What is postnatal period?
Postnatal or postpartum period is the first 42 days after the birth of a child. In this period of recovery, the new mother is encouraged to be mobile to help the mother’s body return to “normal”. Definition of exercise Exercise is defined as an activity that requires physical effort. It is carried out to sustain or to improve health and fitness. (Oxford dictionary) It is a planned, structured and repetitive physical activity for the purpose of conditioning any part of the body. (cited from: the free dictionary)
The importance of postnatal exercise
 |
|
Fig. 1
Source : Unit Fisioterapi, Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah |
Pelvic floor muscle The pelvic floor muscles are tightly slung between the tailbone (coccyx) and the pubic bone, providing support for pelvic viscera (organs). e.g. the bladder, intestines, the uterus (in females), and in maintenance of continence as part of the urinary and anal sphincters. Fig.2 Childbirth can weaken these muscles and cause problems of uterine prolapse and incontinence later in life, due to stretching and trauma sustained during vaginal or instrumental delivery.
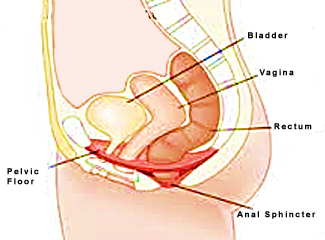 |
|
Fig. 2
Source : google.image.com |
Pelvic floor exercise (PFE), also known as Kegel exercises, may improve the tone and regain back the function of the pelvic floor muscles, which is of particular benefit for women who experience urinary stress incontinence. Perform this exercise as often as you can (recommended hourly) anytime, anywhere and in any position. Continue doing your exercises for at least 3 months after the birth of your baby, it can take several months for the pelvic floor muscles to return to their pre-pregnancy strength.
Abdominal muscle The abdomen is completely enclosed and supported by its muscles. As the baby grows, stretching of the muscles occur, and sometimes they separate centrally. The entire abdominal “corset” will be weakened because of the changes in hormonal levels and/or prolonged inactivity postnatally. A combination of a strong abdominal muscle, pelvic floor muscle and deep abdominal muscle are essential to provide stability to the back.
Back pain Back pain may not be a symptom during pregnancy but it frequently occurs following delivery. The possible factors are; the resultant stretching of the ligaments of the pelvic joints, the lithotomy position, poor feeding or nappy-changing postures, tension and fatigue.
Oedema Many women complain of heavy, oedematous, aching legs, swollen feet and ankles during the immediate postpartum period. The causative factors may be due to prolonged pushing during labour, pelvic congestion or dysfunctional urinary tract.
Exercise guidelines For the first 6 weeks post delivery, all the exercises should feel comfortable and should not hurt. However, pelvic floor exercises may feel a little difficult at first. Consult with your obstetric doctor or physiotherapist for more information before starting on any postnatal exercise program. Listed below are some exercises to strengthen abdominal, pelvic floor, upper back and lower back muscles.
Warning signs to slow down Don’t overexert yourself. Your body gives out warning signs if you are exercising too hard, and these signs may include:
- Increased fatigue
- Muscle aches and pains
- Colour changes to lochia (post-partum vaginal flow) to pink or red
- Heavier lochia flow
- Lochia starts flowing again after it had stopped
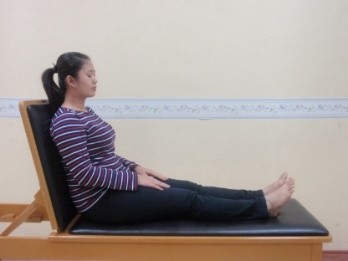
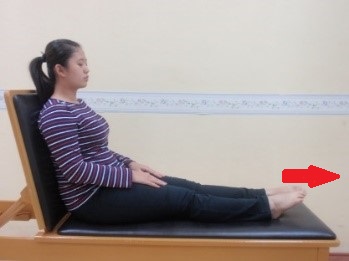
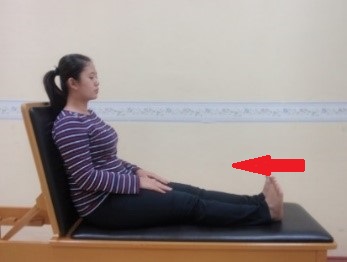
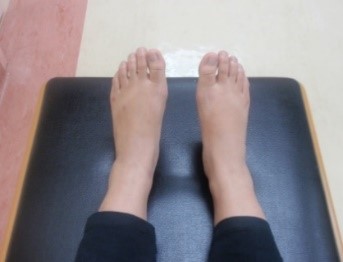
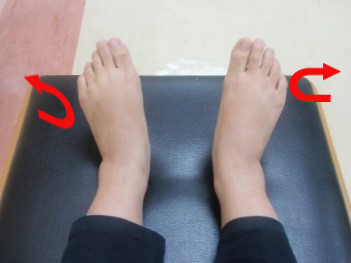
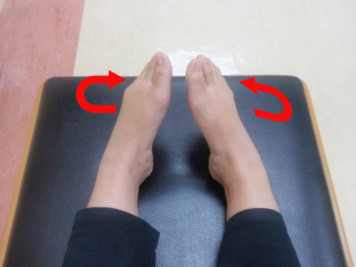
Exercise 1 : Circulation exercise Ankle exercise
