What is HFMD?
- Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is an infection caused by viruses from the enterovirus group which includes enteroviruses, coxsackie viruses, echoviruses and polioviruses.
- Among these viruses, enterovirus 71 (EV 71) and coxsackie virus A16 are the most common pathogens.
Who are at risk?
Anyone can get HFMD. However, children younger than 5 years old are most likely to get HFMD.
Signs and symptoms of HFMD
- HFMD begins with fever, feeling sick with poor appetite. One to two days later, painful ulcers develop in the mouth. Some children have red spots developing on their palms or soles, which may turn into blisters. This skin rash may sometimes occur on the knees, elbows or buttock of the child. This skin rash is usually not itchy.
- Due to the poor appetite and painful mouth ulcers, the child may refuse to drink and will be at risk of dehydration.
- The symptoms vary among infected children. While some children develop the typical signs and symptoms, others may just have the skin rash or mouth ulcers. Some infected children experience no signs and symptoms.
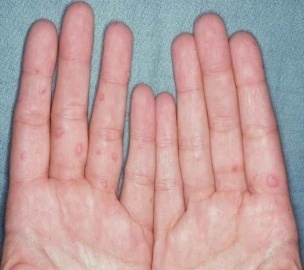
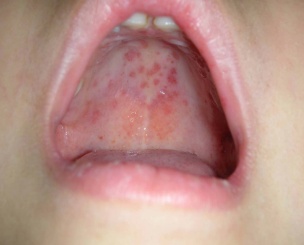
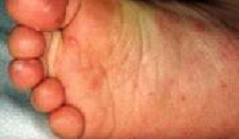
How is HFMD spread?
HFMD is a contagious disease. The viruses that cause HFMD can be found in the nose and throat, fluid in the blisters and faeces of an infected person.
The viruses spread from the infected person to another by
- Coughing or sneezing
- Close contact
- Contact with the blister fluid or faeces
- Sharing of eating utensils or personal belongings such as towels, toothbrush
- Touching of contaminated surfaces or objects
A person with HFMD is most infectious during the first week of illness.
How is HFMD diagnosed?
- Although laboratory tests that detect the viruses are available, HFMD is usually diagnosed clinically by looking at the signs and symptoms of the disease.
- Laboratory tests are not required in most instances.
How is HFMD treated?
- HFMD is treated symptomatically.
- There are no specific medicines that can kill the viruses. Healthcare providers prescribe fever medicines and pain killers to reduce the fever and pain in the mouth. It is important to give the child adequate fluids during the course of illness.
- The infection usually resolves after 7-10 days when immunity develops in the body.
How to manage HFMD at home?
Children with mild disease can be managed at home:
- Ensure adequate rest
- Serve medicines as prescribed to relieve the fever and pain
- Encourage the child to drink plenty of fluids
- Watch out for signs and symptoms of severe disease
Is HFMD dangerous?
HFMD is generally a mild viral infection.
Rarely, some viruses, especially EV71, may affect the brain and the heart. The severe form of HFMD may lead to permanent damage to the body or even death.
How to recognize severe disease?
When HFMD affects the brain or the heart, the child may experience these symptoms:
- Headache, giddiness or stiffness of the neck
- Irritability, drowsiness or disorientation
- Fits or abnormal jerky movements
- Fast breathing or turning blue
- Lethargy
A child with HFMD demonstrating any of these symptoms needs to be admitted to the hospital immediately.
Can HFMD be prevented?
At this moment, there are no specific medicines or vaccine for HFMD. Hence, prevention is important to reduce the risk of getting it.
HFMD can be prevented by these measures:
- Keep the hands clean by frequent handwashing, especially after contact with a person with HFMD or soiled objects
- Avoid close contact with a person with HFMD
- Avoid sharing of eating utensils or other personal belongings
- Avoid touching the eyes, nose or mouth after contact with a person with HFMD
Keep the environment clean by frequent cleaning and disinfect the frequently touched areas when someone has HFMD
How to keep other children safe?
Outbreaks of HFMD have occurred in childcare centres, kindergartens and schools. If your child has HFMD, you can help to protect other children from getting the same illness by:
- Informing the childcare centres, kindergartens or school
- Keeping your child away from childcare centres, kindergartens, school and other public places
- Keeping the child’s belongings clean and not sharing eating utensils or other personal belongings
Frequently disinfecting frequently touched surfaces or objects with diluted bleach.
| Last Reviewed | : | 28 August 2020 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Charm Kwai Cheng |
| Accreditor | Dr. Revathy Nallusamy | |
| Reviewer | : | Dr. Zainab bt. Kusiar |







