of suitable auditory training activities |
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
Play pretend cooking, play role acting (for example as a doctor or police), question and answering, hearing the parents read the storybook, play hide and seek Understanding sound which brings meaning, for example the sound of knock on the door means that someone is outside and wants to enter the house or to visit, the sound of the car horn is the signal for danger |
The ultimate goal in auditory training is focusing on helping the children to use speech.
References
- Nor Azizah Nurdin, Yusmeera Yusof (2008) Buku Latihan & Penilaian Modul Latihan Auditori, MOLA, Malaysia, Saahifah Global Resources
- http://www.tsbvi.edu/seehear/fall03/training.htm
- http://www.asha.org/Publications/leader/2008/080415/080415e.htm
- http://www.heara.ca/content/why-do-i-need-auditory-training
- http://www.hearingpro.com.au/hearing-solutions/auditory-training
- http://devdelay.org/newsletter/articles/html/34-auditory-training.html
- http://www.betterhearing.org/aural_education_and_counseling/Hearing_Loss_retraining_brain/
| Last Reviewed | : | 4 August 2017 |
| Writer / Translator | : | Ummu Athiyyah bt Abdul Razak |
| Accreditor | : | Juliana bt. Samsudin |