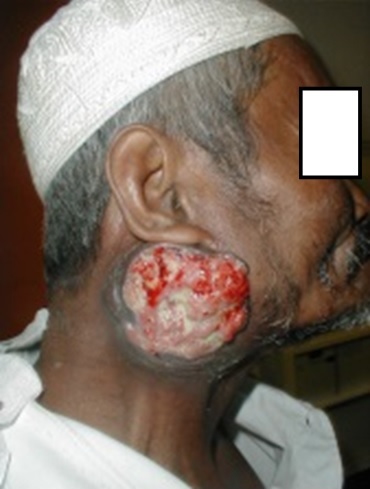
 |
DON’T WAIT UNTIL THIS STAGE ! Early detection results in the best outcome. Most cancer can be treated if treated at an early stage. |
INTRODUCTION
Cancer is an abnormal tissue growth in the human body. Depending on the type of cancer, some progressively enlarges and some are slow growing. Most of the cancers have signs such as nonhealing ulcer, swelling at certain area of the body, prolonged bleeding, hearing changes or voice changes. If you experience any of the above, please visit the nearest hospital, where tissue will be taken for examination to identify what type of cancer and have it treated accordingly.
Cancer that occurs in the head and neck cancer involves the lips, mouth, palate, nose, pharynx, larynx and ears. It may also involve the parotid and submandibular glands. These cancers are dangerous because it may cause airway or digestive tract obstruction. It can also spread locally or may cause distant spread to other organs such as the liver, lungs, or bone. The options of treatment for these cancers are surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy or combination of these.
MOUTH CANCER
 |
 |
|
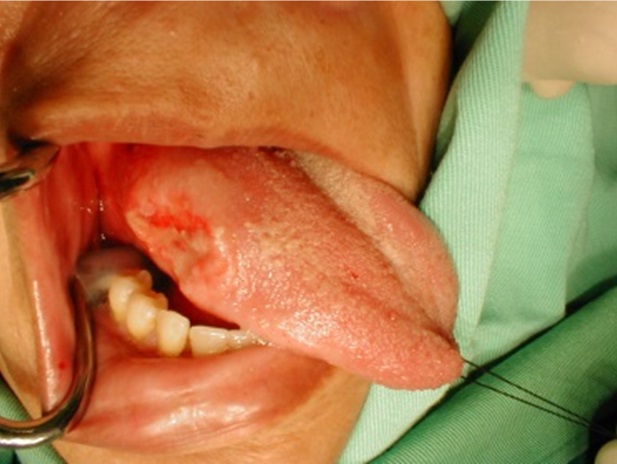
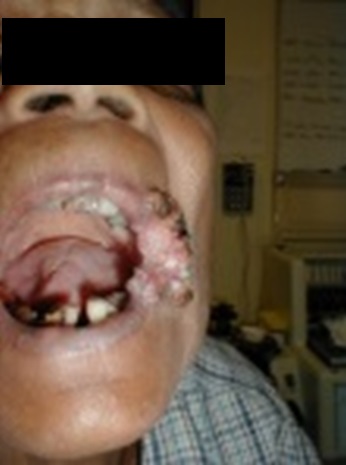
| Fig. 1: Cancer of the tongue | Fig. 2: Cancer of the upper lip |
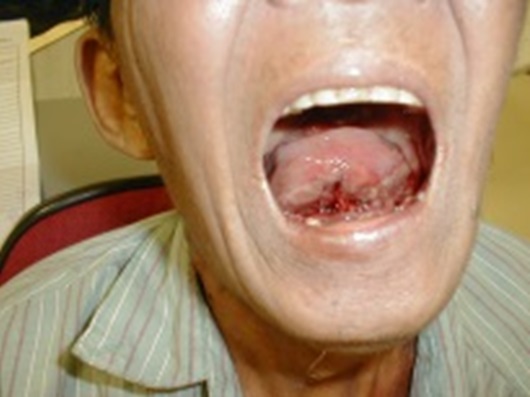 |
| Fig. 3: Cancer at the floor of the mouth |
Patient who suffers from this type of cancer, usually complaints of severe pain in the mouth, nonhealing ulcer, loss of appetite and weight loss. Sometimes there will be lymphatic mass at the neck, difficulty in swallowing and foul smelly breath.
