Introduction
Wounds can be categorised into:
- Non-penetrating wounds- this type of wound occurs due to pressure against a surface that result in injury over the skin but does not involve penetration into the deep skin. For example abrasion, superficial cuts, contusion and concussion.
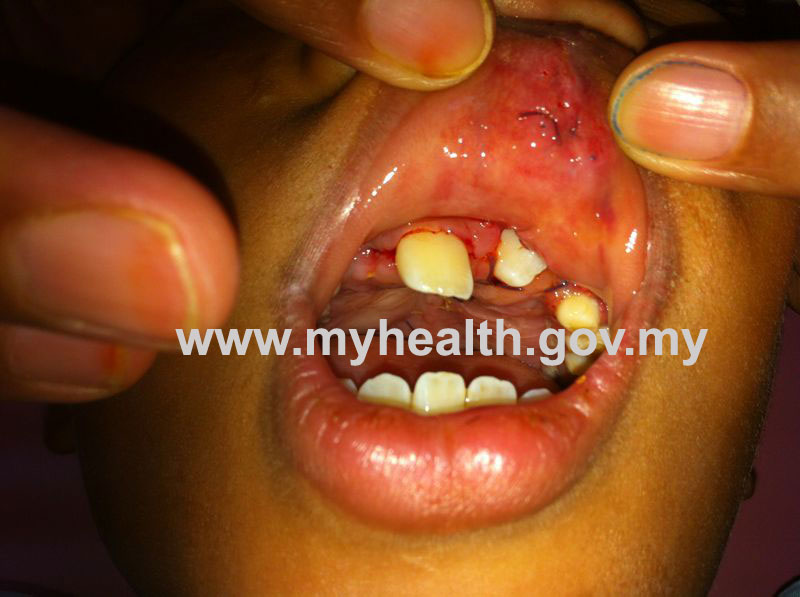
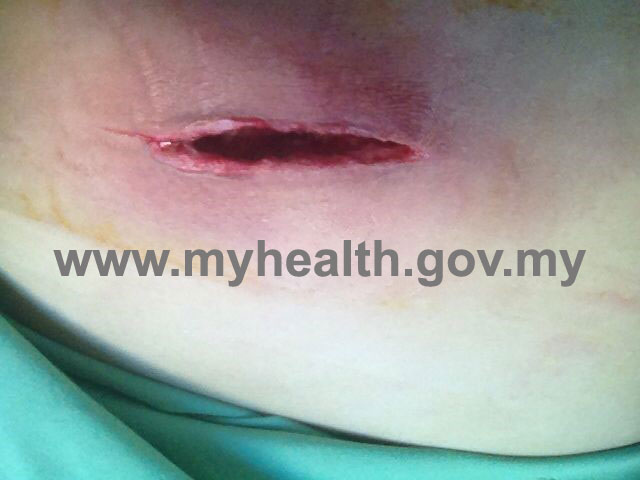
Figure 1: Non penetrating wound – Superficial laceration wound at inner side of the upper lip. - Penetrating wounds – this type of wound involves penetration of the whole skin thickness and involve deep and internal vital organ. For example stab wound, cut skin, surgical wound or gun shot wound.
- Miscellaneous- It involves thermal wound such as burn and froze bite; chemical wound such as acid; bite or sting wound; and electrical shock wound.
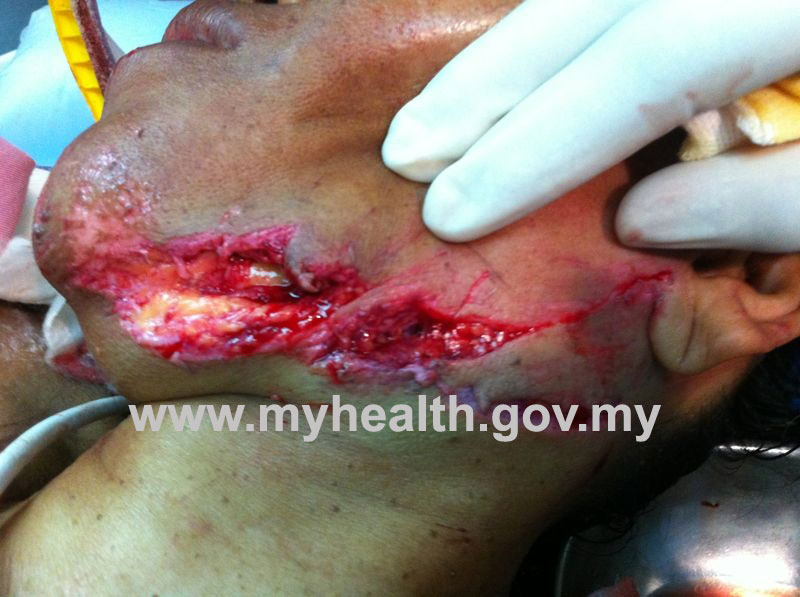
Figure 3: Severe laceration wound exposing bone of the lower jaw which needs proper and thorough management at hospital.
