Is it possible for the special needs child to have braces? Could braces improve their quality of life and acceptance within the society? The answer is yes. Braces for special need children is considered normally considered as an elective treatment. The indication and criteria for treatment are similar as to the normal children. What are different are the treatment planning and the provision of dental care which may be modified in view of the patient’s capabilities, likely future cooperation and home care.
Who are the Special Needs Children?
They are children who are disabled by a physical and/or intellectual or emotional condition that prevent them from being treated in a routine manner
They can be categorized as children with developmental disability, medically compromised and those with high risks. The figure below is a short example of children who can be classified as special needs children.
Do the Special Needs Children Need Braces?
There are several benefits for having braces. These include:
- Improving the arrangement of teeth and aesthetics of the smile.
- Improving the dental health when teeth are easier to clean after they are well arranged.
- Improving speech and mastication in cases where the front teeth are not in contact with each other. With braces, the position of teeth can be corrected and thus improves its function
Similar to other normal children, special needs children may not necessarily need braces if they do not wish to wear braces. Generally braces would make it easier for food to get trapped around the surfaces of the teeth. Thus this would increase the risk of getting dental diseases such as tooth decay if good oral hygiene is not maintained throughout treatment.
Why Special Needs Children Require Special Attention During Braces Treatment?
This is because special needs children
- Often has reduced comprehension, increased apprehension, short attention span and limited tolerance
- Have uncontrolled limb and head movements making them difficult to seat in the dental chair
- Have reduced cooperation during treatment
- Have exaggerated gag reflex and dental phobia
- Have increased drooling of saliva
What Are The Types Of Braces For Special Needs Children?
The type of treatment provided for special needs children may not necessarily be any different than any other normal patient. Usually, treatment would be based on the malocclusion (dental arrangement). However, the clinician would take into consideration the child’s or care taker’s ability to maintain the braces in the mouth safely.
Below are the types of treatment that could be given to special needs children:
- Removable brace
The patient would be able to remove and insert the braces by themselves. In order to get a successful result, compliance from the patient because this braces need to be worn 24 hours except during brushing the teeth. This removable brace is used to treat simple malocclusion which requires minor teeth movement. Removable brace is also usually used in maintaining or holding the alignment of the teeth after finishing braces treatment. - Removable functional brace
The removable functional brace is used to enhance the growth of the lower jaw in growing patient. This brace is suitable for the patient with small lower jaw and sticking out of upper front teeth. - Space maintenance Space maintenance is usually placed on the first permanent molar in cases, which the baby tooth adjacent to it is damaged due to caries or need to be removed (extracted). A space maintainer will restrict the forward movement of first permanent molars and prevent the development of crowding (teeth overlap each other because there is not enough space to allow the teeth to develop in a straight alignment).
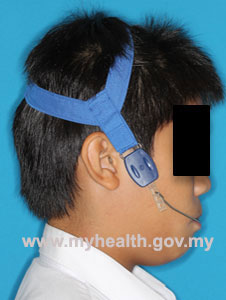
- Head brace (or Headgear)
Head brace is used to restrict the growth of the upper jaw and simultaneously correct the sticking out of upper front teeth. This brace is suitable for growing patient with forward positioned upper jaw and sticking out upper front teeth. - Bone brace
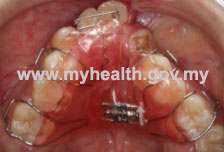
The bone brace is a small pin-like metal screw, which is inserted through the gum into the jaw bone. In adult patient, the bone brace sometimes is used as an anchor to correct the sticking out upper front teeth. This brace is used temporarily during treatment. It will be removed after the treatment is completed. - Expanding brace This brace is fixed and used to widen the upper jaw in order to match the width with the lower jaw. Special needs children who have narrow or inadequate space to accommodate their teeth in the upper jaw may be suitable to use this brace.
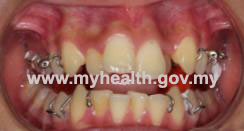
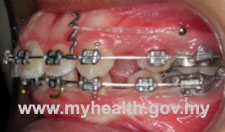
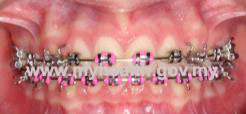
- Fixed braces
Fixed braces are usually made from metal. These braces are visible and glued on the front surface of the teeth. If the patient or parents are concerned about the visibility of the metal braces, they can choose to have ceramic braces, which have almost the same colour as the teeth.
What are the dental situations in the Special Needs Children that May Be Referred To The Orthodontist And May Involve Both Orthodontist And Pediatric Dentist?
- Thumb/Finger Sucking
Thumb or finger sucking habit may cause distortion of the teeth and a habit breaker may be constructed as a reminder to stop the habit. 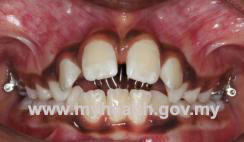
- Lack of space for tooth eruption Inadequate space in mixed dentition needs to be intercepted by removing the baby teeth to allow the eruption of adult teeth. If the upper jaw is narrow and there is lack of space, widening of the upper jaw may be needed.
- Unerupted teeth If the tooth is still buried in the bone after the eruption time, opinion from the orthodontist or paediatric dentist may be needed to prevent potential damage to the other teeth. This may happen when the unerupted tooth moves within the bone and knocks against the underlying root structure supporting the position of the other tooth.
- Early loss of baby teeth
Space maintenance may be needed to prevent the forward movement of the teeth and development of crowding.