NASAL CANCER
 |
 |
|
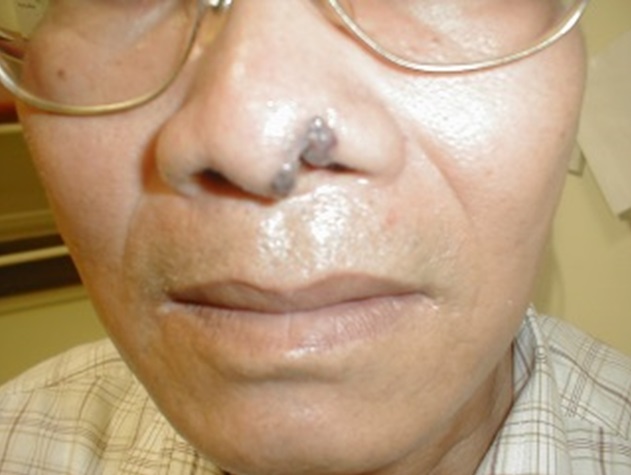
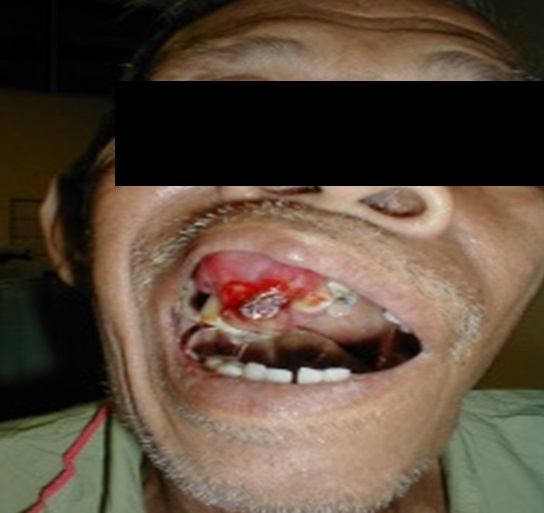
| Fig. 4: External nasal cancer | Fig. 5: Cancer of the sinus extending into the hard palate |
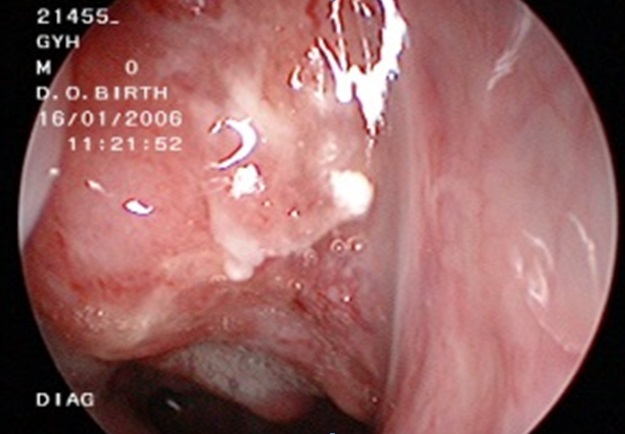 |
| Fig. 6: Endoscopic view (examination of the nasal cavity with endoscope). Cancer in the nasal cavity |
The nose is divided into three parts i.e. outer nose, sinus, and base of nose/ nasopharynx. Cancer can occur in any of these ares. The presentations of cancer in these areas are different. Outer nasal cancer may present with a nonhealing wound or mole that is progressively increasing in size.