Non-penetrating wounds may be treated easily with first-aid kit. However, for complex wound like penetrating wounds and other wounds that involve deeper structure, a thorough and specific treatment should be given by the professionals.
First-aid for non penetrating wounds
- Apply pressure onto the wound using a clean cloth or bandage for about 10-15 minutes to arrest the bleeding.
- Using a clean hand, wash the facial wound using soap and water without rubbing the wound.
- Remove dirt from the wound under running water.
- Apply antiseptic cream/ lotion onto the wound. Avoid eyes area.
- For a small superficial cut, you may use surgical tape such as Steri strip to approximate the wound. Change frequently if necessary.
- Cover the wound with plaster or gauze. Change frequently if necessary.
- Inspect the wound everyday- make sure the wound is clean and dry.
- Apply ice pack onto a swelling, haematoma or abrasion wound for every 10-15 minutes over 1-2 hours. Avoid direct contact with skin.
- Apply sun screen cream (SPF>15) onto the facial wound (after 72 hours of treatment) to reduce darkening of the scar.
Get an urgent treatment at the nearest clinic or your panel when you find:
- Excessive Bleeding From The Wound Even Though Pressure Has Been Applied For More Than 15 Minutes
- Facial Wound That Involves Eye And Surrounding Region
- Stab Wound From Sharp, Rusty Or Dirty Object
- Dirty Wound That Is Covered With Sands, Soils And Others.
- Deep Wound Or Length That Is More Than ½ Inch
- Large And Jagged Wound
- Bite Wounds From Human Or Animals
- A Very Painful Wound That Involves Facial Bone Fracture Or Head Injury
- Wound That Shows Sign Of Infection Eg. Redness, Swelling, Warm And Presence Of Discharge
- Never Had Or Unsure Of Receiving Tetanus Vaccination Within 5 Years
Care for complex facial wounds
Treatment for deep and complex wounds have to be referred urgently to the nearest clinic before its getting worse. The treatment can be done under local or general anaesthesia depends on it severity, health issues and patient compliance. Meticulous work and surgical skill is needed to treat facial wound injuries that involve not only soft tissue but also the hard tissue. Therefore, patient need to really adopt to the instructions of facial wound care so as to get the optimum result. Please refer to the instructions below:
- Dressing on the wound should be left in place for the first 24 hours. If the dressing is soaked, soiled or dirty, it has to change immediately. After 24 hours, the dressing should be remove and the wound is left open until it heals.
- Patient is allow to take bath after 24 hours post operation. There is no problem for the wound to get contact with water. If you feel uncomfortable, the wound can be cover with sterile gauze and the gauze need to be removed after bath.
- You may use surgical tape such as Steri strip to the sutured wound for reinforcement to increase strength against separating forces. Change frequently if necessary.
- Wound toilet have to be done at least twice daily using normal saline.
- After wound toilet, antibiotic ointment such as Chloramphenicol 1%, bacitracin zinc ointment or neomycin sulphate have to be applied over the wound to reduce infection and scab formation.
- Rinse with normal saline or mouth gargle that contains Chlorhexidine gluconate 0.12% such as Difflam C for intra oral wounds. Clean wounds will promote faster healing.
- Make sure that you complete the antibiotic by following proper dosage, time and frequency prescribed by your doctor. If you encounter any of the side effects or adverse reaction after taking the medicine, please consult your doctor or go to the nearest clinic urgently.
- Stitches on the facial need to be removed in 5-7 days. Please follow your appointment date given.
- Facial wound from injury or surgical wound will take a few months to completely heal. During the initial healing, the skin tissue is weak and wound breakdown can occur under certain tension. Therefore, it is crucial to take good care of the wound.
- As mentioned above, sun screen cream (SPF>15) application onto the facial wound (after 72 hours of treatment) is important to reduce darkening of the scar. Use cap/ hat or an umbrella to cover your face from sun light.
- Should the wound shows any sign of infection eg. redness, swelling, warm and presence of discharge, get an urgent treatment at the nearest clinic or your panel.
Please follow the above instructions regarding facial wound care. If you have any inquiries, please consult your doctor or go the the nearest clinic.
References
- Medel N, Neeraj P and Ellis E. Postoperative care of the facial laceration. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction 2010; 3(4):189-200
- Nicks BA, Ayello EA, Woo K, George DN and Sibbald RG. Acute wound management:revisiting the approach to assessment, irrigation and closure considerations. International Journal of Emergency Medicine 2010; 3:399-407
| Last Reviewed | : | 8 July 2015 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Farah Aliya bt. Mohamed Azahar |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Nur Ikram Hanim bt. Abd. Rahim |