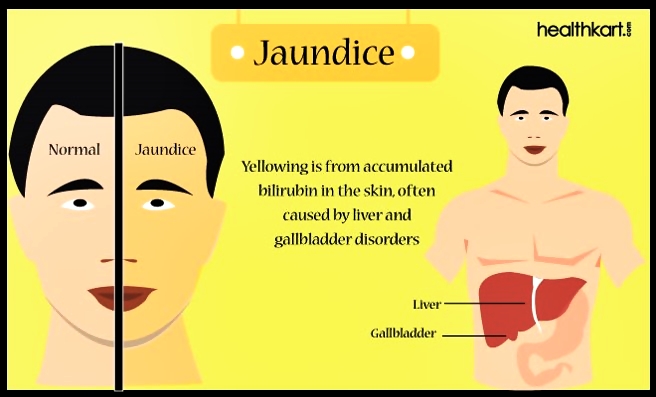
Figure 1 : The difference between normal and jaundice person
Definition
Jaundice is not a disease. It is a problem related to liver or gall bladder. Jaundice causes your skin and white eyes turned yellow.
High bilirubin in red blood cells causes jaundice. Bilirubin is a yellow chemical in the haemoglobin, the substance that carries oxygen in red blood cells. As red blood cells break down, your body will builds new cell to replace them. If the liver cannot produce new blood cells as they break down, bilirubin builds up in the body and your skin may look yellow.
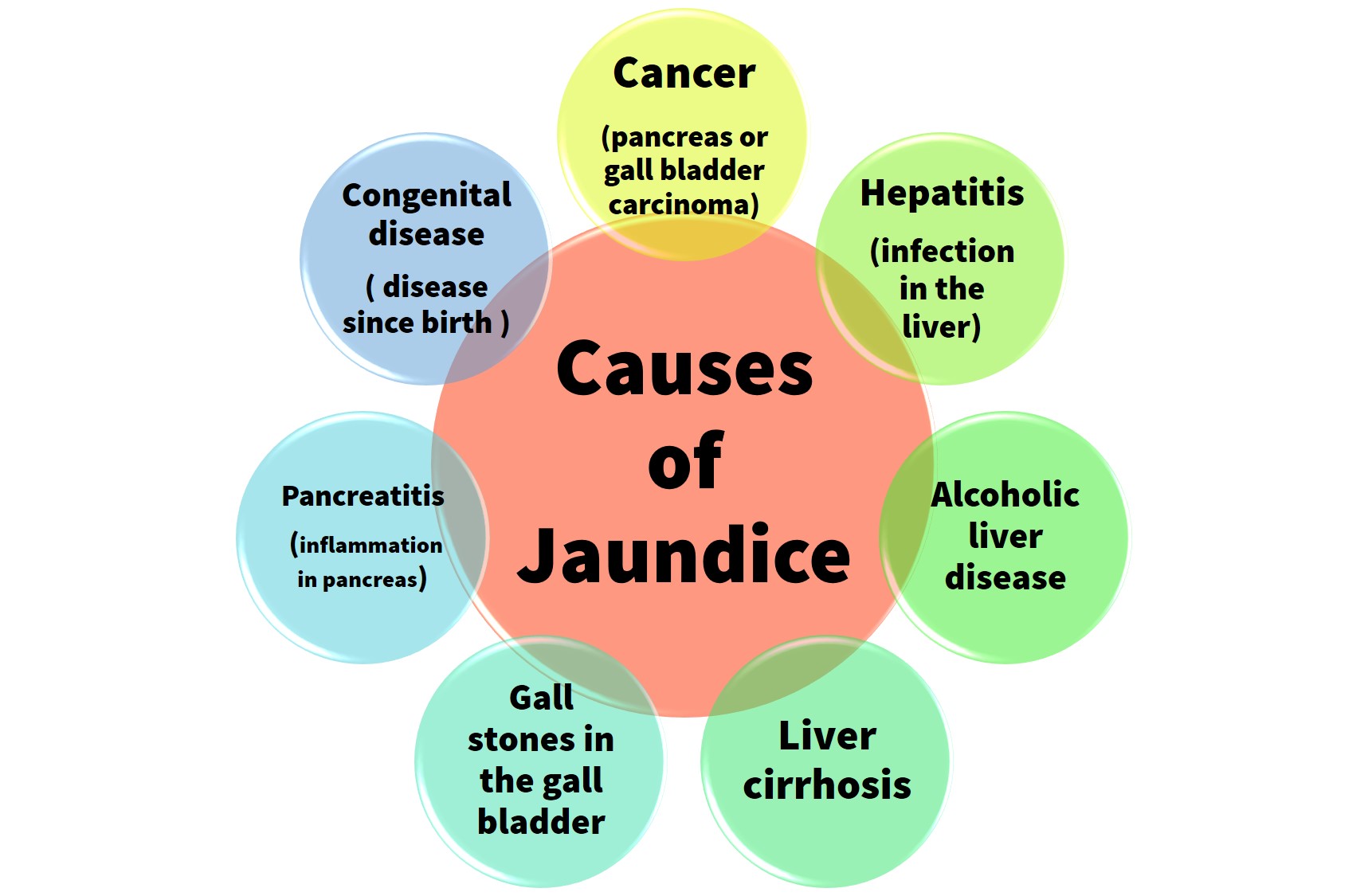
Causes of Jaundice
Infant jaundice is a common condition. Infant jaundice usually occurs because a baby’s liver is not mature enough to get rid of bilirubin in the bloodstream.
In some cases, an underlying disease may cause jaundice. Although complications are rare, a high bilirubin level associated with severe infant jaundice or inadequately treated jaundice may cause brain damage.
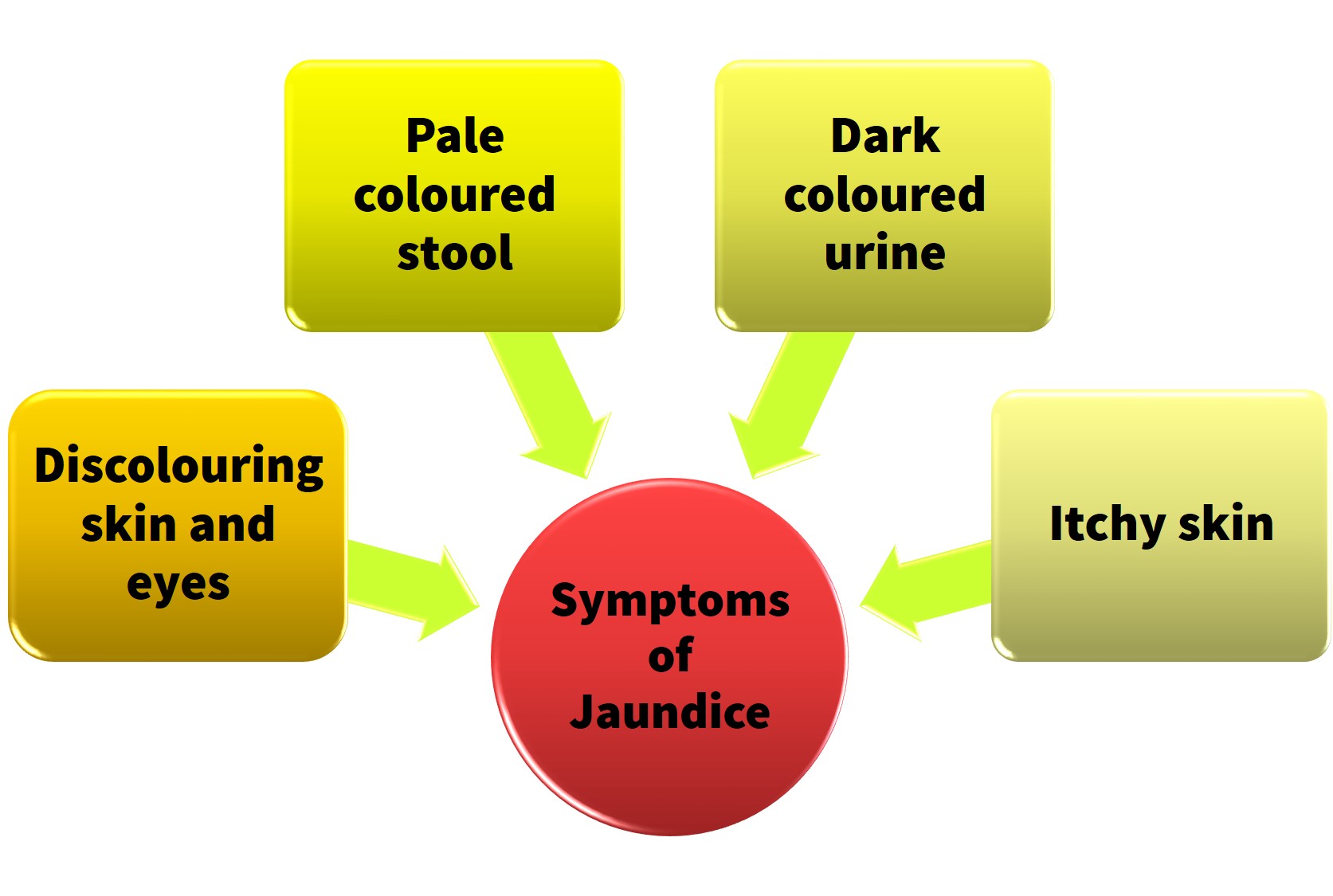
