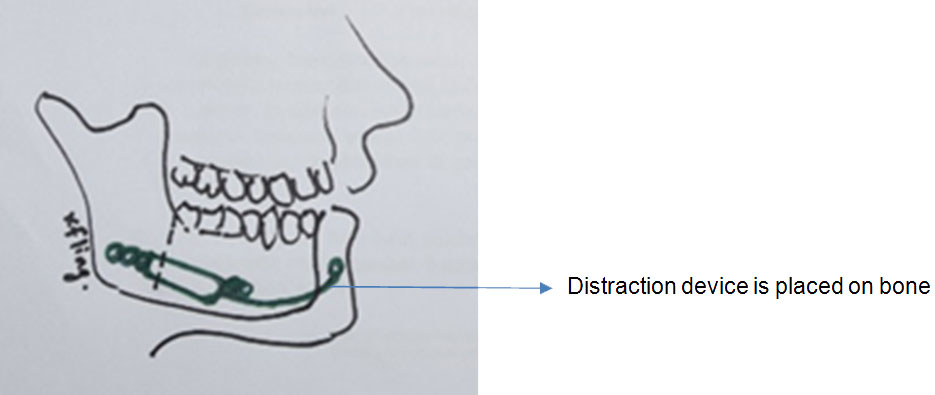
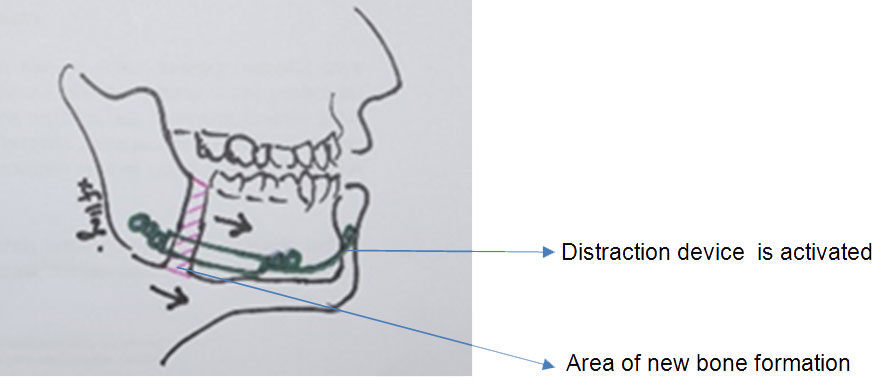
Introduction
Distraction osteogenesis is a surgical technique that gradually lengthens the jaw bone. It lengthens the jaw bone up to 30 mm without the need for bone grafting thus minimizing the donor site morbidity1. The first 4 cases of human mandibular distraction were performed by McCarthy in 1992 using a Hoffman Mini Lengthener which lengthened the mandible up to 24 mm.
There are 2 types of distraction devices namely, intraoral distraction devices (placed inside the mouth) and extraoral distraction devices (visible on the face).
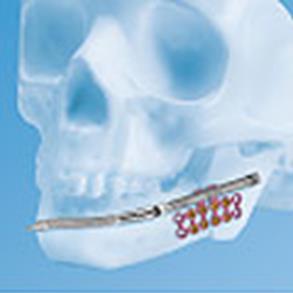
Example Of Intraoral Distraction Devices
|
Craniomaxillofacial Distraction System (DePuy Synthes)
|
Wood Zurich Intraoral distractor (KLS Martin)
|
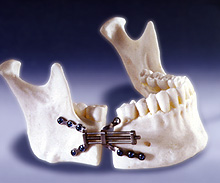
Mandibular distractor (Walter Lorenz)
|
Example Of Extraoral Distraction Devices
|
Craniomaxillofacial Distraction System (DePuy Synthes)
|
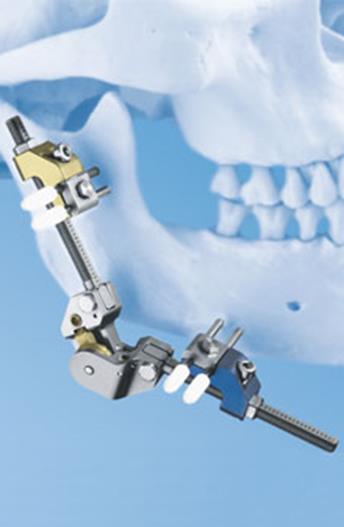
Multi-Guide II external distraction device
(Stryker Leibinger, Portage Michigan) |
Indications
Severe mandibular hypoplasia
Severe maxillary hypoplasia
Severe mandibular asymmetry
Cleft Lip and Palate
Post traumatic deficient maxillary and mandibular growth
Temporomandibular joint ankylosis
Mandibular defects after tumour surgery
Revision orthognathic surgery
Craniofacial syndromes : Hemifacial microsomia, Treacher Collins syndrome, Pierre Robin Sequence, Nager Syndrome
What Surgery Involves?
