Introduction and Definition
Functional appliances are orthodontic appliances that utilize the forces of orofacial musculature and the modification of growth to correct malocclusion via varying amounts of dental and skeletal effects. They are mostly used to correct Class II malocclusions and only some mild cases of Class III malocclusions. They do not incorporate active components that move teeth, thus cannot correct irregularities of teeth.
Type of Functional Appliances
They can be categorized into removable functional appliances (Activator, Bionator, Frankel appliance, Twin Block appliance) or fixed functional appliances (Herbst appliance). They can also be classified as passive tooth-borne appliances (Activator, Bionator, Herbst appliance, Twin Block appliance), tissue-borne appliances (Frankel appliance), and active tooth-borne appliances (modifications of Activator and Bionator).
Indications
Functional appliances are generally indicated for growing patient, of which dentitions are relatively well-aligned, in mild or moderate skeletal Class II and motivated patients.
Treatment effects
Functional appliances are used to correct moderate Class II malocclusion by enhancing mandibular growth of growing children. Although there are various types of functional appliances in the market, the mode of action is basically the same for all. As the mandible was postured (and held) forward in a Class II child, growth of the distracted condylar head and remodeling of the glenoid fossa would be enhanced to achieve skeletal correction and profile improvement. The effects of functional appliances include dentoalveolar changes and skeletal/orthopaedic changes. Dentoalveolar effects contribute about 60-70% of the changes. There is inhibition of downward and forward eruption of maxillary teeth, eruption and mesialization of lower molars, retroclination of upper incisors and proclination of lower incisors. The skeletal effects that contribute about 30-40% of changes are increased condylar remodelling, increased glenoid fossa remodelling, restriction of forward growth of maxilla, increased lower face height and increased mandibular length.
Criteria for use of Functional Appliances
