Orthodontic Services in MOH?
Orthodontic is the speciality of dentistry concerned with the management and treatment of patients with improper positioning of teeth.
In the Ministry of Health (MOH), Orthodontic Units receive referral cases mainly from the Primary Oral Health Care services and also from other specialists. The target groups are school children below 18 years old and individuals who need multidisciplinary specialist care.
The Scope of Orthodontic Treatment
Orthodontic treatment is undertaken for3:
- The management of malocclusion
- To facilitate restorative treatment
- The management of severe skeletal discrepancies in combination with orthognathic surgery
- The management of severe craniofacial deformity
- The management of obstructive sleep apnoea
The Demand and Need for Orthodontic Treatment
The patient’s perceived need for orthodontic treatment does not necessarily always correspond with the professional’s opinion. A local study shows that 27.1% of schoolchildren aged 13 – 14 years need orthodontic treatment6.
In Malaysia, there is a very high demand for orthodontic treatment in government orthodontic clinics, which is heavily subsidized. This has resulted in long waiting lists for orthodontic treatment in all government clinics5. Due to the increasing burden on the public healthcare services, many countries attempt to develop indices to prioritise orthodontic treatment for those who would genuinely benefit greatly from specialist care.
What Is Index of Treatment Need (IOTN)
The Index of Treatment Need (IOTN) is a clinical index to assess orthodontic treatment need. The IOTN was developed within the UK. This index consists of two components which are the Dental Health Component (DHC) and the Aesthetic Component (AC).
The DHC is based on the Swedish Medical Health Board index. It has five categories, defining the need as 1,2:
|
Grade 1: No treatment need |
|
|
Grade 2: Little need for treatment |
|
|
Grade 3: Borderline need for treatment |
|
|
Grade 4: Need Treatment |
|
|
Grade 5: Need Treatment |
|
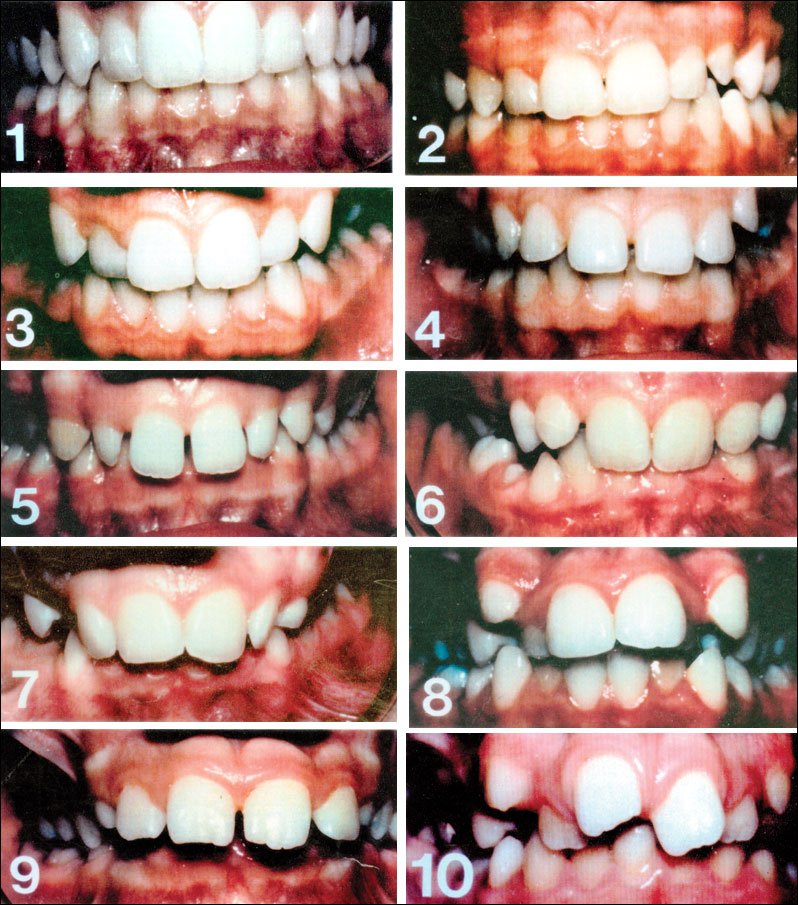
The Aesthetic Component (AC) is based on a series of ten photographs to assess the degree of dental attractiveness. The patients should be involved in the subjective assessment. The Hierarchical scale for the AC is:
- Grade 1 – 4: No or slight treatment need
- Grade 5 – 7: Moderate or borderline treatment need
- Grade 8 – 10: Treatment need
IOTN in MOH
To qualify for orthodontic treatment in government orthodontic clinic, a patient must show obvious need, as opposed to merely a desire for treatment. In MOH, the IOTN is used as a guideline to prioritize the orthodontic treatment to the patients who most need orthodontic treatment, so that limited resources can be targeted at those patients in greatest need, avoiding the provision of expensive treatment to mild cases. For those who does not need immediate attention, their names will be placed in a list. In Ministry of Health Malaysia, we apply these rules with scrupulous fairness and care.
References
- British Orthodontic Society (2015). What is the IOTN? Retrieved March 18, 2015 from www.bos.org.uk/Public-Patients/Orthodontics-For-Children-Teens/Fact-File-FAQ/What-Is-The-IOTN.
- Cobourne, M.T. & DiBiase A.T. (2010). Handbook of Orthodontics. Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier.
- Gill, D.S. (2008). Orthodontics at a Glance. West Sussex: Blackwell Munksgaard.
- Image of IOTN Aesthetic Component (2015). Retrieved March 18, 2015 from http://www.nature.com/bdj/journal/v193/n4/fig_tab/4801530a_F5.html
- Loke, S.T. (2006). Training Dental Officers and Nurses in the Index of Orthodontic Treatment Need (IOTN) as a Screening Tool in Public Health Facilities. Malaysian Journal of Public Health Medicine, 6(2), 49-55.
- Siti Zuriana, MZ, Ishak AR & Rashidah E (2014). Normative and Perceived Need for Treatment of Malocclusion among Malaysian Adolescents. Sains Malaysiana, 43(7), 1037-1043.
| Last Reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Then Poh Kiun |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Maria Jirom Gere |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Hjh. Rashidah bt. Dato’ Hj. Burhanudin |