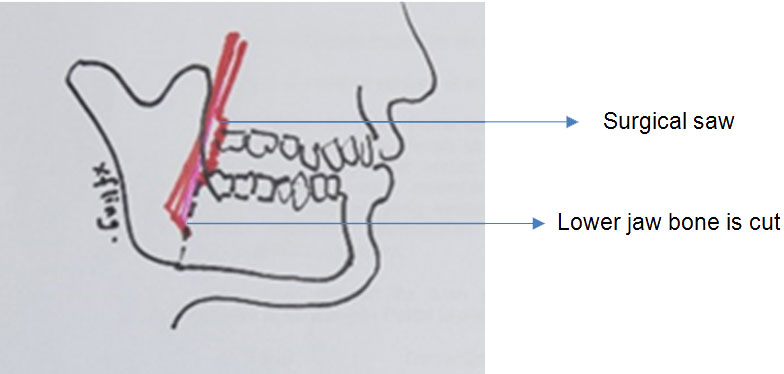
During the surgery, the surgeon will cut the jaw bone and place the distraction device. The device is activated 3 to 5 days after the surgery. (1) The recommended distraction rate is 1 mm per day, meaning that the device will separate the bone segments by 1 mm daily. The function of the device is to stretch the healing bone, hold it in place while it heals and the process goes on until adequate bone length is achieved. When adequate bone length is achieved, the activation is stopped and the device is left for proper bone healing which takes 2 to 5 months. (1)The patient will undergo another surgery to remove the device when radiograph shows adequate ossification of the new bone, usually after 5-6 months.
Post Operative Care
Post operatively, soft diet is recommended for 6 – 8 weeks. (1) Patient will be taught the technique to activate the device on post operative day 5. Patient will be discharged home after 1 week if the surgery is uneventful. Oral antibiotics and oral pain killer will be prescribed. Patient compliance and good oral hygiene are the two important factors that determine the success of the surgery.
Possible Problems
Distraction device complications
Distraction device complications include loosening of the device, device malfunction, breakage of the device and the need of the second surgery to remove the device.
Infection
Poor oral hygiene can lead to persistant wound infection especially around the activation rod.
Others
- Wound dehiscence
- Bleeding
- Hematoma
- High cost
Conclusion
Distraction osteogenesis is a new surgical technique in jaw surgery. Distraction osteogenesis seems to be a technique with less risk of relapse after large advancements (10mm or more) but it all depends on the surgical skill and experience of the surgeon. Successful application of proper preoperative planning, good surgical technique and good patient compliance will ensure the success of distraction osteogenesis.
References
- Landon J, Patel M, Ord R, Brennan P (2011). Operative Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. (2nd edition) London : Hodder Arnold.659-674.
- Mc CarthyJG et al. Lengthening the human mandibule by gradual distraction.Plast Reconstr Surg 1992;89:1-8
| Last Reviewed | : | 14 May 2015 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Ling Xiao Feng |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Abdul Latif bin Abdul Hamid |