Introduction
Discharge from the ear canal and most commonly associated with infection. Normal discharge may be ear wax or water. Ear wax is light brown brown, dark brown, or orange brown in color.
Main causes of abnormal discharge is an infection with drainage of cloudy fluid or pus through a ruptured or hole in the eardrum.
Common causes of ear discharge :
- Swimmers ear – common in swimmers accompanied itching, scaling, a red and moist ear canal
- Infection
- otitis externa (external ear & ear lobe)
- otitis media (middle ear space)
- mastoiditis (mastoid air cells)
- Injury from blow to the head, foreign objects, very loud noises, or sudden pressure changes (such as in airplanes), resulting in a rupture or perforated eardrum.
- Eczema and other skin irritations in the ear canal can cause some bleeding.
- Cholesteatoma
- Tumours
Signs & symptoms
The character of discharge provides the clue of the underlying cause of the affected ear. Commonly patient complains of hearing loss and pain. Pain is a common complain associated with outer ear infection (earlobe or external ear canal). Itchiness can be another associated symptom (infection cause by fungus/otomycosis)
Signs
|
NATURE OF DISCHARGE
|
ASSOCIATED EAR CONDITION
|
|---|---|
| Watery | Eczema |
| Pus | Acute Otitis Externa |
| Mucopus / Blood |
|
| Foul smelling |
|
In acute otits externa; the ear canal is occluded due to gross swelling. Manipulation of the earlobe is painfull and chewing commonly produces discomfort. Pain is throbbing and persistant in nature.
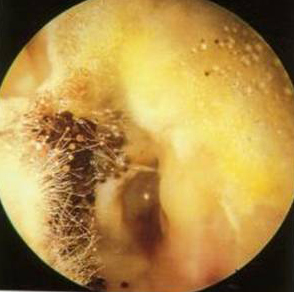
Picture showing acute otitis externa with fungal infection
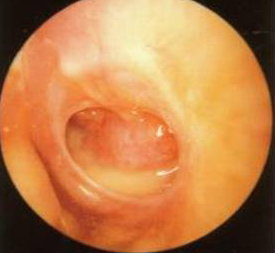
Picture showing Chronic otitis media
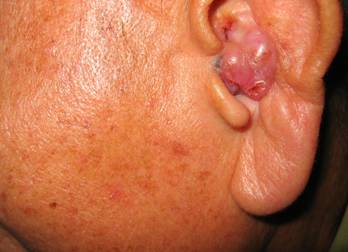
Picture showing tumour of the ear canal
Complications
Complications are occasionally seen in chronic discharging ear or in association with cholesteatoma. E.g. :
- Brain abscess (pus collection in the cranial vault /brain) causing headaches, drowsiness, confusion, impaired consciousness or paralysis.
- Labyrinthitis (infection of the balancing & hearing apparatus) causing nausea, vomiting, dizziness and hearing loss.
- Facial paralysis causing facial asymmetry.
- Mastoid abscess (pus collection mastoid air cells) – pain and swelling behind the ear.
Treatment
The initial treatment of a discharging ear is cleansing.
- In eczematous condition; 1% hydrocortisone cream local application is required.
- Furunculosis (localized pus collection) in the ear canal may require an anaesthetic examination and drainage.
- In acute infection antibiotics and analgesics are required.
- In chronic suppurative otitis media a combination of topical antibiotics and steroid eardrops will dry up most of the discharging ears.
Surgery is recommended for :
- recurring discharging ear
- patients who are regular swimmers
- to produce an hearing improvement
Chronic suppurative otitis media with cholesteatoma, because of the dangerous nature of this disease, surgery is invariably recommended.
Excision of the disease with preservation of hearing involves surgery on the mastoid and middle ear (mastoidectomy).
Tumours in some patients may be untreatable because of systemic metastasis ( spread ) or poor general health. The most favoured form is surgery and post operative radiotherapy.
Prevention
Prevention of recurrence is not always possible , the patient should be advised to keep the ears dry :
- Avoid water entering the ear :
- Washing & showering : advice to use cotton wool coated in vaseline and place it in the ear
- Swimming – to use silicone ear plugs
- Avoidance of scratching & poking the ears
| Last reviewed | : | 26 April 2012 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Dipak a/l Banarsi Dass |
| Reviewer | : | Dato’ Dr. Narizan Ariffin |







