“Please doctor, I wonder, why are my teeth elongated?” This is among the frequently asked questions by patients referred to Periodontics Specialist Unit.
(Figure 1a demonstrates an example of elongated teeth)
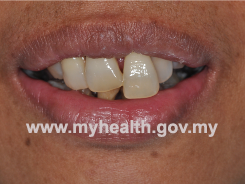
Figure 1a : Elongated Teeth
Anatomically, our teeth can be devided into crown, neck and root. As for the tooth supporting tissues, they (periodontal tissue) consist of gingiva (gum) which is located at the level of neck of the tooth, jaw bone (alveolar bone), cementum which covers the root surface, and ligaments that support the tooth. All these tissues strongly hold and stabilise the tooth in its position.

Source : http://www.britannica.com
Periodontal disease (periodontitis) is an inflammatory disease of the tooth supporting tissues following
Bacterial infection. Bacteria is abundantly found in dental plaque. Periodontitis is usually associated with poor oral hygiene due to ineffective plaque control (Figure 1b).
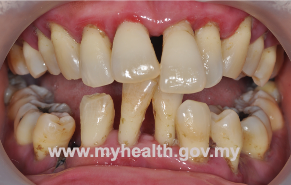
1b : Periodontitis (inflammation of tooth supporting tissues)
Once inflammation has occurred, gum and bone will be affected in terms of quality as well as quantity. If periodontitis is not treated early, there will be continous reduction in the level of the supporting tissue, thus exposing the root surface of the tooth. Root exposure causes sensitivity and the tooth appears elongated. Severe reduction of tooth supporting tissue can cause lost of support to the tooth, causing it to become loose, tilted and change in position. Eventually, the tooth with compromised support cannot function optimally. It can also generate pain and discomfort as well affecting appearance. When the damege is too severe, the tooth may need to be extracted.
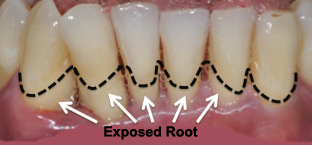
Figure 2: Exposed roots associated with damage tooth supporting tissues can cause sensitivity
Therefore, dental examination needs to be performed on a regular basis. This is important to detect and identify whether you are having dental problems including periodontal disease. Most of the patients with periodontitis do not notice they are having this problem because the disease is not painful at early stage. An early sign such as bleeding gums, is always thought to be normal. Usually, they will notice the problem at an advanced stage whereby the gum has already receded (tooth appears elongated), swollen and suppurated.
“Prevention is better than cure”. The easiest way to control dental plaque effectively is by brushing with a proper technique, flossing correctly and going for regular dental check-ups
Patients with periodontitis need to have specialised periodontal treatment to prevent further lost of the tooth supporting tissues. Elongated tooth and tooth loss can be prevented if treated early.
| Last Reviewed | : | 9 January 2017 |
| Writer / Translator | : | Dr. Sharifah Maznah bt. Wan Mohamad |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Rosrahimi bt. Abdul Rahim |







