A number of children are highly anxious about dental treatment and this prevents them from accepting dental treatment in the conventional manner. There are a number of techniques available to help your child deals better with dental treatment, either using non-pharmacological or pharmacological method (use of drugs).
There are few pharmacological methods available for coping with dental anxiety. The most common modes of pharmacologic behavior management in children are conscious sedation and general anaesthesia.
Conscious Sedation
Conscious sedation is the use of a mild sedative (calming) drug to ease and comfort anxious children while receiving dental care, but during which verbal contact with your child is maintained throughout the period of sedation.
Unlike general anaesthesia (GA), it is not meant to make children become unconscious.
It allows your child to retain the ability to breathe independently and respond appropriately and normally to physical tactile stimulation and verbal commands.
Conscious sedation can be given in several ways:-
- Inhalation sedation
- Oral sedation
- Intravenous sedation
What Is inhalation sedation?
- Inhalation sedation is a light form of sedation using a mixture of nitrous oxide(N2O) and oxygen through a small nose piece.
- N2O is also known as ‘laughing gas’ or ‘happy gas’
- When inhaled and absorbed into the body, N2O gives a natural calming effect that lasts only as long as the dental treatment
- Your child will NOT go to sleep and will be fully aware of their surroundings.
- Your child will usually feel somewhat “tingly” or “ticklish”
- At the end of the treatment, it is eliminated after a short period of breathing 100% oxygen
What are the advantages of N2O?
- Acts very fast and reversible
- Can be adjusted in various concentration
- Enhance communication and patient cooperation
