Introduction
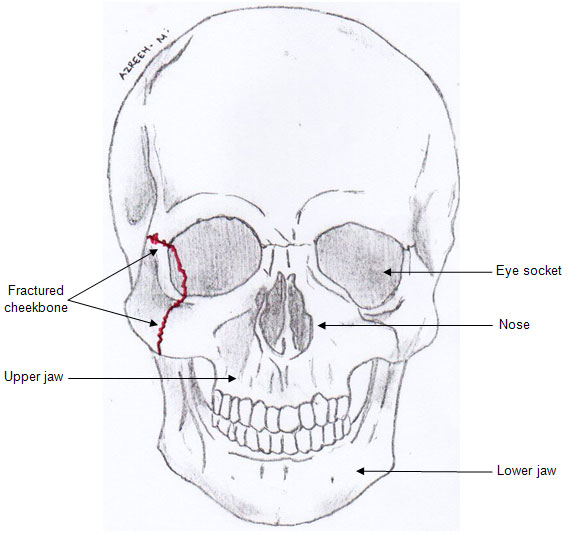
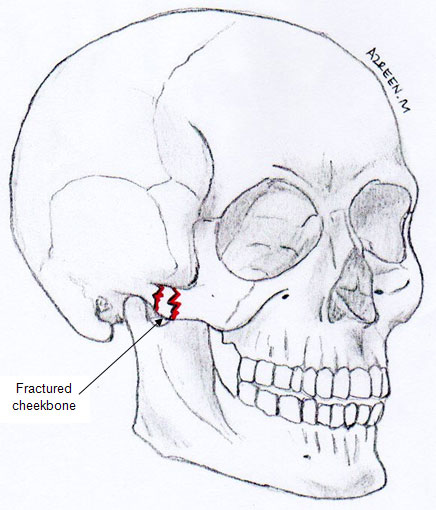
The cheekbone (zygoma) is an important component of the face because it determines the facial outline and contour. It forms part of the eye socket and it protects and supports the eyeball. The zygoma is also connected to the upper jaw and sides of the nose.
Causes
A zygoma fracture is usually caused by blunt trauma to the cheek that occurred during:
- Road traffic accidents
- Assault
- Falls
- Contact sports (eg: karate)
Clinical Presentation
A broken cheekbone usually appears with the following signs and symptoms:
- Pain in the affected area
- Bleeding in the eye (bloodshot eye)
- Bruising and swelling around the cheek and eye
- Numbness and tingling sensation on the cheek, nose and upper teeth
- Limitation of mouth opening
- Blurred and double vision
- Flattened cheek
- Eye appears ‘sunken’
- Restriction of eye movement
Tests
What tests will be required to confirm the zygoma is broken? One or more of the following:
- X-rays
- CT scan
- Eye movement and vision test
Treatment
No operation is recommended when the cheekbone fracture is stable, undisplaced and without other complications to neighbouring structures. However, surgery is advised if there is a cosmetic defect or if it affects your daily function.
The operation on the cheekbone is to:
- Ease the pain
- Reposition the flattened cheek thus restoring facial appearance
- Reduce the chance of permanent cheek numbness
- Increase the mouth opening
- Correct double vision (if present)
- Improve eye movement and appearance of the eye
The operation involves the following:
- It will be done under general anaesthetic (you are asleep).
- A cut is made on the gums near your teeth (inside the mouth). Further cuts near the eyebrow, temple and lower eyelid are made if deemed necessary.
- The cheekbone is then repositioned.
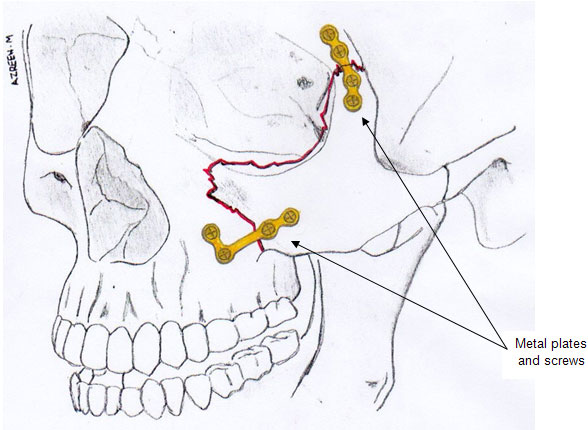
- If needed, metal plates and screws are inserted to hold the cheekbone in place.
- Finally, stiches are placed to close the cuts made.
Risks and Complications
Every surgical procedure carries a risk and therefore complications can occur. The possible problems are:
- The cheekbone may not be restored to its original prominence leading to a cosmetic deformity.
- Persisting numbness on the cheek. However, most people regain sensation after a period of several months.
- Scars at the area wherethe cuts were made. They usually fade with time.
- Infected or exposed metal plates and screws that need removal. Only a small percentage of people require it.
- Bleeding in and around the eye socket causing eyesight problems.
- Damage to teeth near the fracture site.
Post-Operation Recovery
Recovery after surgery could involve the following:
- At least 2 weeks off classes / work
- Avoid vigorous physical activity for 2 to 3 months
- Eat soft foods for at least 2 weeks
- Do not blow your nose for 2 to 3 weeks
- Keep good oral hygiene
- To complete the medications given as prescribed
- Regular follow-up visits at the Oral Surgery clinic after leaving the hospital
References
- Ramli R, Abdul Rahman R, Holmes S. Atlas of Craniomaxillofacial Trauma. Imperial College Press (2011)
- www.aocmf.org
- www.baoms.org.uk
| Last Reviewed | : | 3 June 2014 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Dharmindra Rajah a/l Gunarajah |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Kok Tuck Choon |