Cancer that arises from the sinuses is difficult to detect until the patient complaints of foul smelling nasal discharge, blood mixed with mucous nasal discharge and nose block. Sometimes, the patient may also complaints of cheek swelling, blurring of vision, loose teeth, and swelling of the palate.
Back of the nose cancer (Nasopharynx) predominantly affects the Chinese. The patient may presents with nose bleed or nose block, blurring of vision, pus discharge from the ear, reduced hearing, and lymph node enlargement of the neck.
CANCER OF THE EAR
 |
 |
|
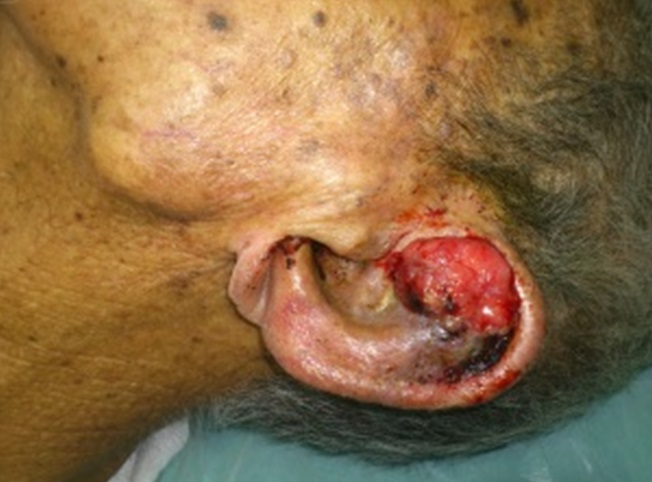
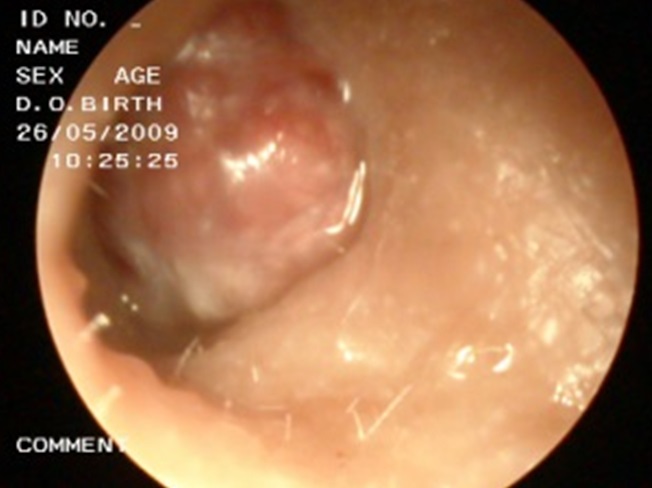
| Fig. 7: Cancer of the pinna | Fig. 8: Endoscopic view (examination of the ear canal using a microscope) showing a mass in the external ear canal |
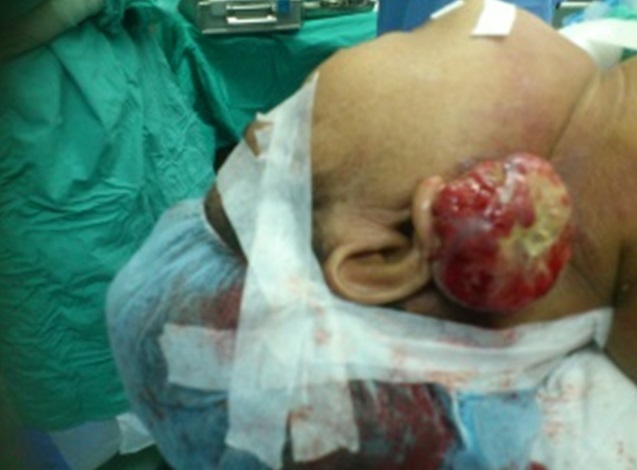 |
| Fig. 9: Cancer from the middle ear canal protruding to the skin surface |
Cancer of the ear is rare. The patient usually complaints of reduced hearing, swelling and bleeding from the ears, facial asymmetry, vertigo or vomiting and severe headache.
