Brachial plexus
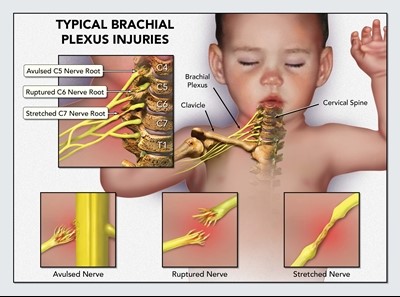
Erb’s palsy primarily affects C5 and C6 (fig.1).
 |
| Source : Wikipedia.org |
Erb’s palsy or Erb–Duchenne palsy is a paralysis of the arm caused by injury to the upper group of the arm’s main nerves, specifically injury of the upper trunk, the C5–C6 nerves. (fig.1) Perinatal injuries are the most common cause of traumatic peripheral neuropraxias / nerve palsies. The incidence is approximately to be 0.35 to 5 cases per 1000 births.
Risk factors
Risk factors of Erb’s palsy include : 1) macrosomia (large baby), 2) shoulder dystocia, 3) prolonged or difficult labour, 4) instrumental vaginal delivery 5) cephalic presentation (head first delivery), 6) trauma to the neck and shoulder, which causes the nerves of the plexus to be violently stretched, 7) direct violence, including gunshot wound and traction on the arm, or attempting to reduce a shoulder joint dislocation. Erb’s palsy can also present with a fracture clavicle bone. The level of damage to the constituent nerves is related to the amount of paralysis.
Clinical presentation
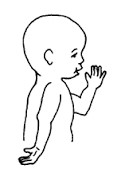
The paralyzed arm hangs limply by the side with the shoulder rotated internally; the forearm turned inwards with the palm facing backwards, the fingers and wrist are bent, (fig.2).The classical sign of Erb’s palsy is the “waiter’s tip hand” (fig.3).
| (fig.2) Erb’s palsy deformity | (fig.3) “waiter’s tip hand” |
 |
 |
| Source : www.google.com/search | Source : www.google.com/search |
Apart from causing muscular impairment (child unable to lift the arm above shoulder height unaided or bringing food to mouth), Erb’s palsy also affects sensory development (sensory is reduced over the outside border of the upper arm).
Treatment
Recovery depends on the nature of the damage to the nerve, if the nerves are only bruised or swollen, the paralysis may get better in a few days or weeks. 80% to 90% of affected children recover completely. Treatment for Erb’s palsy injuries includes immobilization, physiotherapy and, in some cases surgery. Surgical exploration of the brachial plexus is indicated to improve the injury outcome when there is no sign of biceps function by five months of age.
Immobilization
In the first week of injury, the recommended treatment is to rest the affected limb (suggested to place pillow alongside the arm with the palm of the hand facing upwards while the child is at rest or sleeping). When dressing up the child, always put the affected arm into clothes first, and take it out last when undressing. Try to dress the child in loose-fitting clothes until there are signs of active movement in the affected arm.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy management during the first 6 months is directed specifically at prevention of deformities and contracture. Physiotherapy approaches include therapeutic exercise therapy (active and passive range of movement), gentle stretching exercises, sensory stimulation, task-orientated exercises to promote activities and kinesio taping. Gentle exercises will help to stimulate the nerves and encourage the return of sense and movement. Exercise therapy should be administered daily to maintain range of movement and improve muscle strength.
Exercises listed below are for parents or carer whose child has been diagnosed with Erb’s palsy. Please consult your attending physiotherapist before starting these exercises especially if your child has an associated clavicle fracture. Exercises should be carried out while your child is relaxed and should never be forced or painful. Do the exercises slowly, steadily and parents or carer are encouraged to do the exercises regularly, preferably three times a day or during every nappy change.
Exercise 1:
Shoulder flexion
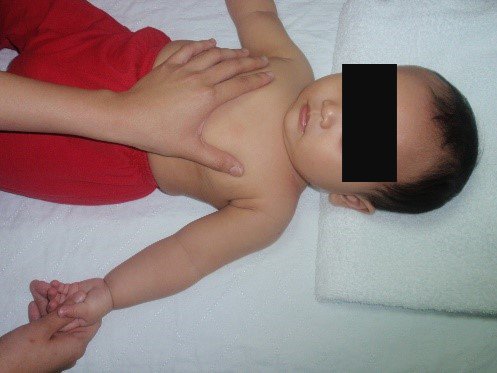
Starting position: place your baby lying comfortably on his/her back, ensure your baby’s arm is by the side with the palm facing up (resting position) (fig.1).
