Introduction
Hearing is one of the important senses for the development of speech and language. Hearing enables an individual to listen, to detect, to discriminate, to interpret as well as to understand the environmental sounds and speech sounds. Babies who are born with hearing impairment, their speech and language development will be affected. The critical age for a child to develop speech and language is from birth until 4 years of life (Yoshinago-Itano; 2000).
Hearing screening is very important. If hearing loss is detected in a newborn baby, the severity of the impairment can be determined and the habilitation process can be implemented as early as possible. Therefore the effect of hearing loss towards the speech and language development can be reduced.
Newborn Hearing Screening Test
Newborn hearing screening is a basic test to identify babies that may have hearing impairment.
There are two types of newborn hearing screening :
- Universal newborn hearing screening : The hearing screening test is performed to all newborn babies. Currently, this type of hearing screening is only implemented in some hospitals.
- High-risk newborn hearing screening : The hearing screening is only performed to babies with presence of high factors to develop hearing loss as listed in Table 1. This type of hearing screening is being implemented in most of the government hospitals.
Table 1 : Indicator list for high-risk babies (Joint Committee on Infabt Hearing, 1994).
- Family history of congenital sensorineural hearing loss.
- Hyperbilirubinemia (jaundice).
- Congenital infection (toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes).
- Craniofacial anomalies (kecacatan pada muka) termasuk keabnomalan morfologi pada cuping telinga dan salur telinga.
- Craniofacial anomalies (facial defect) including abnormality morphology of ear lobe and ear canal.
- Bacterial meningitis.
- APGAR score of 0 to 4 at 1 minute or 0 to 6 at 5 minutes.
- Perinatal Use of ototoxic medication.
- Mechanical ventilation for 5 days or more.
- Stigmata or other findings related to syndrome known to get conductive or sensorineural hearing loss.
- Diseases or condition of babies that requires admission to Neonatal Infant Care Unit (NICU) for 48 hours or more.
When is the appropriate time to undergo for hearing screening test?
Hearing screening is best done before the baby is discharged home. Hearing screening that is done shortly after birth may be influenced by the presence of vernix/amniotic fluid in the bay’s ear canal. The hearing screening is also easy to be done while baby is sleeping or after feeds.
How is the test done?
There are two types of hearing screening test that can be implemented in order to detect hearing loss and that are:
- Otoacoustic Emission test (OAE)
This test is able to detect any abnormality or defect in the auditory system. A suitable probe that suit with child’s ear canal is inserted into the ear canal. The probe that is connected to the testing machine will produce soft and painless sound. In a normal child, the hearing organ will detect the sound signals and in return, an acoustic signals is produced which will be detected by the machine.
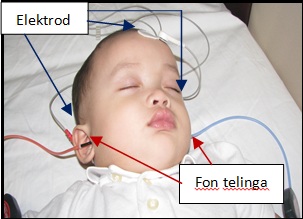
- Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR)
This test is to measure the function of the hearing and including the hearing nerve. Areas behind the ear and the forehead are cleared of sebum and sweats. Conductive Gel are applied followed by conductive electrodes. Sound stimulus is delivered via earphone and the electrodes will detect the baby’s brain wave as a response towards the sound.
There are three types of result that may be obtained ;
- PASS
- REFER or
- NOISE
What is the meaning of the test result?
- PASS
Baby’s hearing is normal. However, babies born with the high-risk factors to have hearing loss(refer to table 1) parents are advised to bring the baby for a periodic 6 monthly hearing screening until the child is 3 years old. This is done to exclude late onset hearing loss. - REFER
Baby’s hearing organ may not be normal and hearing loss is suspected. The baby needs to repeat the hearing screening or undergo the diagnostic hearing test to confirm the hearing loss that has been detected. Please ensure that your baby is given a follow-up appointment for a repeat confirmatory test. - NOISE
This is a situation whereby a definitive result cannot be produced. The result is not accurate due to environmental noise of the testing room or the baby does not stay quiet during the testing (crying, moving). The hearing screening needs to be is repeated until the PASS or REFER result is obtained.
Pediatric Hearing Screening Test
There were other hearing screening tests that can be done in order to identify the presence of hearing loss ;
- Distraction test
This test is done on babies who have developed strong neck support baby. The baby will be seated on the mother’s lap while being distracted by the father from the front without making any noise. Sound stimulation from sound maker such as rattle, chime bar is produced from behind (distance between 50-100cm) each ear away from his/her visual field. Baby’s response for example a head turn will be observed. Responds towards the softest sound will be recorded as the minimum level of sound that the child can hear. The test will be then repeated to the other ear.

- Visual Reinforcement Test (VRA)
Baby as early as 6 months of age to two and a half years old child can be tested with the VRA test. This test needs the child to turn their head towards a lighted, moving or sounded toys, object or picture that is given by the tester after the child hears a sound. The sound is delivered via an earphone or speaker. Responds to the softest sound that is heard by the child will be recorded as the child’s hearing threshold.

- Play Audiometry test
This test can be used to test the hearing of children aged between two and a half years to seven years old. This test requires a higher thinking from the child. Sound is delivered via the ear phone and the child needs to respond through play technique such as putting balls into a basket picture or object arrangement every time he or she hears the sound. The child’s hearing threshold depends on his/her response to the measured sound stimulation.

- Pure Tone Audiometry test (PTA)
PTA test is used for testing children’s hearing aged seven years old and above. PTA is also used to test the adults hearing. The child wears an ear phone and sound is then delivered. The child needs to push a button or raise his/her hand each time the sound is heard. Responds toward the softest sound that can be heard will be recorded as the child’s hearing threshold.

CONCLUSION
All the tests listed above are only a screening test. The purpose of the test is to identify whether a child’s hearing is normal or not. Children with an abnormal result may have hearing problem and need to undergo further diagnostic/test to determine the level of the hearing loss.
If your child is confirmed to have hearing loss, he/she will need to go through a full ear, nose and throat evaluation by the Otolaryngology doctor, audiologist and speech therapist.
Options of definitive treatment and rehabilitation plan will be discussed and offered by the respective member of the team.
| Last Reviewed | : | 16 January 2014 |
| Writer | : | Pn. Nurul Ain bt. Abdullah |