- Increase tolerance for longer appointment
- Reduce gagging
- Reduce or eliminate anxiety
- No “hangover” effect
- No injection is required
- Very safe and quickly eliminated from the body
- Non allergenic
- Painless to deliver
- Wears off within a matter of minutes
What are the disadvantages of N2O?
|
 |
Can my child eat before having N2O?
- Your child may feel sick or vomit. Thus avoid heavy/fatty food prior to the procedure
- Best to feed your child only liquids or a light meal a few hours before the procedure
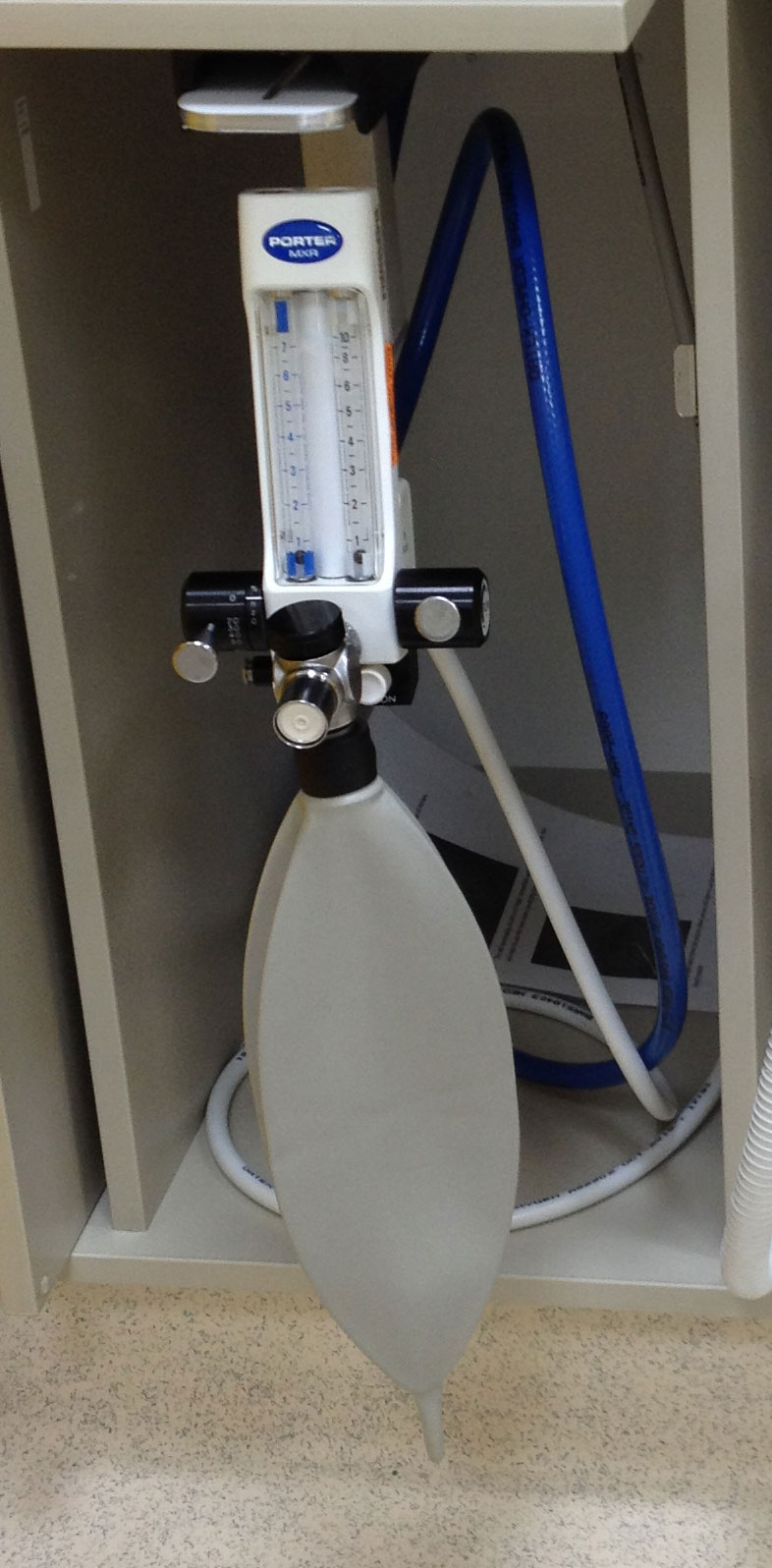
How is N2O administered?
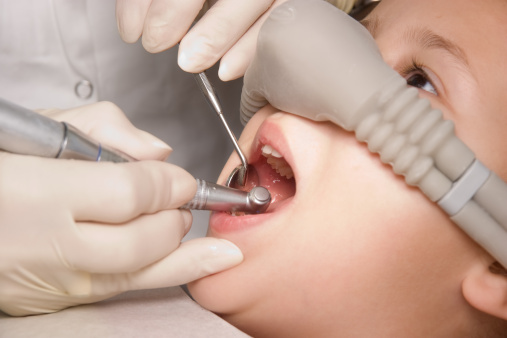 Source : www.smileandshinergv.com |
The “happy gas” is delivered via a quite simple equipment. The desired nitrous oxide-oxygen mix is fed through a tube to which a nasal mask/nose piece is attached. The nasal mask/nose piece is put over your child’s nose, and he/she just has to breathe normally through his/her nose. |
Oral Sedation
|
 |
What are the advantages of oral sedation?
- Convenient and easy
- Inexpensive
- Relatively safe depending on dose
What are the disadvantages of oral sedation?
- Drug cannot be titrated
- Delay on onset
- Higher doses and use of multiple drugs increases risk
- No oral reversal agent
Prior to your child’s appointment
- Dress your child in a loose-fitting, comfortable clothing
- Restrict food and liquids in the hours prior to sedation. Fasting is the best as it decreases the risk of vomiting and aspirating stomach contents into the lungs
- Prepare to stay with your child throughout the procedure and after the procedure
Intravenous (IV) Sedation
IV sedation is when a sedative drug is given into the blood system via a vein during dental treatment. It has to be administered and monitored by a trained medical doctor.
How is IV sedation given?