LARYNGEAL CANCER
 |
 |
|
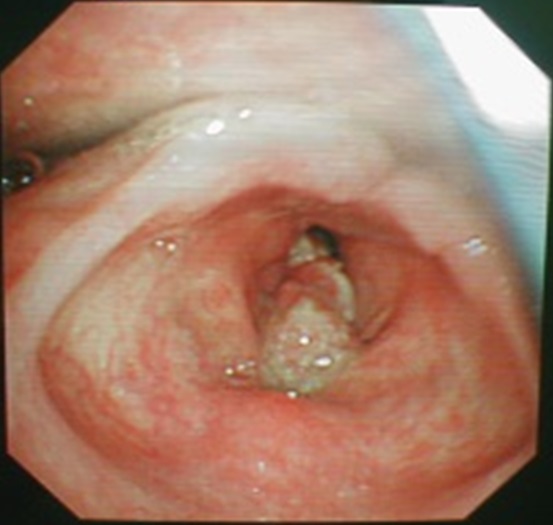
| Fig. 10: Endoscopic view (examination of the larynx using a endoscope) showing a erosive mass at the vocal fold (voice box) |
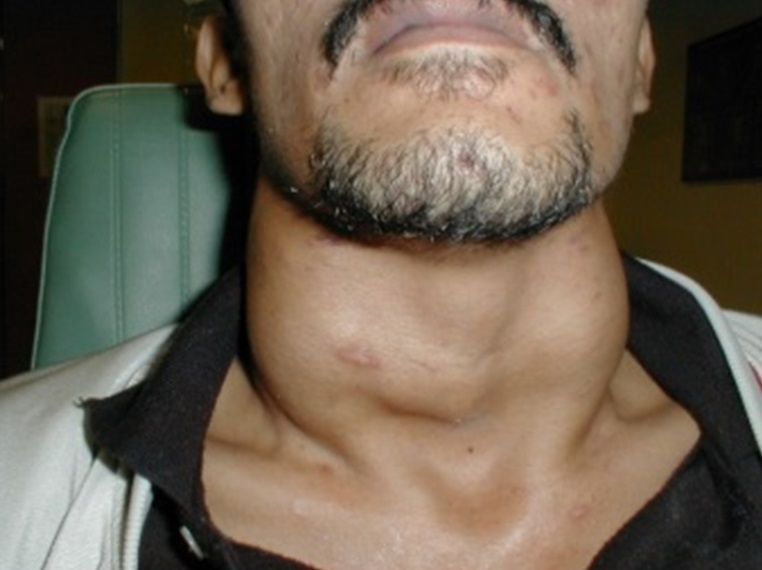
Fig. 11: Neck nodes enlargement |
Voice changes and persistence cough are the main complaints of patients with laryngeal cancer. The airway becomes progressively narrow and may cause noisy breathing. They will have difficulty in breathing and at later stages have neck node enlargement. This type of cancer is caused by ciggerrate smoking.
