Introduction
Is your work situation surrounded by hazard? If yes, you are at high risk to get eye injuries and possible loss of vision. You should wear the right protection at work to prevent eye injury and keep your eyes safe.
Eye injuries can happen to workers in many industries. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) at least 2,000 workers experience eye injuries each day and more than 800,000 eye injuries occur annually.
However, many workers skip the safety precaution in their workplace because they are not comfortable or the eye protection was not properly fitted and sometimes they believed protection was not required for the situation. The extend of the injury depending on severity and immediate action prior to injury.
Common work related eye injuries
Hazards in the industrial setting can range from dirt or metal particles to corrosive chemicals, welding light, falling objects or exploding debris. Following are some situations for which treatment is most urgent.
- Foreign body and corneal abrasion
Carpentry and construction work can produce small particles, dust, flying woods, metal dust and concrete chips that can blow and fall onto the eye and trapped under the eyelid or surface of the eye. The embedded particle may scraped the cornea cause irritation, redness and tearing. If the particle is not removed from your eye, it may scratch the corneal surface cause corneal abrasion.
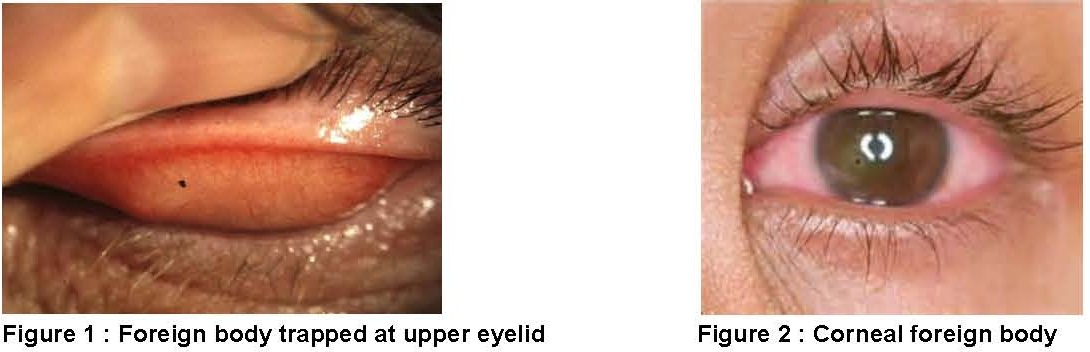
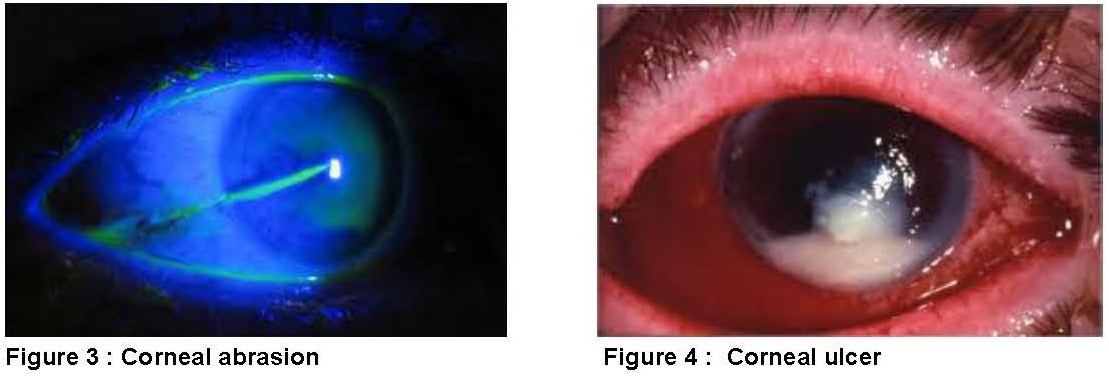
Sometimes a scratch on the cornea doesn’t heal and it can get infected. Corneal ulcer is a complication due to infection that invades the cornea following eye injury, trauma or other damage. A corneal ulcer typically occurs as a painful, red eye, with mild to severe eye discharge and reduced vision. Untreated corneal ulcers can lead to corneal scarring, severe vision loss and even loss of the eye.
- Laceration and Intraocular Foreign Body
Industrial workplaces especially at manufacturing and construction side pose the treats of eye injury from tiny pieces of metal and fragments of sharp object. A piece of fractured metal can fly at high velocities and cut through the eyelid tissue or any part of the eye. If the injury does not penetrate to the eyeball, your vision possibly could be saved.
