What are non-verbal signs?
Communication skills are fundamental for the success of interpersonal relationships. In our daily life, we communicate via a combination of verbal and non-verbal ques. However, people who are cannot speak rely on their ability to convey their needs non-verbally.
Non-verbal communication consists of an array of physical feature that we unknowingly display during interaction with other people. These consists of our facial expressions, gestures, eye contact, posture, demeanour and tone of voice. In other words, non-verbal communication utilizes body language as a means to express one’s opinion, feelings or experiences.
In people who are non-verbal, pain is usually expressed via:-
- Changes in facial expression such as frowning and grimacing
- Emotional changes such as crying (Figure 1)
- Unusual behaviour such as sudden aggression, self-injurious behaviour
- Refusal to participate in their usual activities, such as refusal to eat or sleep
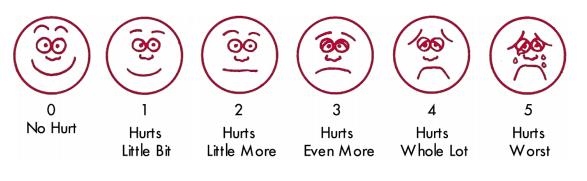
Figure 1 : Wong Baker Faces pain scale used for the assessment of pain
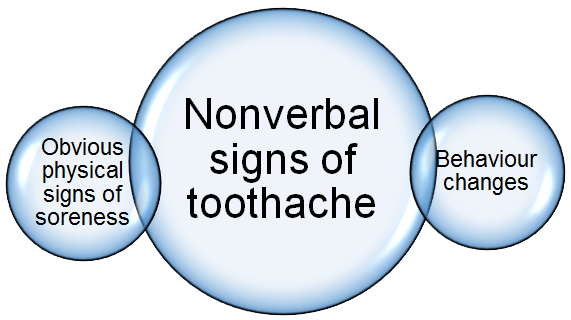
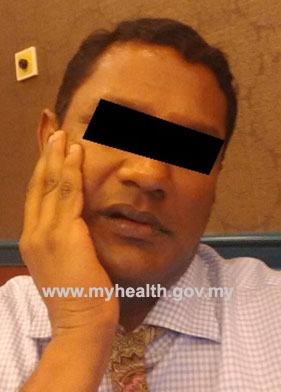
Figure 2 : Nonverbal signs of toothache
|
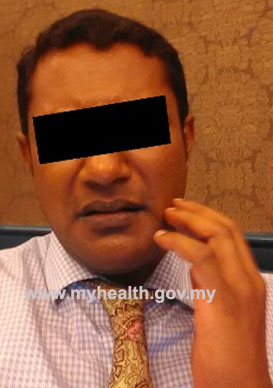
Figure 3: Sign of toothache |
Figure 4: Tapping or touching of painful part of jaw |
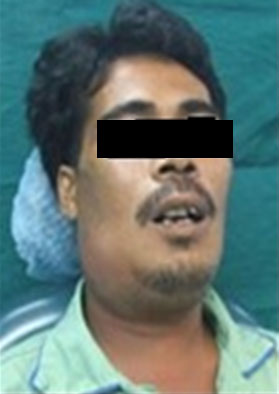
Figure 5: Facial swelling as a physical sign |
|
|
|
*Photo source : Facial Swelling
|
Toothache in people who are non-verbal
Pain is a highly unpleasant physical and emotional experience that is caused either by illness or injury. People who are verbal can readily vocalize this experience of pain and seek the necessary treatment. However, people who are non-verbal are unable to do so and may rely on their carer to identify and rectify their source of pain.
Toothache may be expressed non-verbally by:
- Suddenly refusing tooth brushing
- Refusing or avoiding certain types foods or drinks, such as hot or cold foods or drinks as well as sweet foods
- Touching, pinching or tapping their face or jaw
- Sudden excessive secretion of saliva (drooling)
- Crying, grimacing, and frowning
- Crying at night or while lying down
- Sudden behaviour change during meal times such as aggression, head banging, cheek biting
Tips for carers
Carer who care for people who are non-verbal may be the first to recognize their loved ones experience of pain, which maybe expressed as symptoms explained above (Figure 1). There may also be physical signs of pain that can be easily detected by carers (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5). These signs are:-
- Obvious swelling of the face and jaw with fever
- Bad breath
- Pus discharge from the mouth or the skin overlaying the jaw
- Presence of decayed teeth and tooth roots
- Presence of loose teeth
- Swollen gums
- Bleeding gums
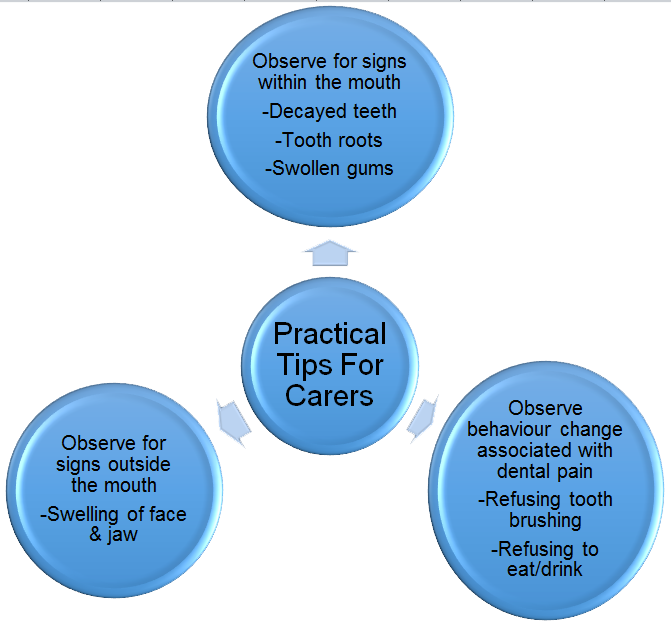
Figure 6 : Practical tips for carers
The presence of these signs and symptoms may indicate the presence of toothache and hence would enable them to seek the necessary professional help for their loved ones.
References
- Knapp, M., Hall, J., & Horgan, T. (2014). Nonverbal Communication in Human Interaction: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
- Raposa, K. A., & Perlman, S. P. (2012). Treating the Dental Patient with a Developmental Disorder: Wiley.
- Wong, D. L., & Baker, C. M. (1988). Pain in Children: Comparison of Assessment Scales. Pediatric Nursing, 14(1), 9-17
| Last Reviewed | : | 11 May 2015 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Dasera Raj a/l Vedha Raj |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Siti Zaleha bt. Hamzah |