Hydrocephalus is the abnormal and excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricles.
Ventricles are the spaces in the brain, filled with CSF. (Figure 1)
CSF is the clear and colourless fluid, containing sugar, salt and cells.
The important functions of CSF are:
- protecting the brain and spinal cord from injury
- nourishing the brain cells
- carrying waste from the brain cells
Under normal circumstance, CSF is constantly produced in the ventricles, then moving around the brain & spinal cord and finally gets absorbed in the space surrounding the brain. The circulation of CSF follows certain pathway. The new production of CSF will replace the absorbed CSF.
Hydrocephalus occurs if there is blockage of the flow of CSF or the production of CSF is more than the absorption.
This will lead to excessive building up of CSF in the brain spaces and put pressure to the brain.
Types and causes
- Congenital versus acquired
- If a child born with hydrocephalus, he / she is said to have congenital hydrocephalus. E.g. : narrowing of the pathway of CFS flow (aqueduct stenosis)
- However, if it develops after birth, then it is acquired hydrocephalus. E.g. : post-bleeding or infection in the brain, brain tumour
- Communicating versus non-communicating
- Communicating hydrocephalus occurs when the production of CSF is more than absorption (usually due to poor absorption of CSF).
- Non-communicating hydrocephalus occurs when there is blockage of the pathway of CSF flow.
Symptoms and signs
The signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus in a baby and a child may be different.
In a baby, he / she may have some or all the following features:
- Increased tiredness, excessive sleepiness
- Excessive irritability
- Poor feeding or vomiting
- Fits
- Too much increment of head size (Figure 2)
- Bulging of the soft spot on the top of the head (fontanelle)
- Slowness in achieving developmental milestones
In a child, he / she may have some or all the following features:
- Headache
- Feel like wanting to vomit or vomiting
- Blurred vision
- Excessive tiredness
- Unsteadiness in walking
- Fits
- Changes in behavior or school performance
If a child is suspected to have hydrocephalus, he / she will need urgent medical attention.
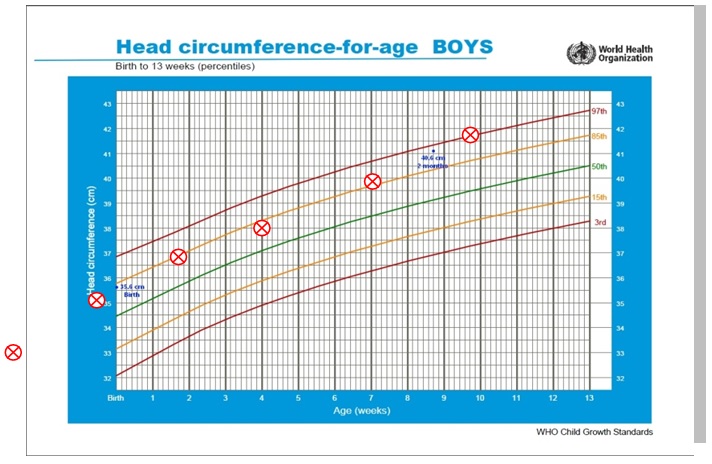
Figure 2: ![]() Excessive increment of head size for a baby boy – one of the sign of hydrocephalus
Excessive increment of head size for a baby boy – one of the sign of hydrocephalus
Diagnosis
Doctor will order a brain scan to confirm the diagnosis of hydrocephalus. Various choices of brain scans may be ordered which include an ultrasound, CT-scan or MRI scan. The doctor will discuss with you on the advantages and disadvantages of these choices of scans.
These brain scans will not only help doctor confirm the diagnosis but also find out the cause of hydrocephalus.
Treatment
If a child is confirmed to have hydrocephalus, he / she will be referred to a neurosurgeon (doctor specializing in brain operation). The neurosurgeon will decide if your child needs any operation.
Most of the children with hydrocephalus will require operation. The goal of the operation is to reduce the pressure inside the brain by providing an alternative pathway for the CSF to be drained.
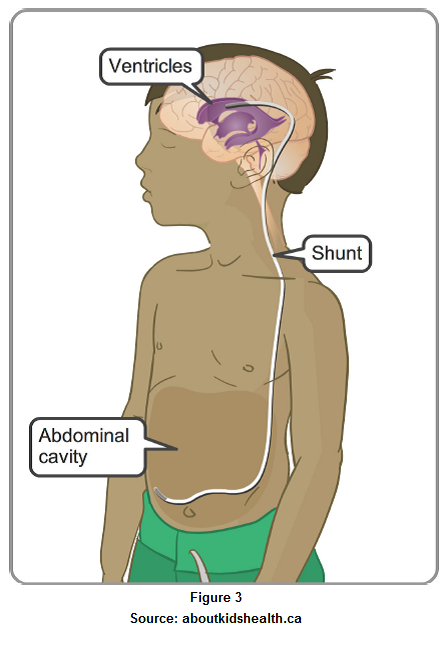
The most common treatment is insertion of a shunt, draining the extra CSF from the brain spaces into the cavity of belly where it will be then get absorbed. This is called “ventriculo-peritoneal shunt” or “VP shunt”. (Figure 3)
The VP shunt may get blocked or infected.
If the shunt is blocked, the child may have the symptoms and signs same as those of hydrocephalus prior to insertion of the shunt. If the shunt has a reservoir, you can check if the reservoir is compressible or refilled after being compressed, to assess the function of the shunt.
If the shunt is infected, in addition to the symptoms and signs of blocked shunt, your child may have fever, stiff neck, belly pain or redness / pain along the pathway of the shunt.
Your child will need urgent medical attention if blocked or infected shunt is suspected.
| Last Reviewed | : | 27 September 2016 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Teh Chee Ming |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Azni b. Yahya |