Introduction
Bacteria and viruses are parts of medical importance microorganism. Bacteria and viruses cannot be seen by naked eyes. There are some useful and harmful bacteria, but almost all viruses are harmful to human.
What is bacteria?
Bacteria are single cells microorganism and found everywhere, including human’s body. Bacteria visible with a light microscope and capable of multiplying by themselves.
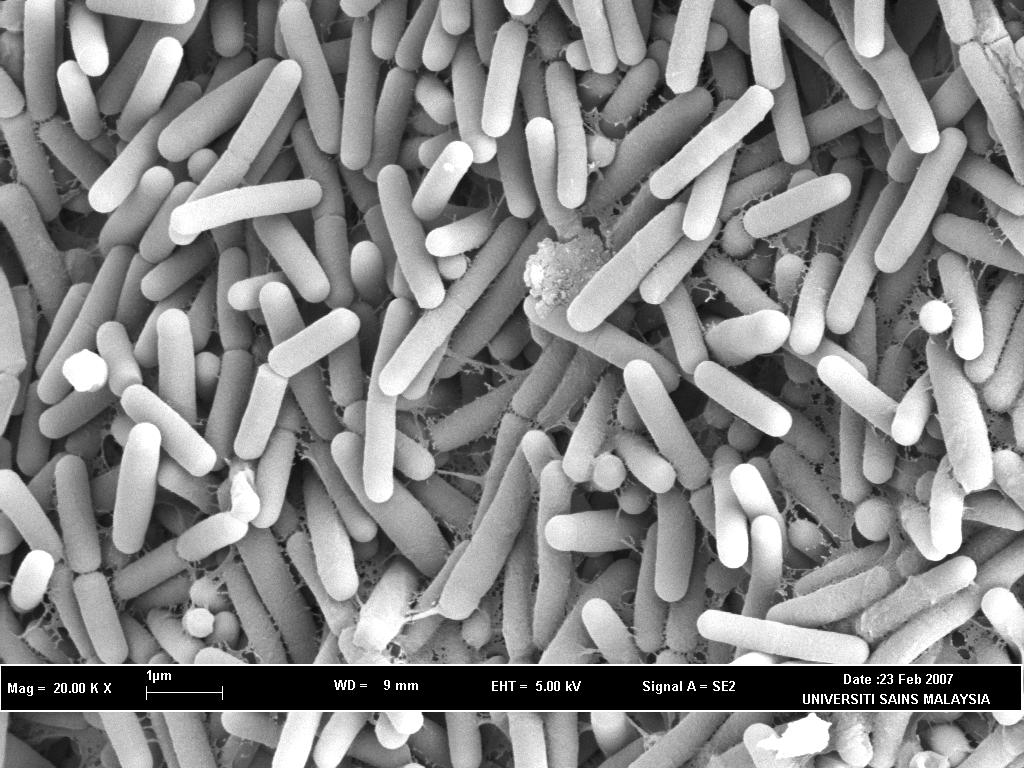

Fig 2 : Bacteria
What is a bacterial infection?
Bacterial infection is an infection caused by bacteria. Bacteria that cause bacterial infection called pathogenic bacteria. Transmission routes of bacteria are :
-
Respiratory tract ; Bordetella pertussis
-
Open wound ; Escherichia coli
-
Direct contact with infected animal ; Bacillus anthracis
-
Oral ingestion of contaminated product ; Brucella abortus
Bacteria also transmitted by sexual contact (Treponema pallidium) and during delivery between infected mother to child (Neisseria gonorrhoeae)
What are the symptoms of bacterial infection?
Bacterial infection symptoms are usually confined to one area of the body. The symptoms are:
-
Redness
-
Swelling
-
Pain
-
Sore throat
-
Fever
-
Headache
-
Aches
What are the diseases caused by bacteria?
Bacteria attack the body and breakdown the immune system. Disease caused by bacteria are as listed below :
-
Whooping cough ( Bordetella pertussis)
-
Urinary tract infection ( Escherichia coli )
-
Ulcer ( Helicobacter pylori )
-
Leptospirosis ( Leptospira interrogans )
-
Tuberculosis ( Mycobacterium tuberculosis )
-
Typhoid fever ( Salmonella typhi )
How to diagnose bacterial infection?
The diagnose of bacterial infection involve microscopy study, staining, cultivation and isolation of bacteria from specimen. Specimens used are as listed below :
-
Sputum for respiratory infections
-
Pus and wound swab for wound infections
-
Blood for blood infections
-
Feces for diarrheas
-
Cerebrospinal fluid for meningitis disease
-
Urine for urinary tract infections
All the specimens will be tested for the present of bacteria.