Lift your baby’s arm above their head whilst supporting their shoulder with the other hand, keeping the elbow straight (fig.1a). Hold the position for 10 seconds and repeat the same exercise for 5 repetitions.
 |
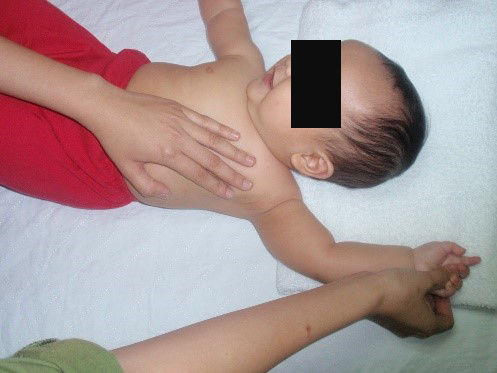 |
| fig.1 Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah | fig.1a Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah |
Exercise 2 :
Elbow flexion
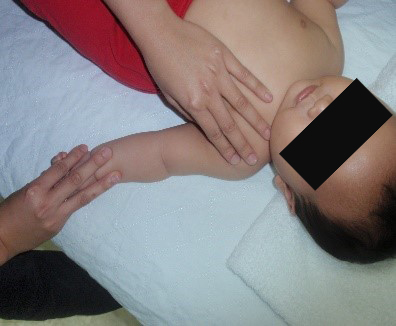
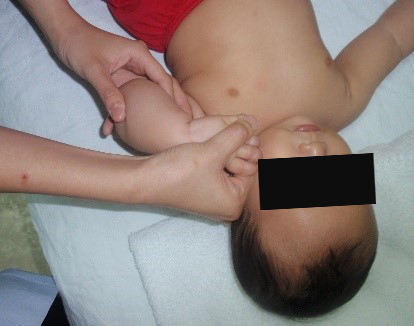
Starting position: place your baby lying comfortably on his/her back, ensure your baby’s arm is by the side with the palm facing up (resting position) (fig.2).
Hold the elbow joint in one hand and bend the elbow to touch the baby’s cheek with their free hand (fig.2a). Hold the position for 10 seconds and repeat the same exercise for 5 repetitions.
 |
 |
| fig.2 Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah | fig.2a Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah |
Exercise 3:
Shoulder rotation
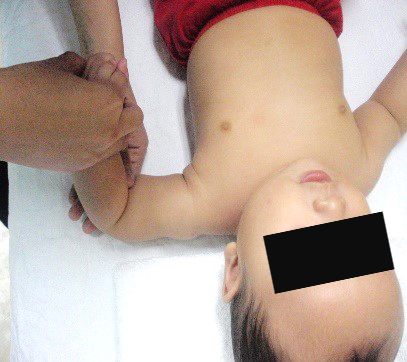
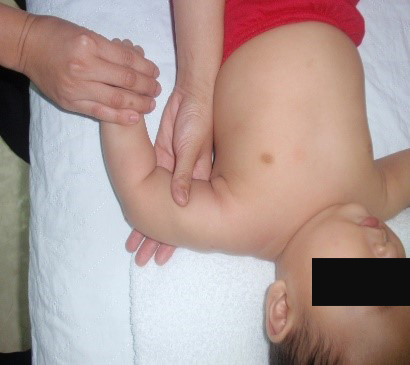
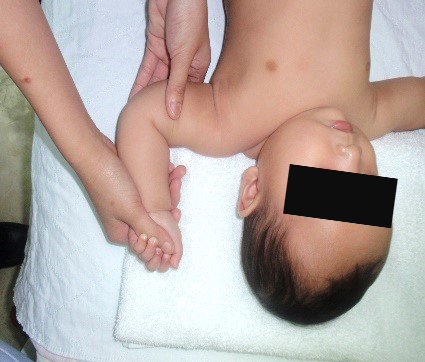
Starting position : Hold the baby’s arm at 90 degrees from the body with the elbow bent (fig.3).
Grasp the wrist firmly between two fingers. Lower the forearm towards the feet, so that the palm of the hand is facing downwards. Hold the position for 10 seconds and repeat the same exercise for 5 repetitions (fig.3a).
Grasp the wrist firmly between two fingers. Lower the forearm towards the head, so that the palm of the hand is facing upwards. Hold the position for 10 seconds and repeat the same exercise for 5 repetitions (fig.3b).
