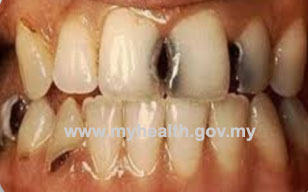
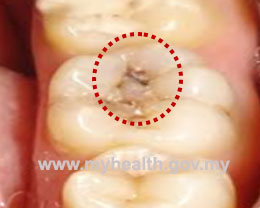
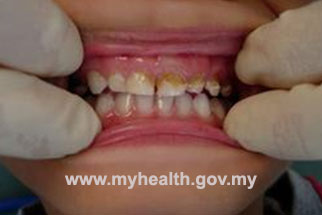
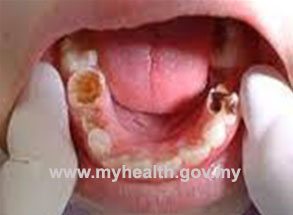
In our society, dental caries is best recognized by presence of decay or cavity on any tooth surfaces. Dental decay can affect anyone regardless of age; children and adult included.It can both afftect the primary or permanent dentition.
|
|
|
|
|
Fig 1: Dental caries : Anterior and posterior region of permanent teeth |
||
 |
 |
|
|
Fig 2 : Dental caries: Anterior and posterior region of primary teeth
|
||
How Do Caries Develope?
Under normal circumstances, bacteria is always found on tooth surfaces in the form of a soft and sticky mass called dental palque. This apparently normal symbiotic condition is subjected to change and become a potential risk when there is a change in your immune system or temperature within the oral cavity.
After every meal, the bacteria can react with the food debris left behind in the oral cavity , the metabolic product of which leaves an acidic pH in the mouth. The continuos presence of acid may cause demineralization of the surfaces of the tooth. This results in formation of decay or cavity.
Signs And Symptoms Of Caries
- Discolouration of teeth ( white spots or black spots)
- Obvious cavitation
- Food retention on tooth surfaces
- Pain and sensitive when you drink hot or cold drinks
Tooth Surfaces That Are At Risks To Dental Caries
- Interproximal surfaces of anterior and posterior teeth
- Malaligned teeth
- Biting surfaces of molars
Types Of Dental Caries
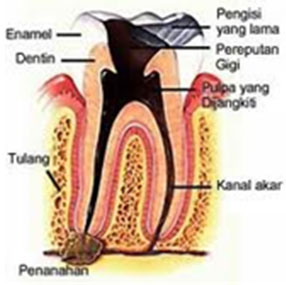
- Caries involving only enamel
- Caries involving enamel and dentine
- Caries with pulpal involvement
- Root caries
Treatment Options For Caries
-
Caries involving enamel (early caries)
Usually this form of caries is symptomless and not easily to detect with your naked eyes. Preventive approach using fluoride sealant and fluoride application can help prevent progression of decay into dentine layer.
-
Caries involving dentine
Usually pain and sensitivity is experience during eating or mouth rinsing .When dentine is involved, the decay is more extensive and easily noticable. It is therefore advisable to restore the decay with proper restorative (filling) treatment.
-
Caries with pulpal involvement
Pain resulting from decay involving the pulp is often more intense.Patient normally complains of sharp and throbbing pain which can be unbearable..When left unattended , it may result in the spread of the disease to the periapical region resulting in tooth abcess.
How To Prevent Caries?
- Healthy diet practices
- Reduce snacks between meals
- Reduce sugar consumption and avoid sweet sticky food
- Reduce consumption of carbonated or cordial drinks
- Good oral hygiene practices
- Brushing properly after every meal and before bedtime
- Use of fluoridated toothpaste to strength the tooth surfaces from acidic attack
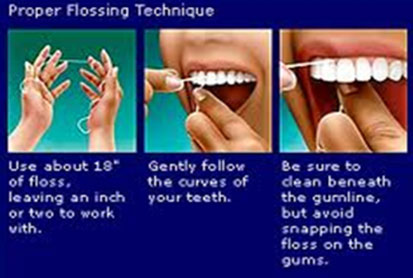
- Use dental floss to clean in between the teeth
- Regular dental check up at least once a year so that dental screening for early prevention can be done.
- Seek dental treatment as soon as it is needed.
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Hasni bt. Md. Zain |
| Translator | : | Dr. Lydia Mason a/k Lionel |
| Accreditor / Reviewer | : | Dr. Sharol Lail bin Sujak |