 |
 |
 |
|
Start position |
Push the foot away from body. Hold for 3 seconds and repeat 5 times | Pull the foot toward the body. Hold for 3 seconds and repeat 5 times |
 |
 |
 |
|
Start position |
Push the foot hold for 3 seconds and outward repeat 5 times | Pull the foot inward hold for 3 seconds and repeat 5 times |
Source : Unit Fisioterapi, Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah
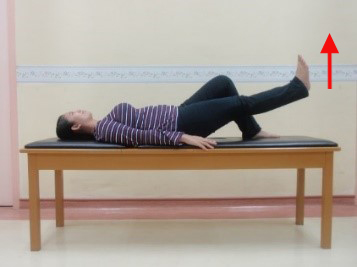
Exercise 2: Abdominal and thigh strengthening exercise Straight leg-raise
 |
 |
|
Start position |
Lift leg off from bed, hold for 5 seconds and bring it down. Repeat 5 times |
Source : Unit Fisioterapi, Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah
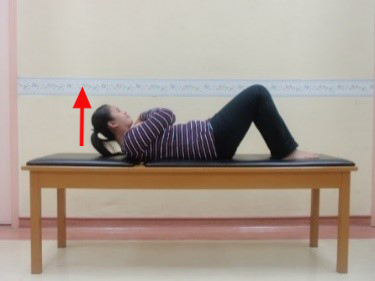
Exercise 3 : Abdominal strengthening exercise Partial sit up
 |
 |
|
Start position |
Lift head off bed, hold for 5 seconds and back. Repeat 5 times |
Source : Unit Fisioterapi, Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah
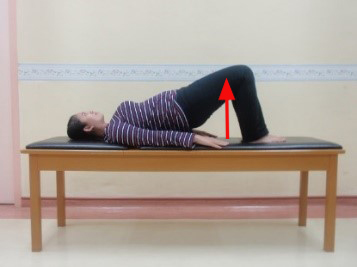
Exercise 4: Back and buttock muscles strengthening exercise Bridging exercise
 |
 |
|
Start position |
Lift Buttocks off bed and hold for 5 seconds and back. Repeat 5 times |
Source : Unit Fisioterapi, Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah
Exercise 5 : Pelvic floor exercise Kegel exercise
 |
 |
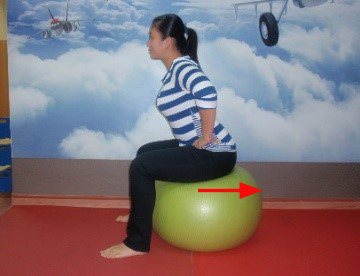 |
| Start position | Bring the ball forward Hold for 3 seconds and return. Repeat 5 times | Push the ball backwards. Hold for 3 seconds and return. Repeat 5 times |
Source : Unit Fisioterapi, Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah
Exercise 6 : Pelvic Tilt exercise Cat and Camel exercise
 |
 |
 |
|
Start position |
Arch your back, Push your spine down. Return to start. Repeat 5 times. | Curve your back, push your spine up .Return to start. Repeat 5 times |
Source : Unit Fisioterapi, Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah
Exercise 7. Exercises for breasts
 Source : Unit Fisioterapi, Hospital Wanita & Kanak-kanak Sabah |
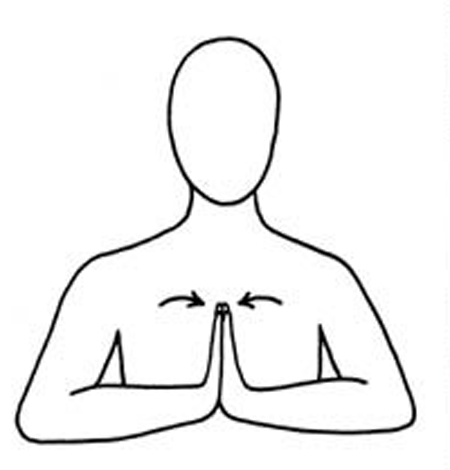 |
| Wall push up against the wall. 15 – 20 repetitions. Perform 2 or 3 times a day | Press your palms together while pointing your elbows out to the sides, hold for 3-5 seconds for 10 – 15 times. Perform 2 -3 times a day |
References
- Artal R and O’Toole M. 2003 Guidelines of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists for exercise during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Br J Sports Med. 37:6-12
- Jawatankuasa Teknikal Profesyen Fisioterapi. 2013 Buku Garis Panduan Perkhidmatan Fisioterapi Di Klinik Kesihatan. Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
- Mantle J, Haslam J & Barton S. 2004 Physiotherapy in Obstetric and Gynaecology. 2nd ed. Butterworth Heinemann
- Postnatal exercise – sample workout. 1999. State of Victoria. Reproduced from the Better Health Channel.www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au
- Unit Fisioterapi. 2009 Senaman Selepas Bersalin. Hospital Wanita & Kanak-Kanak Sabah
- Women’s Health Physiotherapy Wythenshawe Hospital. 2009 Physiotherapy Post Natal Exercises and Advice. University of South Manchester. Review date: Feb 2011
- Postnatal Exercise For The First first 6 weeks. http://www.babycenter.in/a749/ postnatal-exercises-for-the-first-six–weeks#ixzz3kOUANOoG29th August 2015
Source images
- Google images.com
- Unit Fisioterapi, Hospital Wanita & Kanak-Kanak Sabah. 2015. Retrieved August 27th 2015.
- Wikipedia.org. Retrieved August 29th 2015. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/pelvicfloor
| Last Reviewed | : | 23 August 2019 |
| Writer / Translator | : | Lily Kong@Kwong |
| Accreditor | : | Daaljit Singh Harbachan Singh |
| Reviewer | : | Halimah bt. Hashim |







