Diet modification is an alteration made on food and drinks which is widely used in the treatment of patients with dysphagia (swallowing disorder). The modification of food or drinks affects the transfer process of what was ingested through the pharynx (food tract) without changing the physiology of the swallowing system.
These modifications are usually effective for patients who are suffering from mild or moderate dysphagia. Changes made may eliminate risk of aspiration (food or drinks entering the airway) for some clients with dysphagia An instrumental assessment of swallowing can be carried out using different diet modification to look into the safe consistency for client’s food and liquid intake
Liquid Consistency Modification
Liquid modification are mostly effective for patients who suffered a stroke or neurological disease. Food thickener is used to change the consistency of a liquid. A thicker consistency will allow the liquid to flow at a slower rate through the pharynx and a lighter consistency will mimick the usual water that we drink daily.
Experts in dysphagia management (e.g. speech-language therapist, dietician, food technologist, nutritional company, etc) recommended a guideline on of the use of commercial food thickeners in thickening food and liquid for consumption (Dysphagia Diet Food Texture Descriptors, 2012; Irish Consistency Descriptors for Modified Fluids and Fluids Consensus Document 2009).
Food thickener may be added to water or other fluids in order to derive the following consistencies:
|
Consistency
|
Illustration |
Regular drinks with similar consistency |
|
Nectar-like |
|
Barley juice, yoghurt drinks |
|
Honey-like |
|
Thick fruit juice |
|
Pudding-like |
|
Baby cereal |
Food texture modification
Food modification is typically used to help clients with oral phase disorder or difficulties. By modifying the food, It helps to ease the food preparation process and deem suitable for client who have weakness of the oral structures such as tongue, cheeks and jaw or teeth.
Food modification is also used to help clients who have difficulties managing or swallowing food with double consistencies (i.e. food with both solids and fluid in them). It is usually caused by weakness of the swallowing muscles in the throat (pharyngeal area). The following are the food modification that are usually prescribed to clients:
|
Food modification |
Other foods with similar texture |
|
Soft Moist diet
|
Jelly, cake, steamed vegetables, fish flesh, soaked biscuits or bread |
|
Easy to chew diet |
Minced meat or vegetables |
|
Blenderized diet |
Mashed potatoes, ice cream, blenderized porridge, baby cereal, mushroom soup. |
Temperature & taste modification
A change in the food or drinks temperature affects the swallowing system greatly. An extreme temperature of hot or cold will increase a client’s oral sensitivity and swallowing reflex.
It helps clients who have absent swallowing reflex and also elderly clients. Example of temperature modification that can be made are:
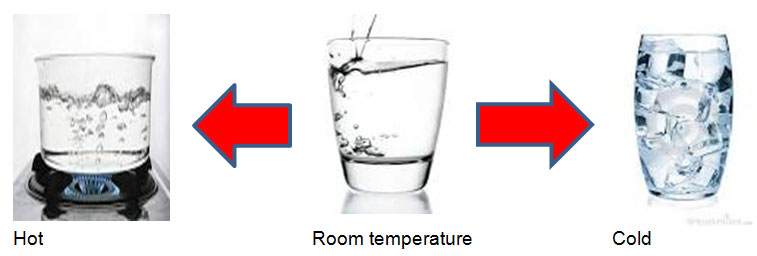
Changing the taste to an extreme such as sour will also increase the oral sensitivity. For elderly clients, sweetened drinks may improve their swallowing reflex as compared to drinking plain water.
Quantity modification
Controlling the quantity of food and drinks taken is important in client who have pharyngeal muscle weakness. A less effective swallowing mechanism causes food to collect in the pharynx after swallowing. An excessive amount of residue may increase the risk of aspiration.
A proper drinking technique might control the amount of fluid taken and the rate of which it flows through the pharynx. Drinking through a spoon can reduce the rate of fluid flow. At the same time, it reduces the amount of fluid which makes it easier for a patient to swallow.
Drinking through a straw helps clients who have difficulty drinking due to weakness in their arms, but beware! The use of a straw increases the rate of fluid flow in the pharynx.
|
|
|
|
||
|
Using a cup |
Using a straw |
Using a spoon |
Changing the amount of food on a spoon can help clients with difficulties to chew. This technique will also reduce the risk of aspiration for clients who may have food residue in the pharynx after swallow.
|
|
|
|
||
|
1/3 spoon of rice |
1/2 spoon of rice |
1 spoon of rice |
Even though diet modification may reduce or eliminate the risk of aspiration, it does not change the physiology of a client’s swallow. Therefore, a client requires rehabilitation techniques recommended by a certified Speech-Language Therapist to help in the process of recovery.
References
- Alberta Health Services (2013). Nutrition Guideline Dysphagia Applicable to: Nurses, Physicians and Other Health Professionals. Retrieved August 1, 2015 from http://www.albertahealthservices.ca/hp/if-hp-ed-cdm-ns-5-2-1-dysphagia.pdf
- Jawatankuasa kerja Pegawai Pemulihan Perubatan (Pertuturan), (2014). Prosedur Operasi Standard Penjagaan Pesakit Dengan Kecelaruan Penelanan. Bahagian Sains Kesihatan Bersekutu, KKM
- Jeri A. Logemann, (1997). Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorder. Pro ed.
- Lizzy Marks & Deidre Rainbow, (2001). Working With Dysphagia. Speechmark, Publishing Ltd UK
| Last Reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writer | : | Marina bt. Abdul Malek |
| Translator | : | Siti Suhana Mohd Khalid |
| Accreditor / Reviewer | : | Nadwah bt. Onwi |
