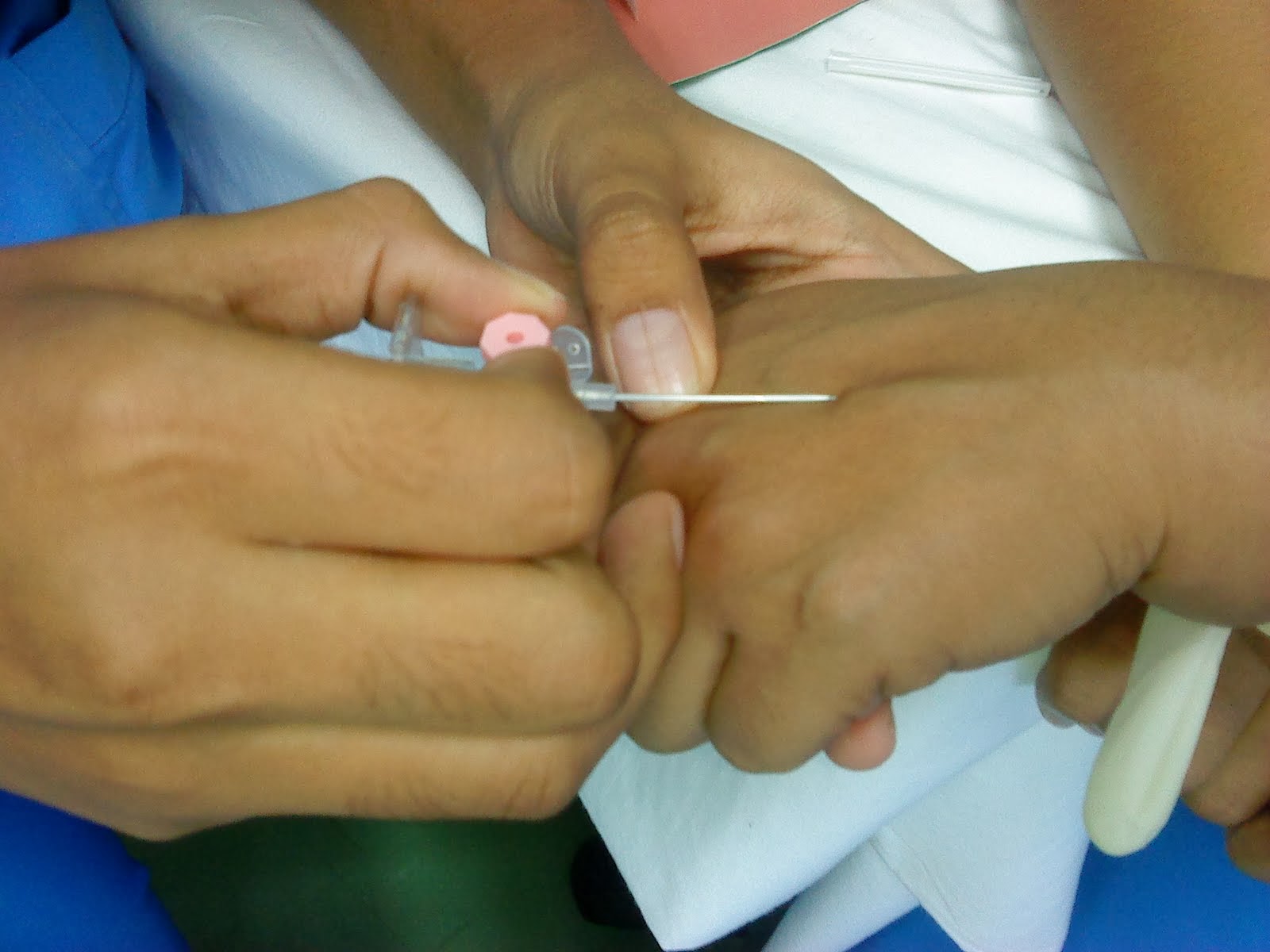 www.mofrust.com |
|
What are the advantages of IV sedation?
- Very rapid onset of action
- Highly effective and reliable
- Deeper maximum level of sedation as compared to oral or inhalational sedation
- No involvement of airway tube
- Reversal agents easily given and have immediate effect
Are there any disadvantages?
- Local swelling of the area where the needle is entered may be encountered.
- Recovery is not complete at the end of the dental treatment
- Venepuncture difficult in needle phobic patients
FAST FACTS ABOUT CONSCIOUS SEDATION
-
For all 3 types of conscious sedation, your sedated child will be monitored during the procedure for vital signs: heart rate, respiration rate, blood pressure, temperature and blood oxygen level by a designated auxiliary staff.
-
Fasting is an important part of conscious sedation. Certain food may “compete” with the sedative agent being administered and delay/alter the desired effect.
-
There is side effect of oral sedation which are called “angry child syndrome”. It is a rare side effect that is self-limiting once the drug wears off.
- Do not bring other siblings or children at the sedation appointment.