Patient can be assessed clinically for the suitability of functional appliance therapy: if the profile improves when the patient was asked to posture the mandible forward till incisors edge to edge bite, then the use of functional appliance can be considered. Effect of functional appliances is greatest when these appliances are used during the pubertal growth spurt, usually 10-12 years old for girls, and 12-14 years old for boys. Patients treated during the peak period demonstrated significant skeletal effects induced by the appliance, whereas patients treated in the pre-peak or post-peak period produced significant dental changes only. Thus, functional appliances are best used when patient is at or near pubertal growth spurt stage. Patient can be assessed for maturational stage based on cervical vertebrae maturation (CVM) method.
Care/ Diet
With any functional appliance, a break-in period is helpful. Having patient wear the appliance only a short time per day to begin with and increasing this time gradually over the first few weeks is a useful method of introduction. Patient should be informed that speaking may be difficult at the beginning, but that comfort and speaking facility will increase. To be effective, removable functional appliances should be worn at least 12 hours per day. All removable functional appliances except Twin Block should be removed while eating. For fixed functional appliances, patient should be advised to avoid biting on hard and sticky foods, large mouthfuls and exaggerated movements to reduce the risk of breakage or debonding. To prevent soreness of teeth, patient should be also instructed that the appliance is meant to remind them to posture the mandible forward, not to force the mandible forward with heavy pressure on the teeth.
Treatment Period
Treatment period varies among different types of functional appliances, as shown in table below:
|
Type of functional appliance |
Treatment period |
|
Twin Block |
12-15 months |
|
Herbst appliance |
8-12 months |
|
Frankel appliance |
15-24 months |
|
Andresen activator |
2-2.5 years |
|
Bionator |
12-16 months |
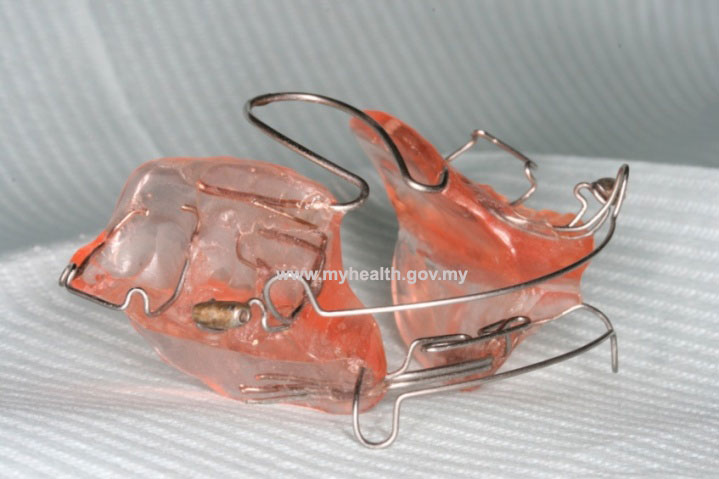
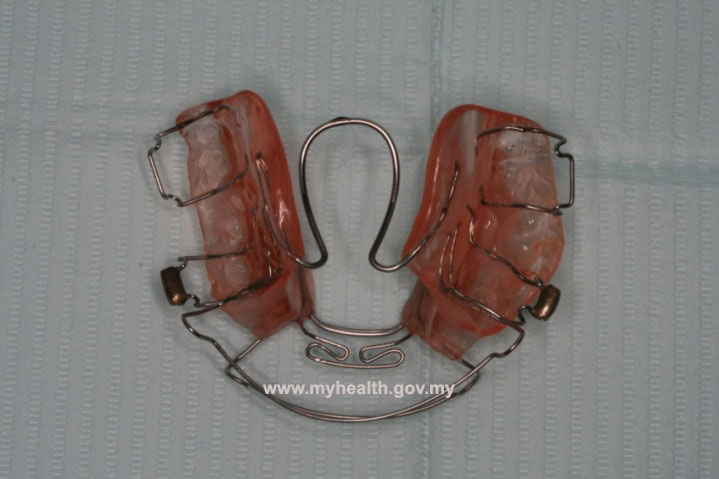