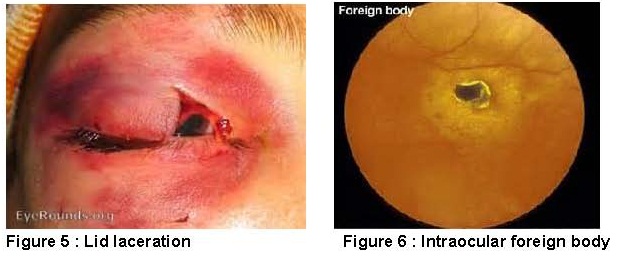
Sometimes the metal fragment penetrates and lodges within the eyeball and result intraocular foreign body injury.
The presence of intraocular foreign body can happen without significant physical findings but may cause significant initial damage. Subsequent damage depends on the content of the intraocular foreign bodies.
Reaction to the foreign bodies may lead to infection or inflammation of the eyeball. Severe tissue reaction may occur within a few days or even years before these foreign body cause inflammation of the eyeball.
- Penetrating injury
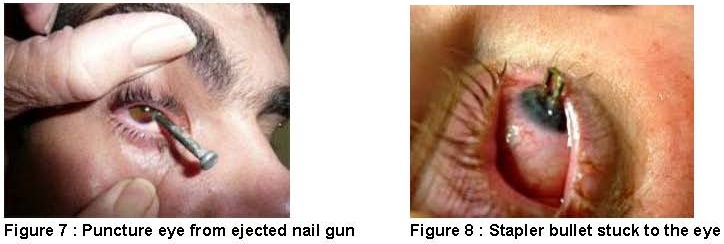
Sharp and pointed instruments that fly in high velocity such as nails, wires, larger pieces of metal, blades or glass that penetrate or stuck to the eye can cause even more serious injuries includes puncture of the eyeball, bleeding in the eye, retinal tear and detachment, ruptured globe, infection of the eye ball or even blind. Urgent visit to emergency room is crucial for immediate ophthalmology treatment.
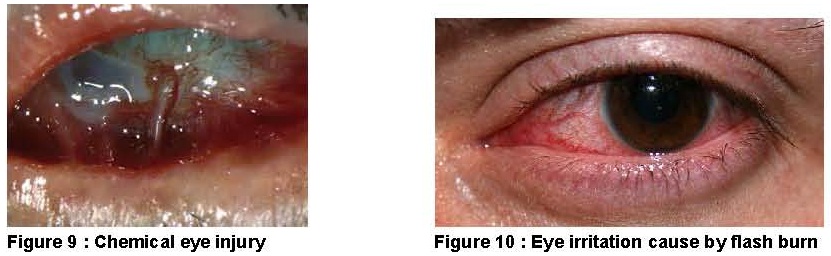
- Chemical injury and flash burn
There is a risk of getting unexpected splashed or sprayed in the eye when working with corrosive chemicals such as acids, alkali, bleach or industrial cleaning products. The severity of chemical burn depending on the substance, how long and how much the amount of substance had contact with eye and how the injury is treated. The effects of chemical exposures causing eye injuries can range from minor irritation and red eyes to serious eye damage and even blindness. Alkaline presence the most risk to the eye.
Eye also can be easily damaged by exposure to the ultraviolet radiation from sun and other sources. Welder’s flash no less harmful than sunlight to the eye. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation without protection can cause flash burn to be serious and lead to some loss of vision.