PHARYNGEAL CANCER
 |
 |
|
| (Fig. 12i) | (Fig. 12ii) |
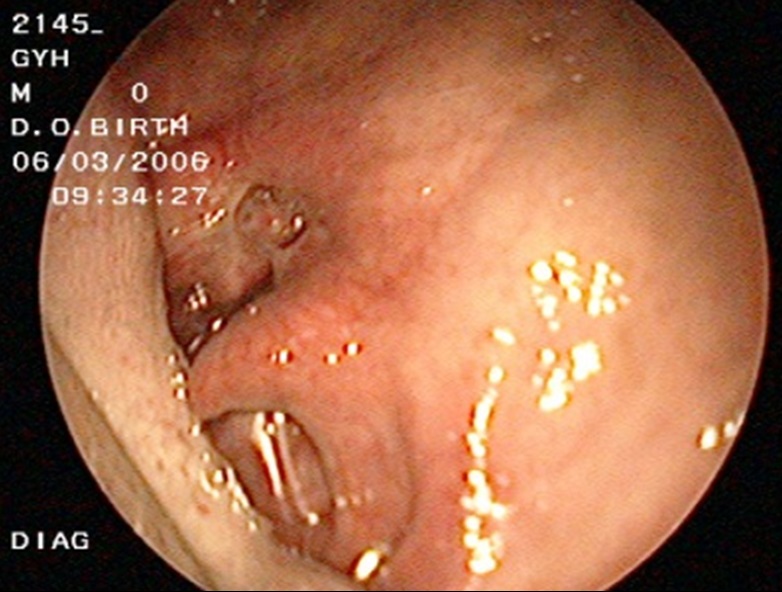
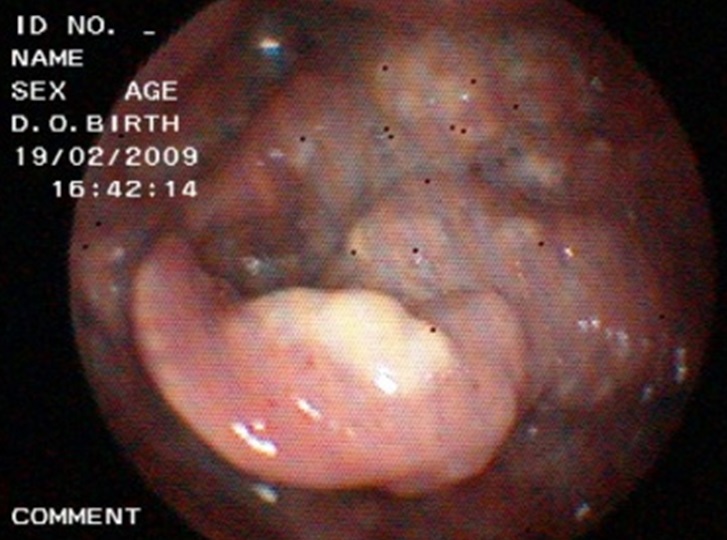
| Fig. 12: Endoscopic view (examination of the upper end of the oesophagus using a endoscope) showing an obstructive mass (Fig. 12 i) and an erosive mass (Fig. 12 ii) at the back of the vocal fold (voice box) which is the upper end of the esophagus |
Pharyngeal cancer/ throat cancer involves the upper digestive tract. Patient’s main complaint is foreign body sensation at the throat. This is followed by difficulty in swallowing, hematemesis (vomiting of blood), or neck masses.
SALIVARY GLAND CANCER
 |
  |
|
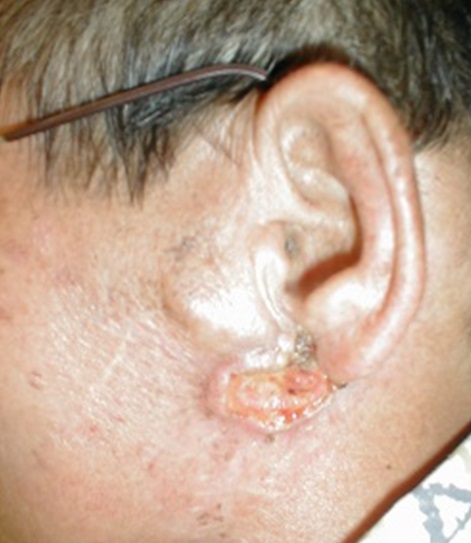
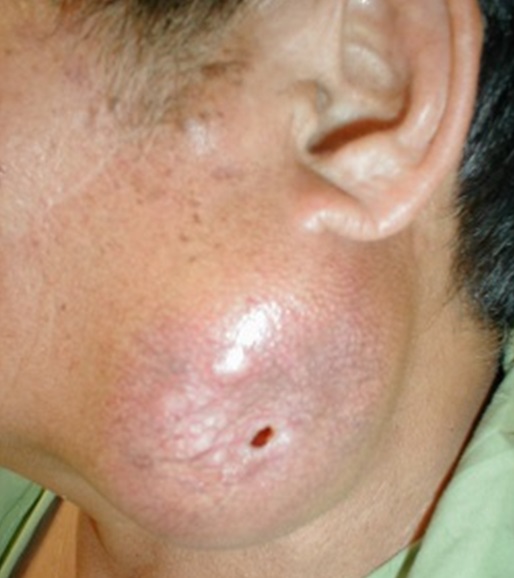
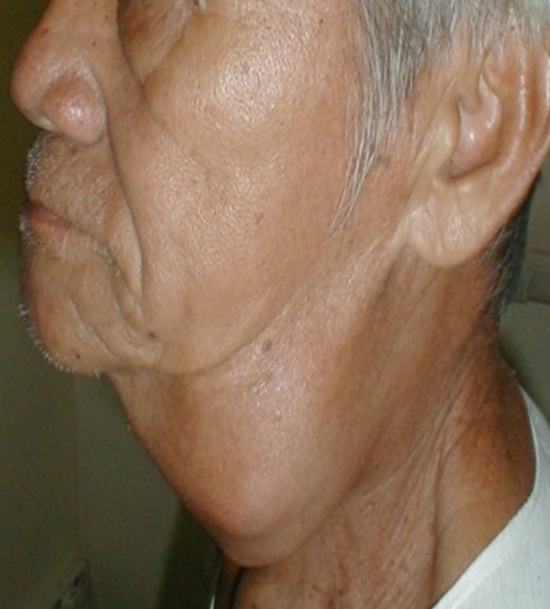
| Fig. 13: Errosive parotid cancer | Fig. 14: Cancerous neck masses |
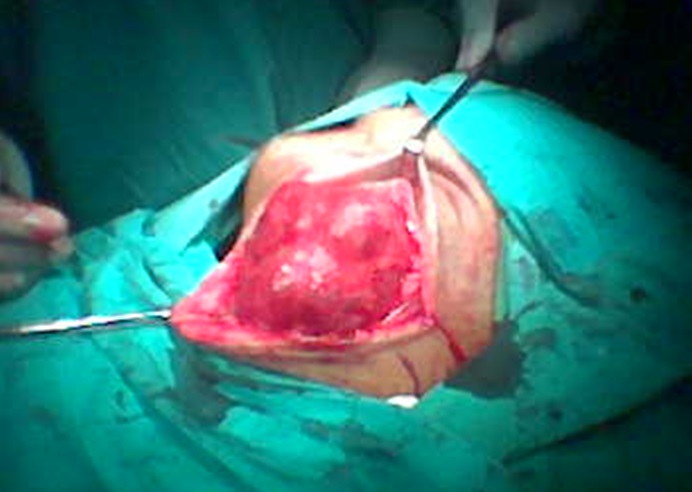 |
| Fig. 15: Surgical view of a parotid cancer |
The salivary glands consists of the parotid and submandibular glands as the major glands and many smaller salivary glands making up of the minor glands located on the palate, in the mouth and the pharynx. The major glands i.e. parotid and submandibular galnds are paired, located on the left and right of the checks and below the floor of the mouth respectively. Most of the time, the cancer grows slowly and not aggresive in its behaviour. Because of its slow growth, the patient may not be able to come early until it is at its advance stage.
CAUSES OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER
Most cancers have no definite cause. However, some may be related to hereditary factor e.g. nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Other contributory causes are smoking, alcohol intake, betel nut chewing, gambier, poor oral hygiene and viral infection.