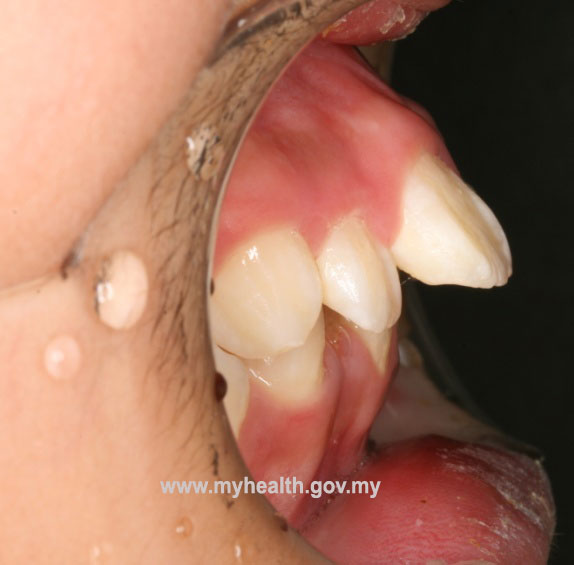
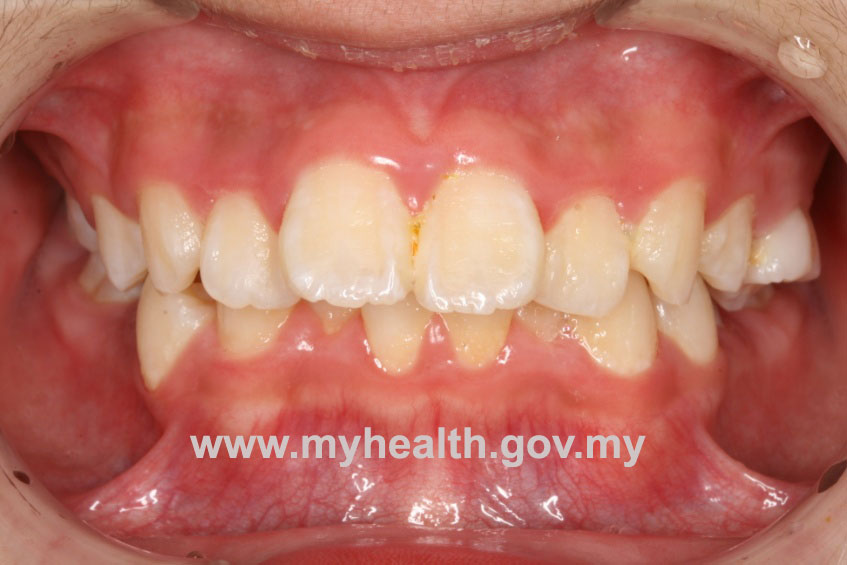
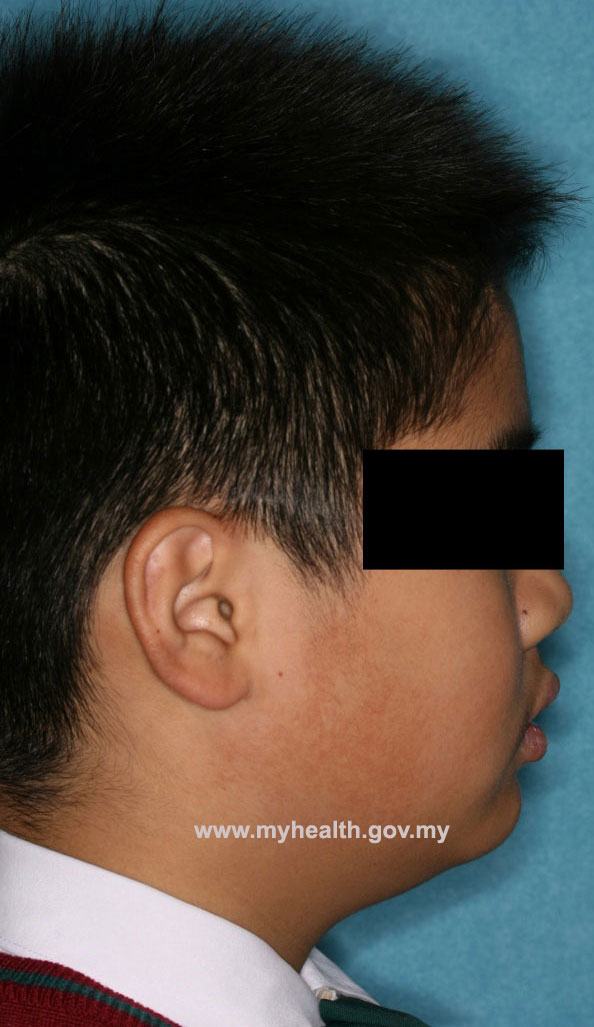
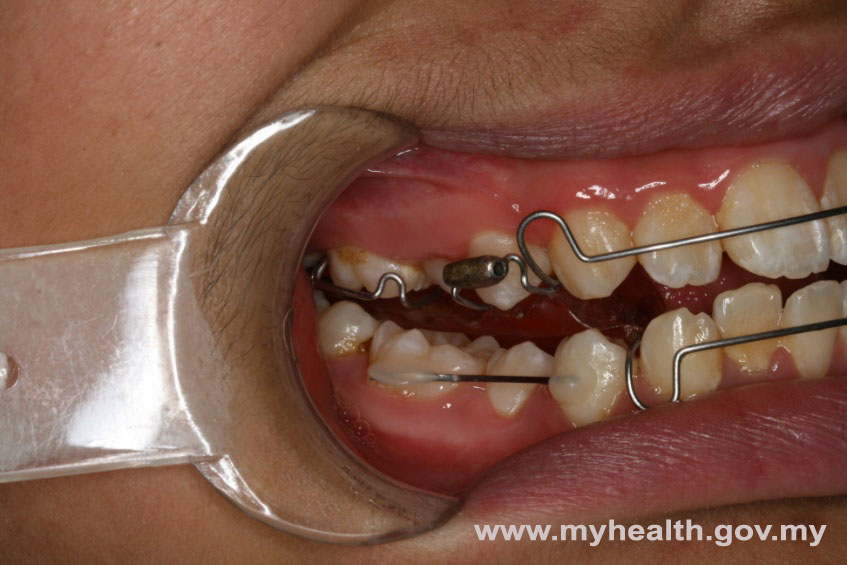
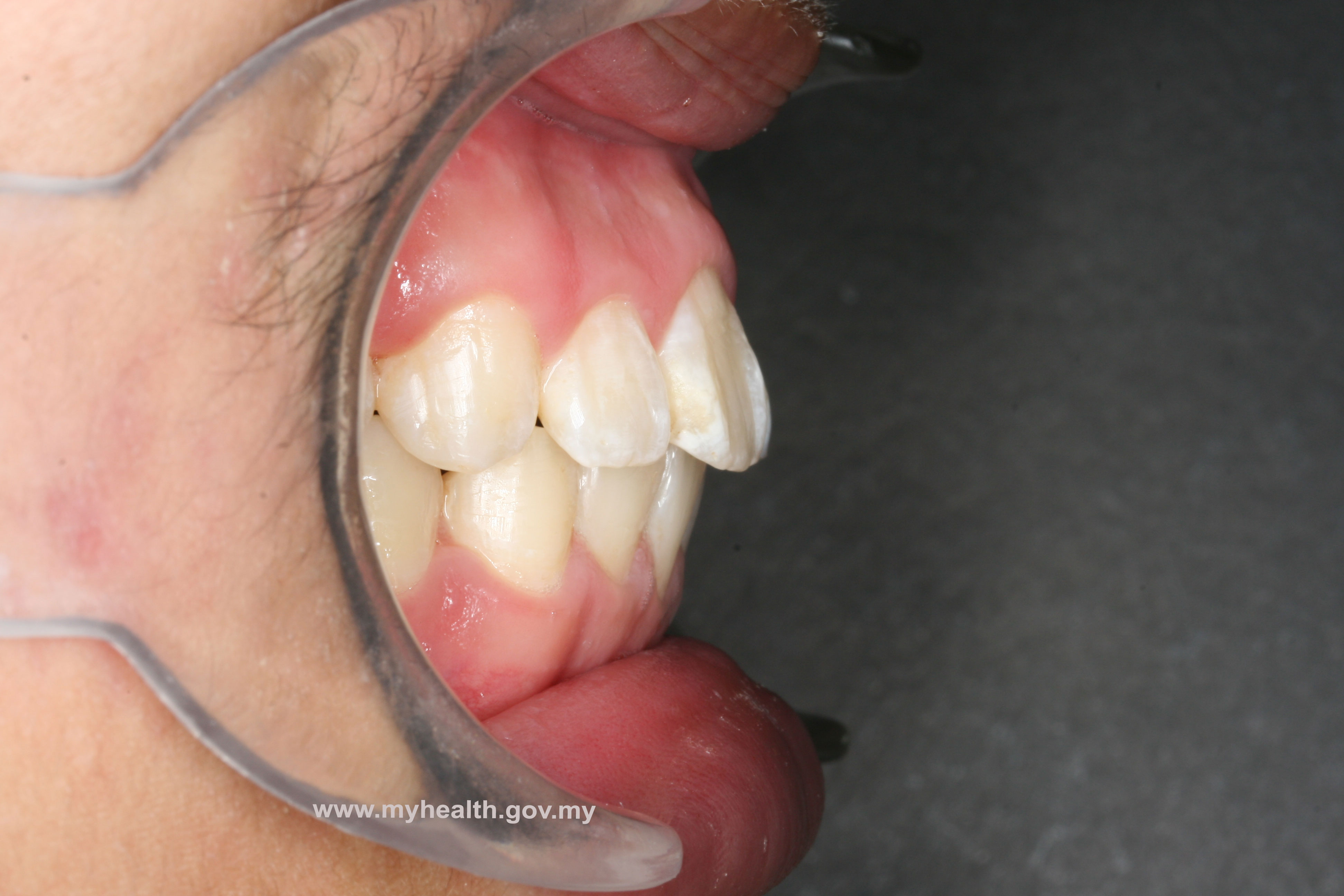
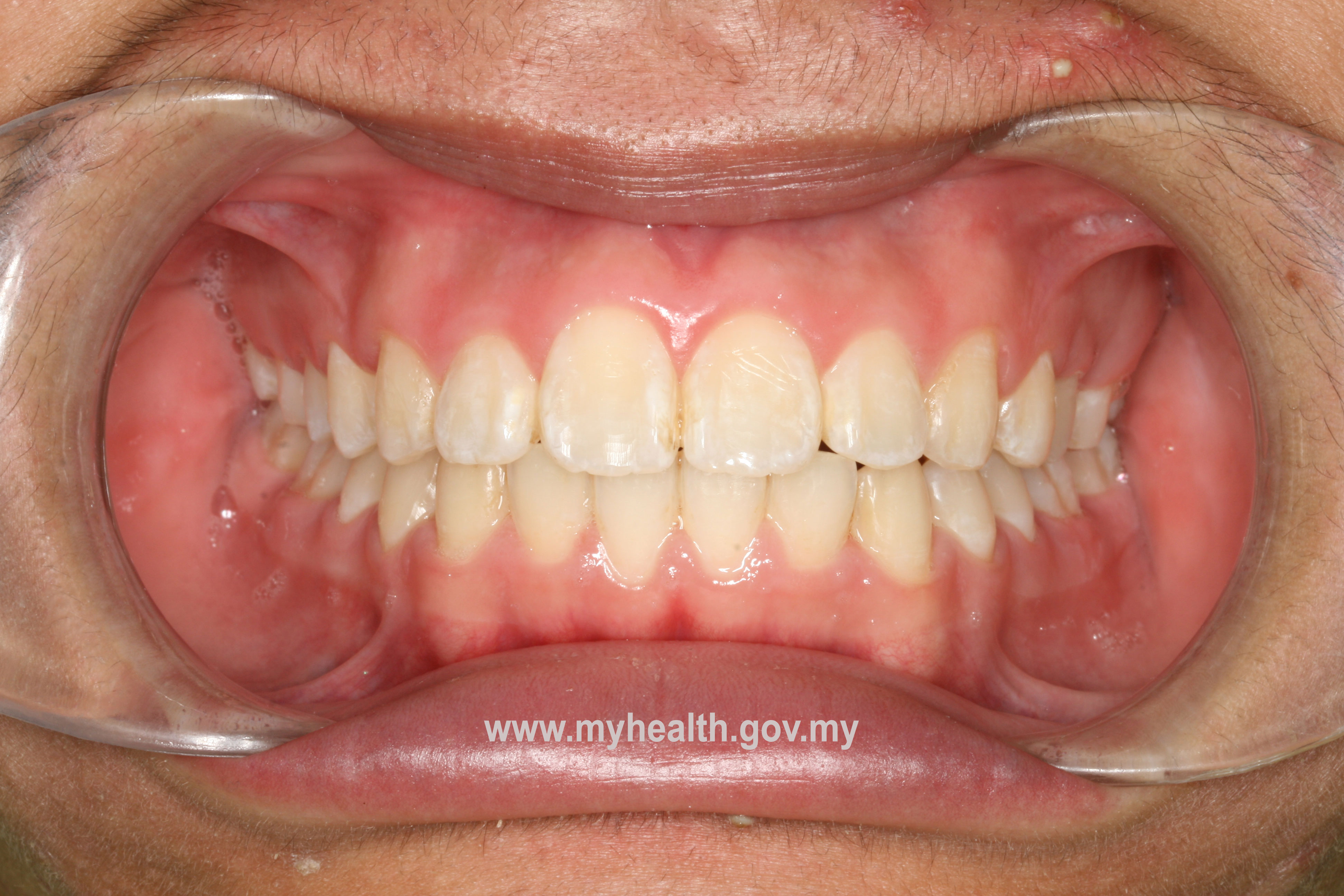
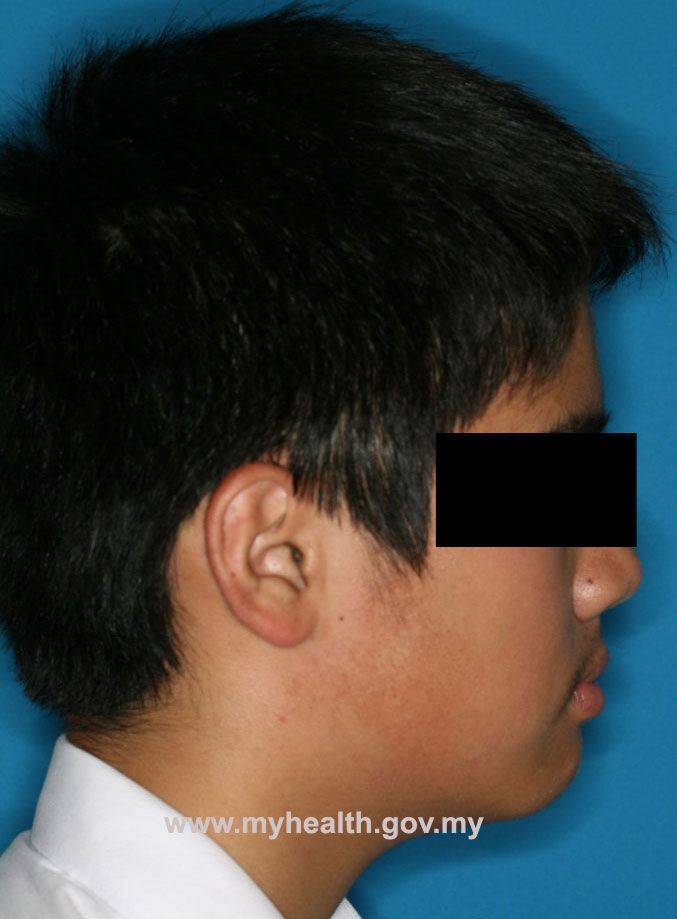
Example of a clinical case treated with Modified Bionator, followed by full fixed appliances
Total treatment time: 28 months (12 months with Modified Bionator, 16 months with full fixed appliances)
References
- Profitt WR, Fields HW, Sarver DM. Contemporary Orthodontics.5th Edition. Elsevier 2014
- Clark WJ. Twin Block Functional Therapy: Applications in Dentofacial Orthopaedics. 2nd Edition. Mosby 2002.
- Wong RWK, Alkhal HA, Rabie ABM. Use of cervical vertebral maturation to determine skeletal age. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009 Oct;136(4):484.e1-6
| Last Reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Tan Ying Ying |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Ahmad Burhanuddin b. Abdullah |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Hjh. Rashidah bt. Dato’ Hj. Burhanudin |