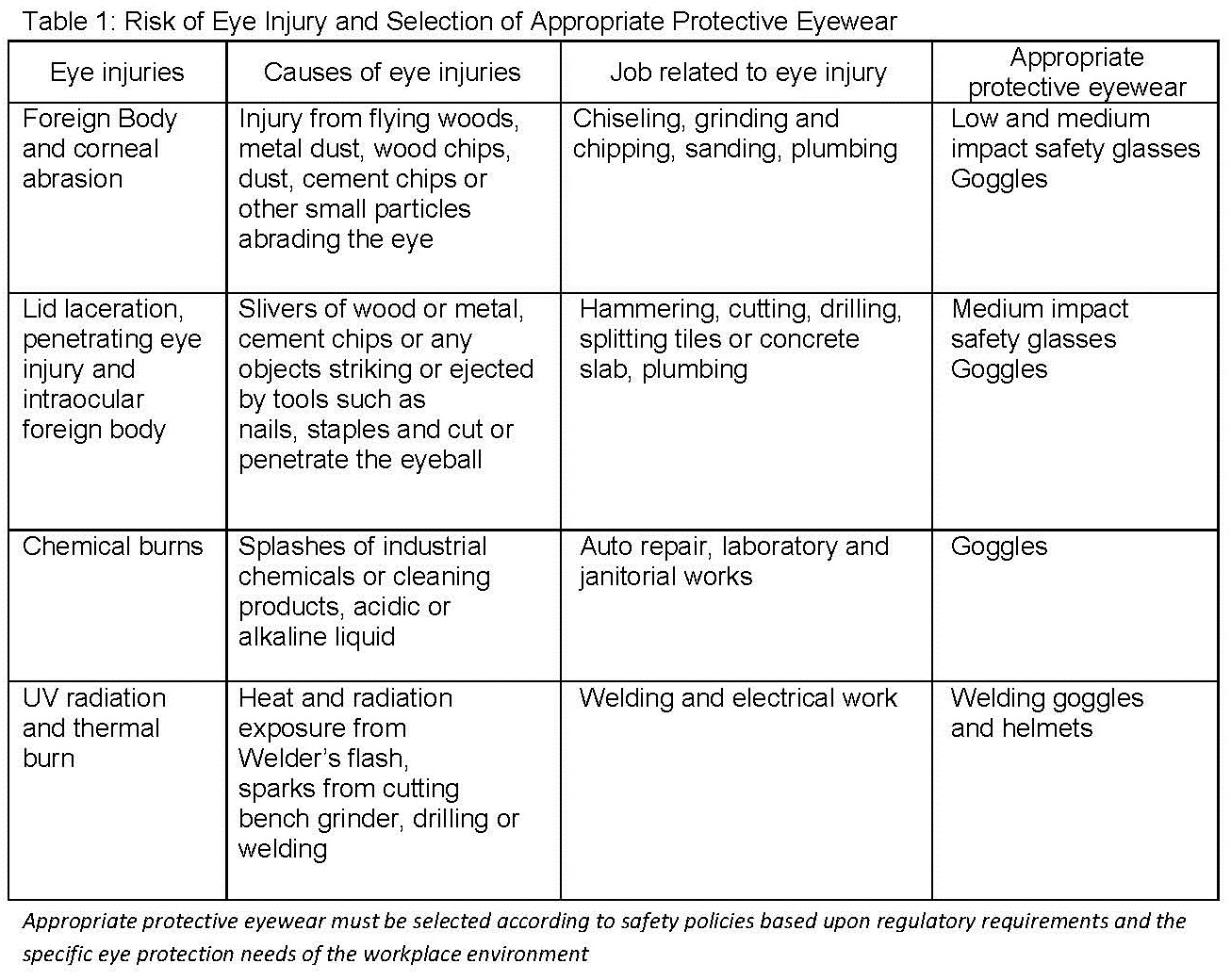
Safety measures to prevent eye injury
To ensure that workers take safety precaution at workplace, a guideline from Ministry of Health for Occupational Safety and Health was developed. It is vital that workers protect their eyes on-the-job and recognize hazards so that necessary precautions can be taken to reduce the risk of injury.
Steps and safety measures to practice at workplace to prevent eye injuries are:
- Risk and hazard assessment
- Dust, wood, glass, concrete, metal and other particles
- Falling or misdirected object, building materials and tools
- Chemicals such as acids, alkali, fuels, solvents, poisonous gases and smoke
- Welding light and electrical arc
- Create a safe work environment by making sure that tools are in good condition and functioning properly and safety features are in place.
- Wearing and select the appropriate eye protection and make sure the eye protection is in good condition and properly fitted to worker’s eye.
Eye protection
Eye protection is a device that is require to be used when worker’s eye are expose to hazard. Wearing eye protection whenever there is a chance of eye injury that could be prevented by such equipment can save the eyes from injury and permanent loss of vision.
The right eye protection chosen for specific work environments depends upon the nature and degree of the potential hazard, the circumstances of exposure and other personal and workplace factors.
Types of eye protection

- Goggles

- Face shield

4. Welding Goggles and Welding Helmets

First Aid for Eyes Emergencies
While protective eyewear are provided for all types of work, accident do happen. First aid steps that can and should be taken to protect the eye from further damage are as shown in the table.
