Every living things, either plant, animal or human, all have the enzymes in their mass. In the human body, enzymes are very important in keeping the body to function normally. Enzymes are found in the mouth (saliva), intestine (gastric juices, juice and intestinal mucosa), blood, all organs and cells in the body.
In living cells, the enzyme is prominent because it plays important roles in the process of new tissue formation, replacement of the tissue, conversion of food to energy, disposal of waste materials in the body, reproduction and all activities that are characterized as life. Enzyme is a protein that forms in the body and act as a catalyst to react to a normal circumstances. Each body part has a special enzyme with specific function each. The reaction of the enzyme is very specific.
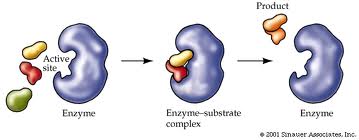
Catalytic properties of the enzyme is depends on the structure of the enzyme. The destruction of the enzyme structure will result in the loss of enzyme activity, in which the process is known as denature. Enzymes are very sensitive to temperature and pH and natural enzymes will be denatured in extreme conditions.
Example: diagram of enzymatic reactions:
In the clinical aspect, we always analyze the concentration of enzymes in the body to detect person’s illness. The examples of the enzymes found in the body that are analyzed in medical laboratories in Malaysia are amylase, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine transferase (ALT), aspartate transferase(AST), lactate dehydrogenase (LH), creatine kinase (CK), and gamma glutamyl tranferase (GGT). In most medical laboratories in Malaysia, the detection of the enzymes was analyzed using Chemistry Analyser and enzymes assay reaction method The normal range of a test enzyme is depends on method and the analyzer used by the laboratory.
The type of enzyme commonly analysed in the medical laboratories are:
Amylase
Amylase is one of the enzymes produced by the pancreas to help digest carbohydrates system. Amylase is also secreted by other organs, particularly the salivary glands. Amylase is normally present in the blood in small quantities only, when there are injuries from the pancreas (pancreatitis) or pancreas are blocked by gallstones or tumors, amylase increases in blood flow, the increase will also occur in urine. Amylase will be measured when a person showed symptoms of pancreatic disorder, such as severe pain in the abdomen or behind the back, fever, loss of appetite and nausea. The doctor will request the test for amylase in urine if it is necessary for treatment.
Normal Range Amylase:
Serum Amylase : 25 – 115 IU/L
Urine: 59 – 401 U/24 hr
Method : 2-ChIoro –4-nitophenyl Linked Substrate (Non Blocked Maltotrioside-CNP-G3)
Analyzer : Beckman Coulter AU2700
Alanine Transaminase (ALT)
Alanine transaminase is an enzyme that is always found in the liver, kidney cells and is a small amount can be found in the heart and muscles. In healthy individuals body the level of ALT in the blood is low. In the event of damage to the liver, ALT is released into the bloodstream. ALT needs to be measured in order to detect liver damage, especially in the patients with hepatitis; or to detect drug / medication or other excessive compounds in the liver. The doctor will request the ALT test if the patients had fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and abdominal swelling.
Normal Range Alanine Trasaminase
Serum Alanine Trasaminase (Adult) : 30 – 65 U/L
Method: L-Alanine ,IFCC 37?C/ Modified without Pyridoxal -5-Phosphate (P5P),
Analyzer: Beckman Coulter AU2700
Aspartate Transaminase (AST)
This enzyme is also known as glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT). This enzyme is normally found in almost every parts of the body, especially in the liver and heart, and least in the kidney and muscle. For healthy individuals, the AST in the blood is low. AST will be secreted into the bloodstream when the liver and the muscle cells damaged. AST commonly used to detect liver damage. The doctor will request the AST together with ALT test as a part of Liver Function Tests.
Normal Range Aspartate Trasaminase
Serum Aspartate Trasaminase (Adult) : 15 – 37 U/L
Method: L-Aspartate,IFCC without P5P, Analyzer: Beckman Coulter AU2700
Alkaline phospatase (ALP)
Alkaline phosphatase is usually known as the ALP and can be found in various body tissues such as in the liver, bone, kidney, intestine and placenta of pregnant women. However, the highest concentration of ALP in the cells can be found in the liver and bone. In the liver, ALP function is to digest fats in the diet. ALP in bone is produced by the cells called osteoblasts (cells involved in bone formation).
