Introduction
Pathological myopia is a type of farsightedness in which it causes elongation of the eyeball size resulting in high myopic refractive power. This condition can occur at any age but mostly between the age of 30 to 50 years old.
Studies showed that people under age 50, pathological myopia is often associated with the growth of immature blood vessels through the outer vascularized layer at the back of the eye (choroid layer) which in turn causes bleeding through the inner layer of the eyeball, the retina. Pathological myopia is also found to be associated with some systemic and other ocular diseases such as in Down syndrome, Marfan syndrome, ocular albinism, and retinopathy of prematurity.
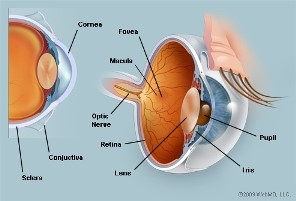 Anatomical Structures Of The Eyeball
Anatomical Structures Of The Eyeball
Clinical Features
i) Extensive axial length of the eyeball & high myopic refractive error
The average axial length of human eyeball is 24.0mm. Refractive power is measured in Dioptre (D). Typically, the axial length of pathological myopic patients exceed 26.0mm in size while the myopic refractive power range at -6.0D to -40.0D which results in wearing thick glasses. Therefore, some highly myopic patients prefer contact lenses as an alternative.
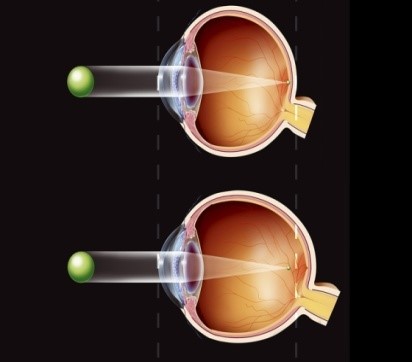 Difference Between Nnormal And Myopic Eyeball Difference Between Nnormal And Myopic Eyeball |
 Patient Wearing Thick Eyeglasses Patient Wearing Thick Eyeglasses |
ii) Staphyloma.
Staphyloma is a bump that forms at the back of the eyeball when the layers of the retina and sclera becomes thin due to the continued elongation of the eyeball.
iii) Macular degeneration.
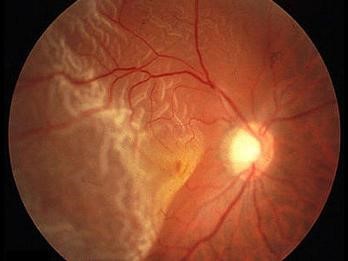
The retina itself consists of few thin layers. The continued elongation of the eyeball will cause cracks in the retinal layer, especially along the peripheral lining. These fissures allow new immature blood vessels from the choroid to grow underneath the retinal layers that could easily burst causing bleeding between the layers of the retina. Involvement of the macular area of the retina can lead to blindness.
 Abnormal Growth Of Blood Vessels At The Retinal Layer
Abnormal Growth Of Blood Vessels At The Retinal Layer
iv) Retinal detachment
Pathologically myopic patients has high risk of developing retinal detachment. This condition occurs when there is fluid leakage from the stretched and cracked retinal layers causing it to tear easily thus causing retinal detachment.
Signs and Symptoms
Patients with pathological myopia may experience some form of visual disturbances due to poor retinal function, such as:
i) Retinal image distortion – the image that you see looks crooked and uneven in shape.
ii) Change in color perception/color vision
Damage to the retinal layer which contains color-sensitive photo pigments will cause interruption to color perception. For example, when a patient with pathological myopia see a green color, the color brightness and intensity might be different from what normal people see.
iii) Scotoma
Scotoma is an obstacle in the field of view. It can be at any point of view, central or peripheral. Patients may also experience scotoma at both distance and near vision. Scotoma gives problem such as face recognition, watching television, driving and reading books. Pathological myopia can lead to blindness when area of scotoma affects central vision, leaving the visible peripheral area.
iv) Signs of retinal detachment
Patients should be concerned with some of the signs that may happen when the retina is detached such as seeing flash light, seeing many floaters hovering in the eyes, and also seeing like curtain obscuring the view. Therefore, patients should seek immediate retinal examination from the ophthalmologist when experiencing one of these signs.
Management
Treatment of pathological myopia is limited because of the elongation of the eyeball cannot be controlled. Treatment that can be provided by using laser radiation to destroy the abnormal growing of blood vessels to prevent progressive damage to the retina. However, laser radiation may also damage the healthy nearby retinal tissues.
In addition to laser treatment, now there is a safer alternative to preserve visual function which is photodynamic therapy by injecting drugs to the retina at regular intervals. Verteporfin (Visudyne) and Lucentis injection are among the most frequently used in photodynamic therapy.
For patients who have low vision, using visual aids can help patients to perform daily routine with ease. Low vision devices such as magnifying glass for near tasks and telescopes for distance vision. Other than optical alone, non-optical modifications can also be done for vision aid, for example; enlarging the font size on the computer screen and wear a hat or sunglasses to reduce glare when going for outdoor activities.
Eye And Vision Care
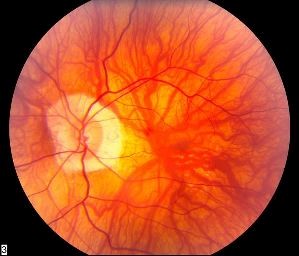
Routine funduscopic examination by a qualified eye specialist is required to monitor the pathological changes in the retina and thus can reduce the risk of blindness. Pathological myopia should be aware of the early signs and symptoms related to retinal detachment, and also the urgencies of seeking medical treatment to preserve visual function.
Involvement in sports activities such as ball sports, jumping and running should be avoided to prevent complications to the retina due to stress and shock. Patients also need consultation and confirmation from ophthalmologist before engaging in activities that could risk the retinal health.
 Retinal Examination/Funduscopy
Retinal Examination/Funduscopy
References
Contents / notes
- Jack J. Kanski; Clinical Ophthalmology – A Systematic Approach; 6th Edition; Butterworth Heinemann 2007.
- http://optometrist.com.au/dealing-degenerative-myopia/
- eyeassociates.com/pathological-myopia.
- fightingblindness.ie/pathologicalmyopia.
- lowvision.org/pathologicalmyopia.
Pictures
- http://seputar-inspirasi.blogspot.my/2012_06_01_archive.html
- https://c3.staticflickr.com/3/2126/2105552252_6e0c72f74a_n.jpg
- http://optometrist.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/degenerative-myopia.jpg
- http://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/122-a12/
- http://www.medicinenet.com/image-collection/retinal_detachment_picture/picture.htm
- http://www.optik-dormann.de/vergroessernde-sehhilfen/
- http://www.thebrunettediaries.com/tips-to-ease-eye-strain-caused-due-to-computers/
| Last Reviewed | : | 17 Disember 2015 |
| Writer | : | Pn. Nur Faiza Binti Jaafar |
| Translator | : | Pn. Nur Faiza Binti Jaafar |
| Accreditor | : | Pn. Nor’aini Binti Anuar |