 |
 |
 |
| fig.3Source : Unit FisioterapiHospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah | fig.3a Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah | fig.3b Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah |
Exercise 4 :
ForearmPronation
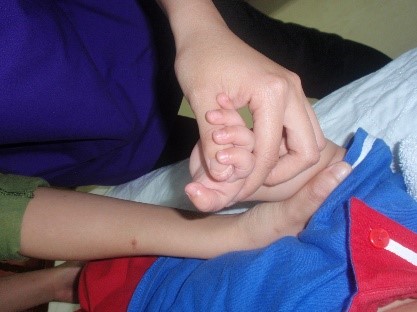
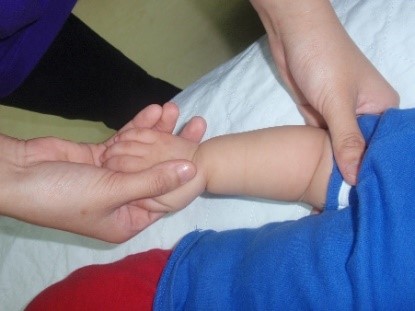
Starting position: Hold the baby’s arm close to the body and the elbow bent to 90 degrees (fig.4). Turn the palm of the hand over so it is facing downwards. Hold the position 10 seconds and repeat the same exercise for 5 repetitions (fig.4a)
 |
 |
| fig.4 Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah | fig.4a Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah |
Exercise 5 :
Forearm Supination
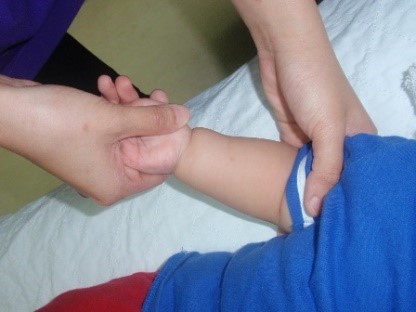
Starting position: Hold the baby’s arm close to the body and the elbow bent to 90 degrees. (fig.5) Turn the palm of the hand over so it is facing upwards. Hold the position 10 seconds and repeat the same exercise for 5 repetitions.
 |
 |
| fig.5 Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah | fig.5a Source Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak -kanak Sabah |
Exercise 6 :
Wrist flexion and Wrist Extension
Starting position : Hold the baby’s arm close to the body. Stabilizing the forearm with one hand, hold your baby’s hand with your other hand. Gently bend the wrist forward. Hold the position for 10 seconds and repeat the same exercise for 5 repetitions (fig.6).
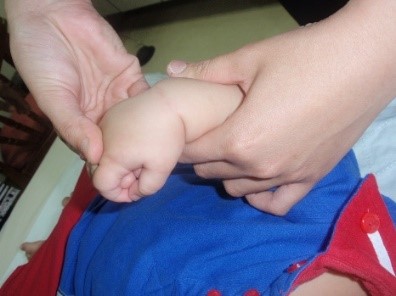 |
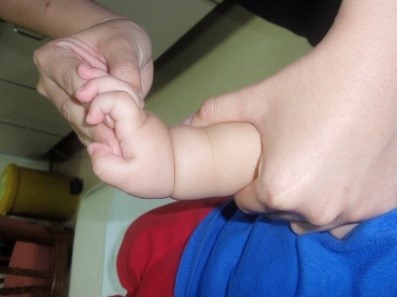 |
| fig.6 Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah | fig.6a Source : Unit Fisioterapi Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah |
Stabilizing the forearm with one hand, hold your baby’s hand with your other hand. Gently bend the wrist backward. Hold the position for 10 seconds and repeat the same exercise 5 repetitions. (fig.6a)
References
- Chater M, Camfield P, and Camfield C. Erb’s Palsy – Who is to be blame and what will happen? Paediatrics and Child Health. 2004 Oct;9(8):556-560
- Forbes H, Erb’s Palsy exercise information. Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust. 2015;1-3
- Gosk J, and Rutowski R. Obstetrical brachial plexus palsy – etiopathologenesis, risk factors, prevention. Prognosis. Ginekol Pol. 2004 Oct;75(10):814-20 [Pub Med]
- Malik S, Bhandekar HS, Korday CS. Traumatic peripheral neuropraxias in neonates: a case series. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014 Oct;8(10):PD10-12 [Pub Med]
- Ritchie L and Walker W. Erb’s Palsy. Physiopedia 2015. http://www.physio-pedia.com/Erb’s_Palsy [Pub Med]
- Tecklin JS. Pediatric Physical Therapy. 3rd Edition. 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Source images
1. Google search engine. Retrieved August 3 2015. https://www.google.com/search?q=erb%27s+palsy+images&oq=erb%27s+palsy+images&aqs=chrome..69i57j0l4.7870j0j8&sourceid=chrome&es_sm=93&ie=UTF-8 2. (2015) Unit Fisioterapi, Hospital Wanita & Kanak-Kanak Sabah. Retrieved July 27 2015. 3. Wikipedia.org. Retrieved August 3 2015.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Erb%27s_palsy
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer / Translator | : | Lily Kong @Kwong |
| Accreditor | : | Daaljit Singh Harbachan Singh |
| Reviewer | : | Halimah bt. Hashim |