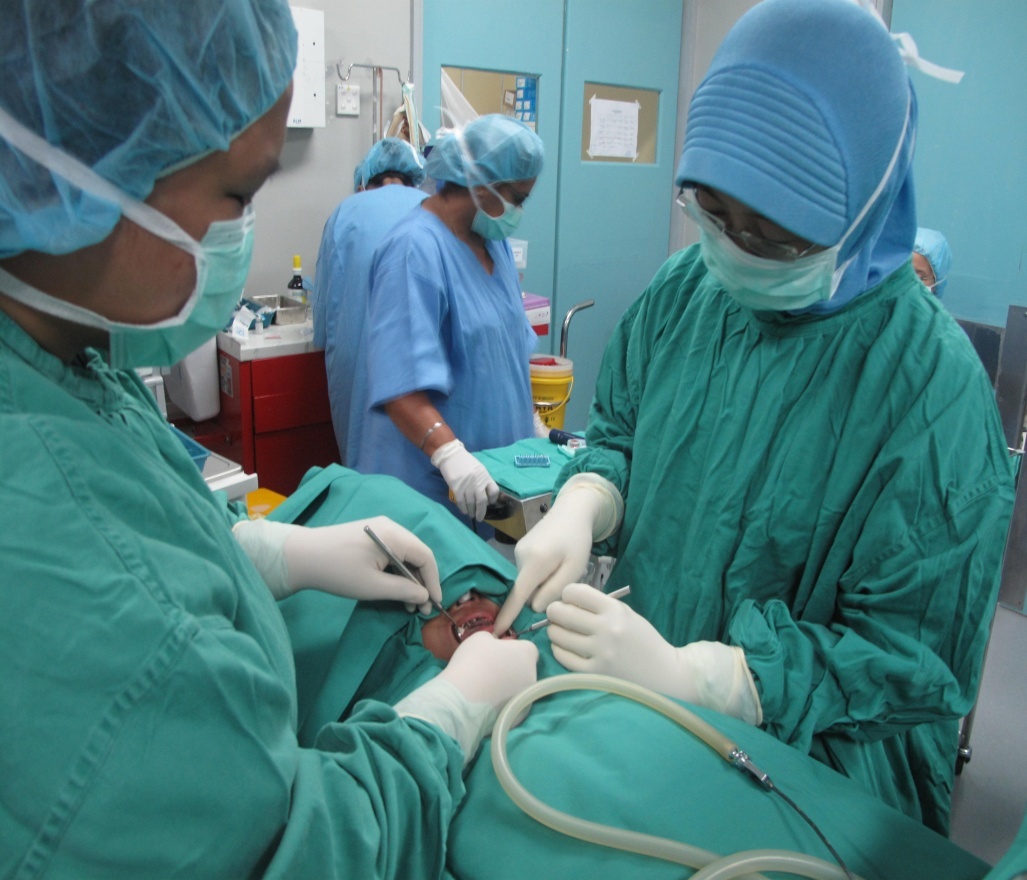
General Anesthesia (GA)
There are certain instances where your children are simply not able to cope with dental treatment at all. If your child is very young, or who have some form of special needs making communication and cooperation not possible, or when there is an extensive work need to be done in his mouth, or cannot cope with the above techniques, general anaesthesia (GA) is recommended.
GA is a state of controlled unconsciousness and freedom from pain.
While this procedure carries some risk, the technique renders your child deeply sedated and unaware of any treatment being performed.
Source : www.myhealth.gov.my/en/oral-healthcare-in-special-needs-children/
Who gives the anaesthetic?
GA is given by anaesthetists. Anaesthetists are doctors with special training and are expert at looking after patients when they are anaesthetised.
It is usually started off with an injection of drugs in the hand or arm. It can also be supplemented by a face mask as well.
The anaesthetist stays with your child all the time during the operation and does careful monitoring .
Once your child is asleep, all the dental treatment is carried out such that when your child awakes, he/she has no memory of the procedure performed.
Why is it important for my child to fast before the GA?
Presence of food or liquid in your child’s stomach during the GA could cause it to come up into the back of the throat and subsequently go into the lungs.
Choking or serious damage to the lungs might happen from this incident.
FAST FACTS ABOUT GA
-
Your dentist will only recommend GA to perform dental treatment only if it is needed.
-
Your child will sleep through the procedure.
-
Your child will have no memory of it.
-
You should stay at the hospital most of the day until GA has completely worn off and should be advised by an anaesthetist that it is safe for your child to go home
References
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Clinical Practice Guidelines. Guideline on Use of Nitrous Oxide for Pediatric Dental Patients. 2013 Reference Manual V 37 / No 6. 15/16 (pg. 206-210)
- Preparing for Your Child’s Sedation Visit. American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Resource Section; V 37:No 6 (15/16): pg. 399-400.
- www.dentalfearcentral.org/help/sedation-dentistry/laughing-gas/
- www.smileandshinergv.com/inhalation-sedation
- www.myhealth.gov.my/en/oral-healthcare-in-special-needs-children/
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 January 2017 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Jama’iah bt. Hj. Mohd Sharif |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Bahruddin bin Saripudin |







