Scars can come in all shapes and sizes and are rarely something that you’d like to show off. The truth is the scar will never completely go away. But there are many ways to hide your scar. It ranges from covering it, reducing its size, changing its appearance or having them removed permanently.
What Are The Types of Scars? Consult your dermatologist.
They’ll be able to tell you what kind of scar you have and suggest the treatment. They will discuss on option for prescription or further action required whether you need peeling, steroid injections, or laser surgery. More importantly, they’ll be able to answer all your scar-related questions.
There are four types of scars:
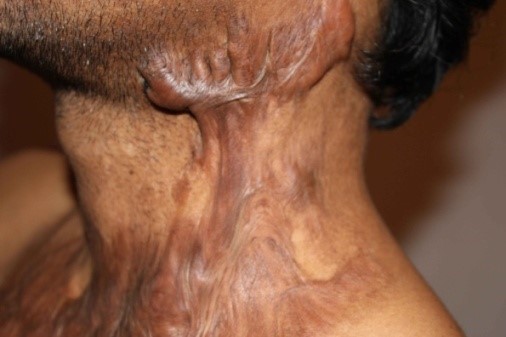
- Keloid scars: It is the result of an overly aggressive healing process. They extend beyond the original injury. It is basically a thick, raised, overgrowth on the skin. Over time, a keloid scar may restrict function or movement. Keloid scars are most common among people with dark skin.
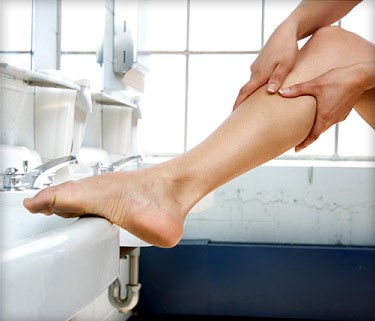
- Contracture scars: The scars usually arise after burn injuries. These scars tighten skin, which can impair your ability to move. Contracture scars may extend deeper, affecting muscles and nerves.
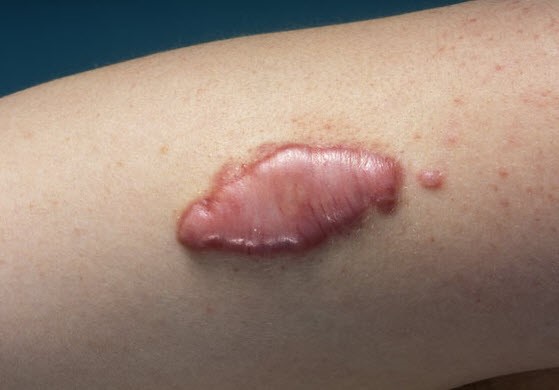
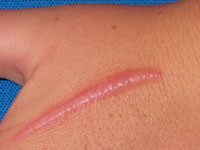
- Hypertrophic scars: raised, red scars that are similar to keloids but do not go beyond the boundary of the injury.
dermnetnz.org Hypertrophic scar
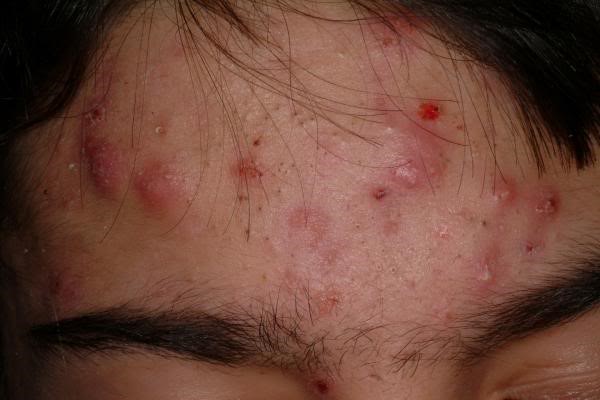
- Acne scars: If you’ve had severe acne, you probably have the scars as evidence. There are many types of acne scars, ranging from deep pits to scars that are angular or wave like in appearance.
What Are Possible Treatments for Scars?
Scar treatments may include:
- Over-the-counter or prescription creams, ointments, or gels.
These products can be used to treat scars that are caused by cuts or other injuries or wounds. Ask your doctor, dermatologist or surgeon, if over-the-counter treatment is an option. These products, must be applied liberally and consistently. Apply your cream according to your daily routine for examples breakfast, lunch and dinner to ensure your compliance. In addition to scar-reducing creams, always use SPF on your scar if you are going outdoor. Sun exposure will darken the scar and make it worse. If over-the-counter treatment did not show improvement, your dermatologists may recommend treatments like steroids or antihistamine creams for scars that itchy and sensitive. - Surgical removal or treatment.There are many options to treat deep scars depending on the type of scar
These include:- Skin graft, the surgeon uses skin from another area of your body. This is often used with people who’ve had burns.
- If your scar impairs function, surgery can help to address the functional problems.
- If your recent surgery t has caused scars, it is best to wait at least one year before making a decision about scar treatment. Many scars fade away and become less noticeable over time.
- Other option may include excision, dermabrasion, or laser surgery
 www.acnescarstreatment.ca www.acnescarstreatment.ca |
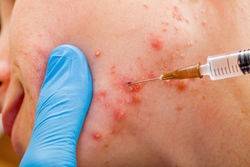
- You may get steroid injections to treat scars that raised, such as keloids or hypertrophic scars. Your doctor may use steroid alone or in combination with other treatments. Other types of injections, such as collagen or other “fillers,” may be useful for some types of pitted scarring, although these are not usually permanent solutions.
- Silicone sheets or patches.These are best for keloid (extra scar tissue where the skin has healed) and hypertrophic (abnormally enlarged) scars. They must be worn everyday for at least 12 hours over a period of 8 to 10 week
- Don’t be deceived by the myth of Vitamin E.It’s a fat-soluble vitamin available in foods and as supplements. There is no scientific studies that prove Vitamin E improves the appearance of scars.
Tips
- Scars fade away over time. You have to be patience and, you may find that your scar becomes almost unnoticeable by itself.
- A dermatologist may recommend various methods. Every scar is different and has to be treated differently therefore pre-treatment consultation is important.
References
- Article Link: http://www.webmd.com/beauty/skin/cosmetic-procedures-scars
| Last Reviewed | : | 28 August 2021 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Zil Falillah binti Mohd Said |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Siti Aishah binti Saidin |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Nazhatussima bt. Suhaili |


 http://media.photobucket.com/
http://media.photobucket.com/




