Overview
Costochondritis (with unknown cause) is a common cause of chest pain in children and adolescents. It accounts for 10% to 30% of all chest pain in children and adolescents. The peak age for the condition is 12-14 years.
What is Costochondritis?
Costochondritis is a painful condition of the chest wall. It causes chest pain. Although painful, it is not a serious condition. Usually it has no obvious cause and dissappears over time. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory medication can be used for relief of symptoms.
Costochondritis happens due to the temporary inflammation of the junctions where the upper ribs join with the cartilage that holds them to the breastbone, or sternum.
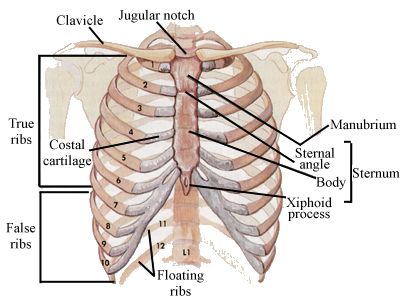 |
Skeletal Series Part 5: The Human Rib cage. These Bones of Mine. thesebonesofmine.wordpress.com
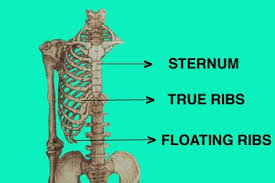 |
www.alientravelguide.com
Costochondritis Causes
The cause for costochondritis is usually unknown. However, some of them are :
-
Trauma to the chest wall such as blunt impact from a car accident, or fall.
-
Physical strain from activities such as heavy lifting and strenous exercise
-
Certain viruses or respiratory conditions, such as cold or flu,
-
Infection like tuberculosis, syphilis, that can cause joint inflammation
-
Certain types of arthritis
-
Severe & coughing
-
Tumors in the costosternal joint
-
Occasionally, costochondritis as a result of bacterial infections can occur in people who use IV drugs.
Costochondritis Symptoms and Signs
-
Pain – usually sharp and located on your front chest wall, at the junction of the ribs and the breast bone
-
Pain increases as you move your trunk or take deep breaths but it decreases as your movement stops, rest or with quiet breathing.
-
The most common sites of pain are your fourth, fifth, and sixth ribs.
-
Tenderness and maybe redness and swelling. The tenderness can be felt when you press on the rib joints (costochondral junctions)
-
Sometimes pain will radiate from the chest to the arms, shoulders, back or abdomen.
-
Pain is generally localized on one side of the body, although both sides are occasionally affected.
-
When costochondritis occurs as a result of infection after surgery, you will see redness, swelling, or pus discharge at the site of the surgery.
Young females are often affected by costochondritis, but it can occur in both men and women.
 |
www.wikihow.comHow to treat costochondritis: 5 steps (with Pictures) – wikiHow.
 |
www.wikihow.com
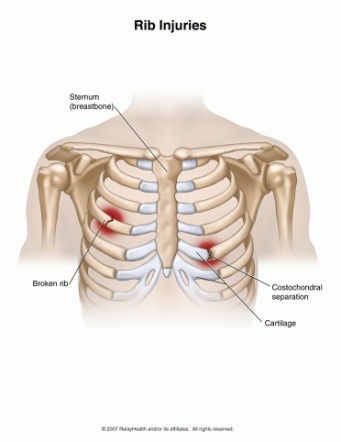 |
Costochondritis / Singapore Orthopaedic Surgeon. www.orthopaedicsurgeon.com
Medications for Costochondritis
Often the pain of costochondritis will dissappear without treatment.
When treatment is being given it is to control the pain and reduce inflammation. It usually consists of :
-
Rest and avoid activities that worsen the pain
-
Non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as mefenamic acid (PONSTAN), ibuprofen (BRUFEN), diclofenac (VOLTAREN) and pain relieving medications such as paracetamol (PANADOL)
-
Ice and/or heat packs applied to tender area.
When to Seek Medical Care
Go to a hospital’s emergency department or health center if you have difficulty breathing or any of the following symptoms occur. These symptoms are generally not associated with costochondritis:
-
Trouble breathing
-
High fever not responding to medication
-
Signs of infection such as redness, pus, and increased swelling at the rib joints
-
Continuing or worsening chest pain despite medication associated with nausea, sweating, left arm pain, or any generalized chest pain that is not well localized: These symptoms can be signs of a heart attack.
If you are not sure what is causing your condition, always go to the emergency department.
Quiz
-
What is costochondritis?
a. It is a temporary form of inflammation of the cartilage where ribs attach to the breastbone, the sternum.
b. It is a chronic inflammation of the body tissues
c. It is a inflammation of the small joints of the hands
d. It is a chronic inflammation of primarily the small and large intestines
Answer : a
-
What causes costochondrtis?
a. trauma to chest wall and physical strain
b. autoimmune disease
c. abnormality of the chest wall
d. short stature
Answer : a
-
You seek medical medical care when you have trouble breathing Yes / No
Answer :Yes
References :
-
Article Link:http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/costochondritis
-
Shiel JR.W.C (2012). Costochondritis &Tietze Syndrome. MedicineNet.com. New York. WebMD.LLC.www.medicinenet.com/costochondritis_and_syndrome/article htm#what_is_costochondritis
| Last Reviewed | : | 29 Mei 2014 |
| Writer | : | Datin Dr. Zil Falillah bte. Mohd Said |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Hargeet Kaur A/P Basant Singh |