SIGNS OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER
- Neck mass
- Nonhealing wound for more than 2 weeks
- Nose bleed that does not stop easily except if there is a definite history of trauma
- Difficulty in breathing due to airway narrowing
- Difficulty or pain during swallowing
- Blurring or double vision
- Rotten tooth or loose tooth
- Nose block
- Ear discharge or ear bleed
- Voice changes
- Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
- Strabismus (squint) that is not congenital
- Prolonged headache
WHAT SHOULD I DO IF I HAVE THE ABOVE SIGNS
You are advice to visit a doctor in your area to refer you to an otorhinolaryngologist or a dentist for further assessment. This type of cancer has a good outcome if treated early. A biopsy of the tissue will be taken for labarotary examination to confirm if the tissue is cancerous. Imaging will also be done to know the stage of the disease, whether it is local or has it spread to other organs. After reviewing all the results, the doctor will explain the findings and the treatment options based on the progression of the cancer.
The treatment options for a particular cancer depend on its type and the current status. Four modalities of treatments are available:
- Surgery
It is usually a complicated and long procedure where a major surgery will be done to remove the cancerous tissues as well as neck lymph nodes to avoid the cancer from spreading to other organs. Reconstructive surgery might also be needed to close the defect after the cancerous tissues are removed. - Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is done at the Radiotherapy center. Usually the treatment is given as out-patient and on daily basis except for wekkends and public holidays. The patients will receive 20 – 40 fraction of radiotherapy over 2 – 3 months depending on the oncologist’s prescription. Radiotherapy will be given for 5 minutes during each session. Most patients will complaint of lip dryness, thirsty, and skin colour changes at the radiated site. - Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is given intravenously. The infusion is given over a few days. Before commencing, blood tests are taken to make sure that there is no contraindication to the treatment. Chemotherapy is given to those who are fit to withstand the treatment. The patient maybe admitted for chemotherapy or it can be done as a daycare procedure. There is usually a 3 – 4 weeks interval between each chemotherapy for up to 6 cycles. Additional doses may be given depending on the type of chemotherapy drug prescribed. The patient may experience nausea, vomiting, hair loss, body weakness and fever. - Combination of the above
If you seek treatment early, there is higher possibility that your cancer can be cured. If you seek treatment late, combinations of the above treatment may be benefitial to you. You are advised to follow your doctor’s recommendations. There are side effects of the above treatment but most patients can tolerate the effects. If they can, why can’t you?
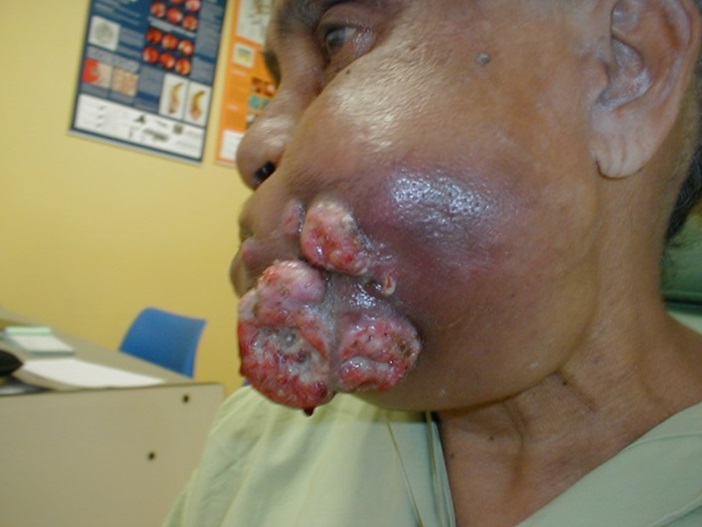 |
LOVE YOURSELF. HEAD AND NECK CANCER CAN BE TREATED. IF YOU DELAY THE TREATMENT, YOU’LL LOOSE THE OPPORTUNITY. REMEMBER, PREVENTION IS BETTER THAN CURE. |
| Last Reviewed | : | 13 August 2015 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Hj. Abd. Razak b. Hj. Ahmad |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Faridah bt. Hassan |