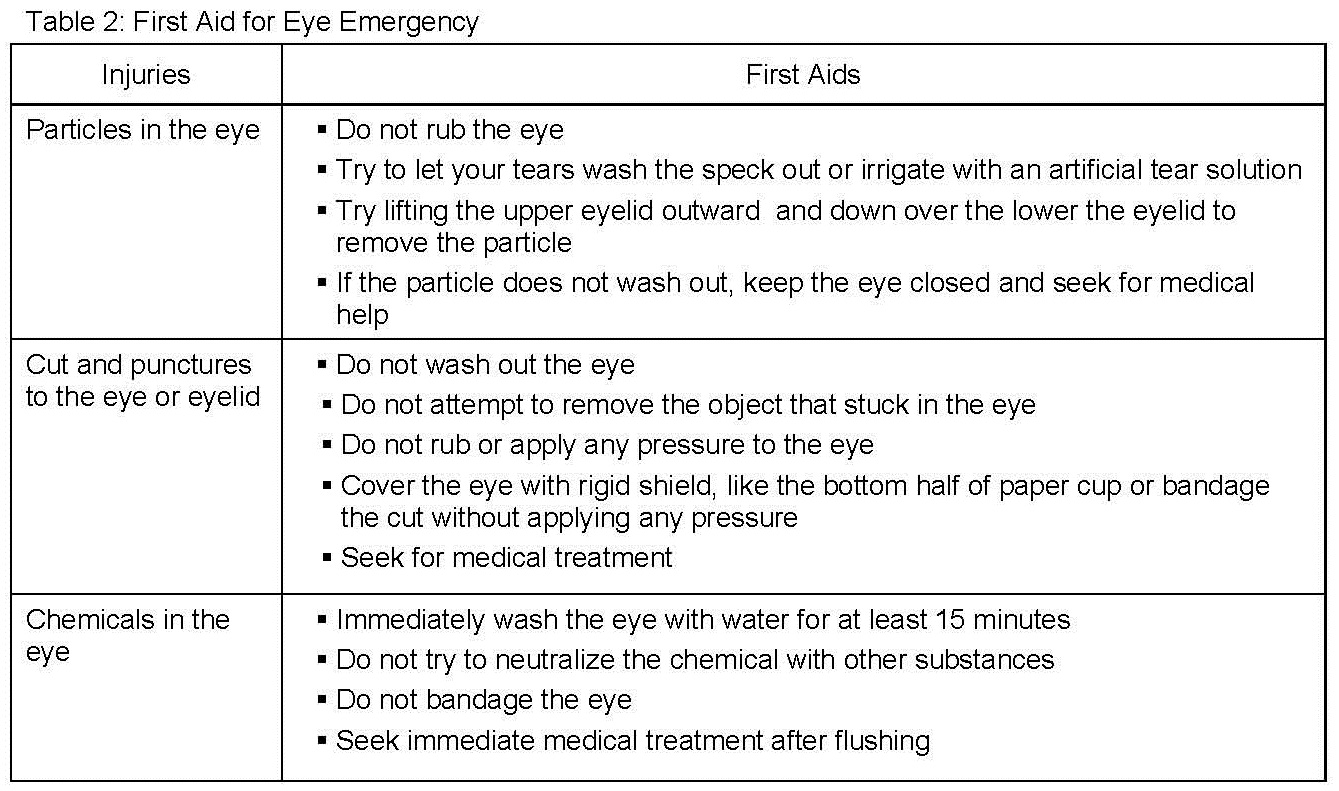
Injury might not be immediately obvious. Seek medical attention as soon as possible following an injury, particularly if you have pain in the eye, blurred vision, loss of vision or loss of field of vision.
Reference
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2010). ”Eye Safety.” Retrieved September 30, 2010. http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/eye
2. Eye Safety at A Glance – Protecting Your Vision At Work. The Vision Council Health And Safety At Work. Eye Protection: A Guide to Provision and Use. Medical Research Council. http://safety.csc.mrc.ac.uk/docs/Eye_Protection_Brochure.pdf
3. Eye and Face Protection.ILO Encyclopedia of Occupational Health and Safety http://www.ilo.org/oshenc/part-iv/personal-protection/item/687
4. Protecting Your Eyes at Work. American Optometric Association. http://www.aoa.org/patients-and-public/caring-for-your-vision/protecting-your-vision
5. Garispanduan Pencegahan Kemalangan Di Tempat Kerja. Unit Kesihatan Perkerjaan, Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
6. Garispanduan Keperluan Kelengkapan Pelindung Diri. Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
| Last Review | : | 20 Jun 2014 |
| Translator | : | Siti Khadijah bt. Osman @ Othman |
| Accreditor | Pn. Noor Zahirah Binti Husain |







