What Is Child (Pediatric) X-ray Examination?
- It’s an x-ray examination done on children. This examination is an easy and fast examination that does not require any special preparation.
- Although most of the illnesses seen are similar to adult patient, various factors and condition of patient such as body size, organs and etc. need to be taken into account when providing care and imaging technique to child patients. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paediatric_radiology)
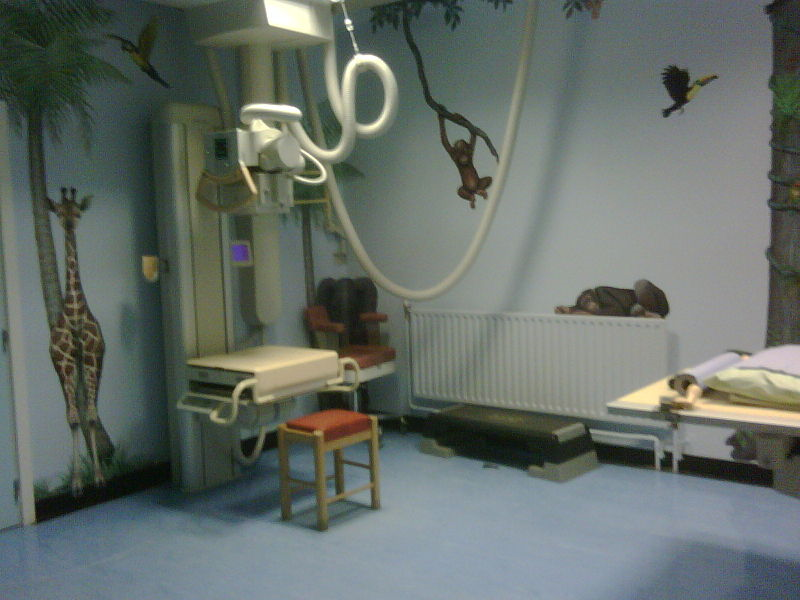
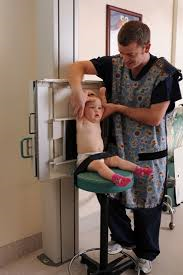
- To achieve this, steps that can be taken is by preparing comfortable X-ray room environment for children. It’s an important element to be considered. For example, bright wall, visual stimulations and toys are also provided to create an X-ray room environment suitable for children.
Picture 1: Example of X-ray room suitable for child patients (Pediatric)
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paediatric_radiology
How And Where Can I Get This Examination?
- When you visit your doctor, he/she will decide if you require the examination.
- If required, the doctor will make a request for the examination using the Radiology Examination Request Form.
- This examination is available in MoH hospitals.
When Is Child (Pediatric) X-ray Examination Is Required?
X-ray examination on children (pediatric) is required in several situations, depending on the indication. Such as (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paediatric_radiology):
- Wilms’ tumour
- Leukaemia
- Teratoma
- Congenital abnormalities
- Osteosarcoma
- Meningitis
- Infant respiratory distress syndrome
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Greenstick fractures
Child (Pediatric) X-ray examinations are also done by radiographers. It’s important to ensure images produced are of quality and high diagnostic value.
Before the examination
- The radiographer will explain the examination. Accompanying person is allowed to listen to the radiographer’s explanation.
- Make sure you or the accompanying person are not pregnant or suspected to be pregnant. Please inform the radiographer if you are pregnant or suspected to be pregnant.
- Patient need to take out metal object such as watch and bangles on the hand to avoid image artifact.
- Radiographer will also explain whether the examination will be done in lying facing up, lying facing down or siting position.
- Patient may also be required to change into hospital attire if needed.
During the examination
- Patient is advised not to move during the examination
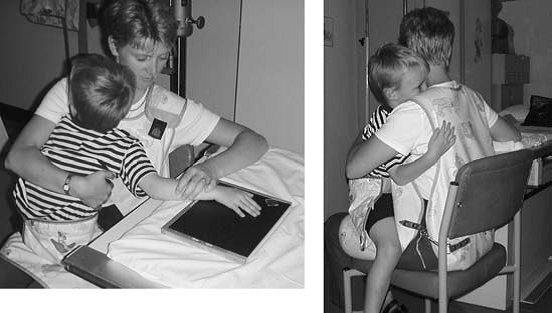
- For patients who are unable to follow instruction, accompanying person can assist in holding the patient during examination.
- Immobilizers may also be used if needed.
- Gonad shield, lead gown etc. will be used for radiation protection.
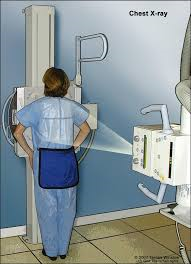
Picture 2 : Example of patient and accompanying person positioning during examination
Source : http://vstudentworld.yolasite.com/resources/final_yr/paeds/paediatric.pdf
After the examination
- No special after care is required.
- Patient will be allowed to leave after the examination.
- If you have any problem, please inform the radiographer on duty.
(a) (b)
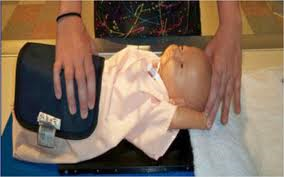
Picture 3: Positioning of patient for chest X-ray examination (patient lying down)
(a) (b)
Picture 4: Positioning of patient for chest X-ray examination (patient sitting)
(a) (b)
Picture 5: Positioning of patient for chest X-ray examination (patient standing)
Examination Report
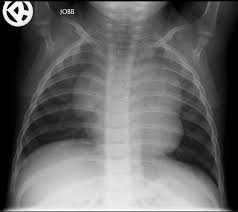
All images produced will be reviewed by radiologist and report will be prepared.
Picture 6 : Examination report for chest X-ray examination
References
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paediatric_radiology
- http://vstudentworld.yolasite.com/resources/final_yr/paeds/paediatric.pdf
| Last Review | : | 28 July 2017 |
| Writer | : | Mary Oommen |
| Accreditor | : | Daud bin Ismail |