What is chickenpox infection?
This is a common infection in children, caused by a virus. The chicken pox virus is also called varicella virus. It is the same virus that can cause shingles. It is a highly contagious disease spread from person to person. Infected persons develop fever and a blister like rash. It is spread:
- Through the air when someone with chicken pox coughs or sneezes.
- By touching the watery stuff that comes out of chickenpox blisters.
What are the signs & symptoms?
Your child can develop chickenpox 10-21 days after coming in contact with someone who has it.
Chickenpox is contagious from one to two days before the rash appears until all the rashes have crusted over and dried up. Most children have a mild illness but adults, adolescents and young infants can be very sick. Symptoms include:
- Fever, feeling unwell and tired about five days before the rash.
- Rash starting as small, itchy, red spots like pimples, all over the body including the mouth. The rash usually starts on the chest and back, and spread to the face, scalp, arms and legs.
- Within 24 hours, the rashes look like water blisters which then burst, dry up and become crusts (four to five days).
- New spots continue to develop for five days and take about two weeks to go away.
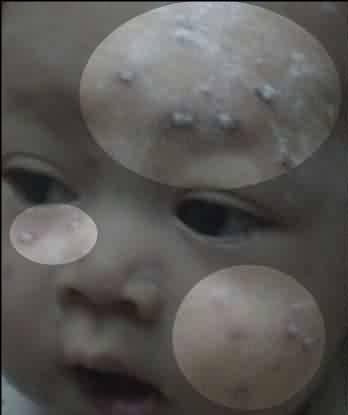
Chickenpox lesions
Chickenpox infection generally results in lifelong immunity. However, this virus may remain hidden and recur as shingles in a proportion of adults and sometimes children.
What are the complications?
Chickenpox is usually mild in healthy children and most will recover. However, some people are at risk for severe complications. These are newborn babies, adults and persons with weakened immune system (example people infected with HIV, cancer, or people receiving steroids).
Complications that can occur include:
- Bacterial skin infection.
- Blood stream infection.
- Pneumonia.
- Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis, cerebellar ataxia).
How is chickenpox infection treated?
General:
- Keeping your child away from school or nursery until the rash has crusted (about seven days from the onset of rash), his friends may get it. Refrain from air travel.
- Take paracetamol for fever.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Take balanced meals or small frequent snacks.
- Keep hands clean.
For itchiness:
- Calamine lotion may be applied on the rash.
- Keep fingernails short to prevent skin damage from scratching.
- Antihistamine medicine may be prescribed by the doctor if the itch is very bad and your child can’t sleep.
Antiviral medicine (oral form) for chickenpox is available and is usually prescribed by the doctor for those at risk for severe disease, namely:
- Those older than 12 years old.
- Those with chronic lung disease/skin disease.
- Those on long term salicylate therapy (like aspirin).
- Those receiving short, intermittent, or aerosolized course of steroid therapy.
- Some groups of pregnant mother.
How can chickenpox be prevented?
- Chickenpox can be prevented by immunization. This vaccine is called “varicella zoster vaccine” and available at private sector (not part of our immunization programme). 2 doses, first given at 12-18 months of age, and the second dose of age 4-6 years old. For older children, 2 doses required with 4-8 weeks interval.
- Infants born to mothers who develop varicella between 5-7 days before delivery or 5-7 days after delivery should be admitted and received prophylaxis.
- If you have chickenpox, prevent spread to others by staying away from school or work until all blisters have crusted.
- Vaccine can also be used following exposure to person infected to prevent disease occurrence if your child had never had this infection before. Consult your doctor.
- Person at risk for severe chickenpox (newborns, those with weakened immune system, pregnant women) may be given antibodies in the form of immunoglobulin to provide immediate short term protection, following exposure to a person with chickenpox.
| Last Reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Lynster Liaw Chiew Tung |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Zainab bt. Kusiar |