How to prevent and treat bacterial infections?
Bacterial infection usually is treated with an antibiotic. Antibiotic could kill bacteria or prevent bacterial growth. Prevention of bacterial infections includes ;
-
Good healthy lifestyle
-
Avoid contaminated food and water
-
Wash our hands regularly
-
Proper food preparation
-
Safe sex
What is virus?
Viruses are the smallest infectious agents. Viruses only can be seen under electron microscope. Viruses replicate only in living cells and able to infect plants, animals, bacteria and humans.
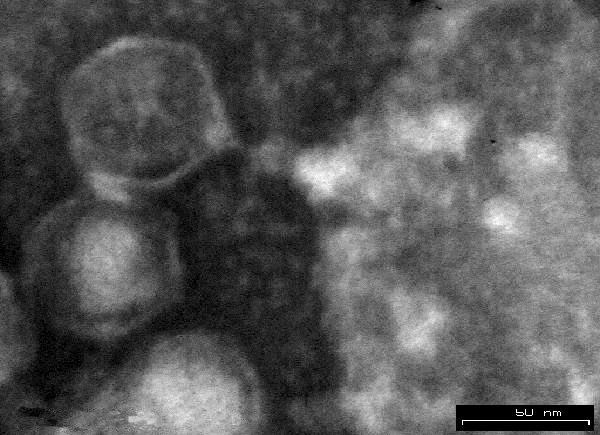
Fig.1 : Virus
What is viral infection?
Viral infection is an infection caused by viruses. Common routes of infection of human by viruses are in the following ways:
-
Respiratory tract ; influenza viruses, measles virus
-
Mouth or Intestinal tract ; herpes simplex virus
-
Injured skin ; HIV, hepatitis C virus
-
Infected insect bites ; dengue virus by mosquito
-
Infected animal bites ; rabies virus by dog
Viruses also transmitted sexually (herpes viruses) and during pregnancy from an infected mother to child (cytomegalovirus).
What are the symptoms of viral infection?
Most of viral infection symptoms are the same and depends on the types of viruses. The symptoms are :
-
Running nose
-
Sinus
-
Cough
-
Sore throat
-
Rashes
-
Aches
-
Fevers
What are the diseases caused by virus?
Various types of viruses cause various types of diseases. Some diseases caused by viruses are as listed below :
-
Hand, foot and mouth disease ( coxsackie virus )
-
Chronic hepatitis disease ( hepatitis B virus )
-
AIDS ( human immunodeficiency virus )
-
Chicken pox ( varicella-zoster virus )
-
Mumps ( mumps virus )
-
Warts ( human wart virus )
How to diagnose viral infection?
A viral infection is diagnosed by several methods and specimens, depends to the site of infections and suspected viral infections. Types of specimens collected to diagnose are as listed below :
-
Sputum, throat and nasal swab for respiratory tract infections
-
Conjunctival swab for eye infections
-
Urine for urinary tract infections
-
Blood, urine and genital swab for sexually transmitted disease
-
Stool and rectal swab for gastrointestinal tract infections
-
Skin scrapping, fluid from vesicles and blood for skin infections.
Methods used, including PCR, cultivation techniques and electron microscopy, in order to detect viral antibody , antigen or particle.
How to prevent and treat viral infection?
No specific treatment for viral infections. Viruses treated with anti viral medications and prevented with vaccinations. Anti viral only fight specific symptoms and boost immune system, so body can fight it off on its own. Viruses cannot be killed by antibiotics. We can prevent viral infections by :
-
Washing hands regularly
-
Maintain a good sexual behaviour ( safe sex )
-
Avoid taking contaminated food and water
-
Avoid sharing needles and syringe
-
Consume a balance diet
Similarities and differences between bacteria and virus
|
Characteristics |
Bacteria |
Virus |
|
Similarities: Observation under microscope? |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Differences: Size Reproduction Treatment |
Larger Binary fission Antibiotic |
Smaller Invades a living host cells and replicate with the help of host cells Antiviral |
| Last Reviewed | : | 31 Mac 2015 |
| Writer | : | Mohd Faizal b. Mohamed Yusuf |
| Translator | : | Mohd Faizal b. Mohamed Yusuf |
| Accreditor | : | Normah bt. Untong |