- Missing teeth Arrangement of the teeth or prosthesis may be needed to maintain aesthetics and function of the dentition
- Forward position of upper jaw/ backward position of lower jaw/ forward position of upper front teeth Functional brace may be needed to correct the position of upper front teeth and simultaneously correct the upper and lower jaw.
If The Special Needs Children Need To Have Braces, What Are The Essential Things That Parents Should Be Aware Of?
- Motivation Parents need to understand that before seeing an Orthodontist, regular follow up by Pediatric dentist is important for monitoring the eruption of teeth and maintaining good oral hygiene. Parents also must take the responsibility to make sure their children have the required standard of good oral hygiene before commencing braces treatment. Regular maintenance of good oral hygiene and attending follow up braces treatment appointment in 6 weeks interval are important factors for the success of treatment.
- Expectation Parents should not put high expectation for the treatment outcome because some special needs children may have anxiety and difficulties to tolerate with braces treatment.
- Medicine Special needs children sometimes require sedatives to make them calm and cooperate during the treatment. This may involve joint management with the Pediatric Specialist.
- Extraction of the teeth In some cases, teeth need to be extracted in order to create space to relieve crowding and reduce the jutting out of the upper front teeth. Admission to the hospital may be required for extraction procedure of medically compromised patients and will be managed by the Pediatric Dental Specialist.
- Duration of treatment Normally braces treatment may take around 2-3 years depending on the severity of the malocclusion. Treatment may be longer for special needs children because of their poor ability to cooperate with the treatment.
- Cost of treatment Complication of the treatment and extended treatment time may increase the overall cost of the treatment.
- Relapse After the completion of the braces treatment, patients must wear retainers to hold the teeth in the new position. Failure to follow the instruction to wear the retainers may lead to the movement of the teeth towards their original position. Nighttime wear of the retainers are required as long as the patients want their teeth look straight.
What Are the Expectations required from the Special Needs Children Who Are Interested to Have Braces? What Are The Obstacles That The Parents Need To Understand?
- Maintenance of good oral hygiene Oral hygiene must be very good to prevent risk of wearing braces. Failure to keep the teeth clean may lead to white spot lesion, caries, swollen gums and bleeding gums. Teeth need to be brushed every time after meal and before going to sleep with fluoridated toothpaste. It is recommended to use electric toothbrush for the special needs children who has neuromuscular problems.
- Records taking
If sedation and GA are needed for taking the records, other dental procedures need to be combined in order to limit the number of visits to the clinic
Taking mould of the teeth (Impression) This process is usually uncomfortable but well tolerated by normal children. However, anxious special needs children may not tolerate this process with good communication alone. An alternative method to make them calm may include providing nitrous oxide conscious sedation alone or with combination with sedative medicine provided by the Paediatric Specialist.
Taking an X-rays Special needs children often frighten or panic when facing the X-ray machine. In patients with poor cooperation, neuromuscular problems or mental retardations, getting good clear image of the X-rays is difficult. Alternatively, the parents may be asked to hold the X-ray films during the procedure as having familiar faces close by may make the children less anxious.
- Treatment
- Treatment plan may be reassessed depending on the cooperation of the patient based on the previous stage of treatment.
- Removable braces are preferred than fixed braces for special needs children because fixed braces require complete dryness of the teeth, accurate positioning of the braces and longer treatment time. Sometimes sedation may also be needed to help the placement of braces. Anti-sialagogue drugs that temporarily reduce salivation may be used to maintain the dryness of the mouth.
- Patients with fixed braces require high motivation to maintain good oral hygiene compared with removable braces. In fixed braces treatment, extraction of teeth may be delayed or avoided in order to reduce the treatment time and simplify the treatment. Treatment with head brace and rubber bands, which require great cooperation, may be avoided to reduce the parents’ and patients’ burden.
- Aspiration (materials entering the lungs) may occur for the patient who has lost the protective reflexes. Care needs to be taken to prevent debris, water, saliva, blood and part of the braces from entering the airway by using gauze pack or rubber dam. Indirect bonding of the braces may minimize the possibility of aspiration.
- Retention Patients need to wear retainers as long as they want their teeth to look straight. Removable retainers will hold the teeth in the upper and lower jaw. But good cooperation from the patient is needed. Fixed retainers that would be glued behind the surface of upper and lower teeth may prevent the movement of the corrected teeth from moving into their original position but the accurate placement of fixed retainers may involve sedation. Furthermore it is more difficult to clean the fixed retainer because it is behind the teeth. This may increase the risk of tooth decay around the retainers.
What Should Be Done If The Special Needs Child Has Accidentally Swallowed The Part Of Braces?
It is very rare for the patient to swallow components of their braces. General precautions need to be taken if it occurs. The parents need to inform the Orthodontist. They must seek emergency treatment at the hospital. Usually the medical doctor may rule out the location of the material, whether it has been inhaled in the lung or swallowed in the stomach. If the material is in the stomach, it will be out from the body after passing motion with the stool. But if it is in the lung, bronchoscopy is indicated to remove the material.
References
- Interceptive Orthodontics, A Practical Guide to Occlusal Management, Joseph Noar, 2014
- Orthodontic Treatment For the Special Needs Child, Andrian Becker, Stella Chaushu and Joseph Shapira, Seminar in Orthodontics 10:281-292, 2004
| Last Reviewed | : | 8 July 2015 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Mohd Zambri bin Mohamed Makhbul |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Laila bt. Abd. Jalil |