|
Introduction Burn is a common injury which is easily prevented. In case of abuse, burns can be intentionally inflicted. Children are naturally susceptible to burn injuries because of their curiosity and immature motor skills. |
 |
Common causes of burns include :
- Scalds from tipped-over hot water, cooking fluids or hot water-bath
- Hot objects such as hot iron, stove
- Flames from overheated cooking oil, fire-crackers
- Chemical burns such as corrosives
- Electrical burns such as playing with live electrical cord, extension wires, unprotected sockets etc
- Prolonged exposure to hot sun
Sign & symptoms
Burns are classified into :
- Superficial
- It involves only the superficial layer of the skin. The skin is red and painful but no blistering occurs.
- Partial thickness
- It involves the outer layer of the skin. Apart from red, hot and painful skin, blisters are formed.
- Full thickness
- It involves all the layers of skin and may involve deeper tissues.
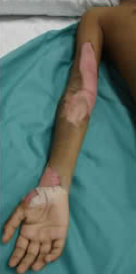
Partial thickness burns
The skin looks pale, leathery and charred. It is painless as the nerves are also damaged.
Complications
Serious complications may occur if large areas are effected and with increasing depth of skin involved :
- Infection – the signs include fever, pus discharge and worsening pain and swelling
- Potential late complications are contracture at joint area and scarring in areas with full thickness burn
Treatment
Superficial and partial thickness of burns involving small area of skin (less than the size of your palm) can be managed at home.
- Remove tight clothing and rings carefully
- Put the affected area under the running tap for about 15 minutes
- Apply soothing cream or lotion indicated for burns
- Do not apply other home remedies such as grease, butter, hair cream or tooth paste which can predispose to infection
- Give Paracetamol syrup to relief the pain
- Do not break a blister. If it has broken, leave the flap alone
- You may need immunization to prevent tetanus. Consult your doctor
Medical attention should be sought in :
- Full thickness burn
- Partial thickness burn involving area more than the size of a victim’s palm
- Any involvement of the mouth or throat, eyes, ears, face or genital area
- Burns caused by corrosive or chemicals
- Burns caused by electricity
- Irritable or lethargic child
Follow the instructions as for the superficial and partial thickness burn. Cover the effected area with clean clothing or bandage. Child will need Tetanus injection if not fully immunized for age or if the last injection was more than 5 years ago.
Prevention
- Children must be kept away from hot stoves, hot water and all types of electrical appliances
- Do not put a child in a walker in the kitchen
- Do not hold a baby or small child while you’re cooking
- Do not carry hot soups or liquids when your child is near you
- Matches, lighters and cigarettes must be kept away from children
- Avoid children from playing with electrical outlets or sockets on the wall of the house
- Avoid dangling wires of any electrical appliances and keeping a hot iron in a safe place
- Avoid using tablecloths as small child can pull and overturn anything on the table
Rehabilitation
- Physiotherapy and occupational therapy depending on the degree and site of injury.
- Some burns may require skin grafting.
| Last reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Content Writer | : | Dr. Norraliza Md Zain |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Mohamad Hamim b. Mohamad Hanifah |