The increases levels of ALP in the blood are normally associated with liver disease or bone diseases. If the ALP level rise very high, the possibility of one or more of the bile ducts blocked is also higher. If the levels of ALP is slightly high, the possibility of getting liver cancer; or cirrhosis caused by toxic drugs that affect the liver; or caused by the infection of hepatitis. In some circumstances ALP also increases as a result of excessive bone formation for example in the case of bone formation disorders such as Paget’s disease or rheumatic disease, or during the process of fracture healing. The level of ALP is usually higher in the children and teenagers due to bone growth.
ALP is also requested as a routine test that included as part of the Liver Function Tests. The signs and symptoms that may be involved are fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting. Another related signs are aches, pains, swelling, jaundice, dark urine or feces in bright coloured and itching.
Normal Range Alkaline phospatase
Serum Alkaline phospatase (Adult) : 50 – 136 U/L
Method: P-nitrophenylphosphate, Analyzer: Beckman Coulter AU2700
Gamma – Glutamyl Tranferase (GGT)
|
GGT is an enzyme that can be found in many organs, for example in the kidney, liver and pancreas, but the main source is the liver. GGT will be increased in most diseases due to the damage of the liver or gall acute. The increasing level of GGT level is associated with the consumption of alcohol or other conditions such as congestive heart failure. GGT can be used for screening the excessive alcohol intake and usually it will be increased by 75% in chronic drinkers. Sometimes it is used to monitor people who were alcoholic abused or as treatment for alcohol or whether comply to the treatment. |
 |
Normal Range Glutamyl Tranferase
Serum Glutamyl Tranferase (Adult) Male : 15 – 85 U/L
Female : 5 – 55 U/L
Method: IFCC 2002 (Enzymes), Analyzer: Beckman Coulter AU2700
Creatinine Kinase (CK)
CK is one of the cardiac enzymes. Cardiac enzymes are proteins that are released from heart muscle cells and secreted into the blood when the heart muscle is injured. CK is secreted into the blood stream 4 to 6 hours after a heart muscle cell injury occurred. It reaches its high level in 18 to 24 hours and returns to normal level within 2 to 3 days. The doctor will request this test if the patient has chest pain and suspected a heart attack.
Normal Range Creatinine Kinase
Serum Creatinine Kinase (Adult) Male : 35 – 235 U/L
Female : 21 – 215 U/L
Method: IFCC 2002 (Enzymes), Analyzer: Beckman Coulter AU2700
Lactate Dehidrogenase (LDH)
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is an enzyme that is found in almost all of the body’s cells , but only small amount is detected in the blood. LDH plays an important role in cell respiration, for example in the process of converting sugar into energy. LDH levels will be low in normal conditions. LDH levels will be increased in the blood when tissue injury occurred. It is due to when LDH was secreted from the cells into the blood, especially in the liver and the heart. LDH was also high in the case of hemolytic anemia (breakage of red blood cell), bone fractures, cancer and infections. However, LDH is often used as an indicator of a heart attack and is requested together with CK and CKMB.
Normal Range Lactate Dehidrogenase
Serum Lactate Dehidrogenase (Adult) Male : 85 – 227 U/L
Female : 81 – 234 U/L
Method: Lactate-pyruvate methods, IFCC Standardization (IFCC 2002 Enzymes),
Analyzer: Beckman Coulter AU2700
Collection samples for enzyme analysis:
|
Type of Enzyme |
Sample for analysis |
|
Amylase |
Blood samples were taken from a vein in the arm, sometimes 24-hour urine collection or peritoneal fluid |
|
AST , ALT, ALP, CK, LDH and GGT
|
Blood samples were taken from a vein in the arm. |
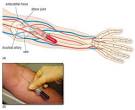
Blood Sample Analysis In Medical Laboratory

Blood sample collection for analysis. Right photo: example blood of samples collection in Chemical Pathology Laboratory in HRPZ II, Kota Bharu


Chemistry Analyser used for enzyme analysis
References
- http://www.labtestsonline.org.uk/understanding/analytes
- Soldin SJ, et al: Pediatric Reference Ranges, AACC Press, Washington DC 1997
Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry. Editors Burtis and Ashwood. WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia, 1999 - Swaroop VS, Chari ST, Clain JE: Acute pancreatitis, JAMA 2004; 291:2865-2868
- Clinical Biochemistry- An Illustrated Colour Text (Fourth Edition), Allan Gaw, Michael J.Murphy, Robert A. Cowan, Denis St. J. O’Reilly, Michael J. Stewart, James Shepherd.
- http://kidshealth.org/parent/system/medical/test_ldh.html
| Last Reviewed | : | 26 August 2014 |
| Writer | : | Rofidah bt. Abu Bakar |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Nik Muhammad b. Mahmood |