Symptoms of Jaundice
The symptoms of jaundice depend on the stage of the disease. The symptoms are:
If the jaundice becomes more severe, the symptoms are :
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
- Confusion
- Abdomen enlargement (Ascites).
Figure 2 : Jaundice.
Diet Management For Jaundice
The list of food that are allowed to be consumed and to be avoided for jaundice
| Food group | Serving recommendation | Allowed food | Food to avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate |
|
|
|
| Protein |
|
|
|
| Vegetable |
|
|
|
| Fruit |
|
|
|
| Dairy product |
|
|
|
| Fat and oil |
|
|
|
| Salt and sugar |
|
|
|
| Fluid |
|
|
|
How to do if patient does not have appetite?
Appetite is different for each individual. Supplements (oral nutrition supplement) is needed to replace energy and protein intake.
Types of oral nutrition supplement is recommended by the Dietitian depends on the problems faced by the people with jaundice. Please seek and get advice from Physician or Dietitian to help you to solve this kind of problem.
Conclusion
Diet management for people with jaundice depends on the severity of the jaundice. You must get advices from the doctor and Dietitian to solve the problem.
References
- Diet Restrictions in Jaundice. Melalui internet: http://www.livestrong.com/article/454027-diet-restrictions-with-jaundice/
- Food and Jaundice. Melalui internet: http://www.thechefonline.com/food_health/jaundice_food_basic_step.php
- Jaundice Diet Treatment. Melalui internet: http://www.diethealthclub.com/health-issues-and-diet/jaundice/diet.html
- Medical Nutrition Therapy Guidelines for Hyperlipidemia. Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia dengan kerjasama Malaysian Dietitians’ Association dan Persatuan Diabetes Malaysia.
- Rajah 1 : Perbezaan individu normal dengan jaundis. Melalui internet : http://www.healthkart.com/resources/deal-jaundice-symptoms/
| Last reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Translator | : | Faulina binti Khamisan |
| Accreditor | : | Harizah binti Mohd Yaacob |
| Reviewer | : | Nik Mahani binti Nik Mahmood |