Injuries to milk teeth tend to occur rather frequently in a young child who is just learning to walk, run and climb. Dental injuries can also happen as a result of falling off the bicycle as well as road traffic accidents.The injuries are classified according to severity and also to help the clinician to manage them accordingly.
What are the Types of Injuries That Can Occur?
- Concussion
- There is trauma to the tooth but as the impact is minimal, there are no obvious changes to the teeth.
- No immediate treatment is necessary. The affected tooth would need to be monitored by your dentist.
- Occasionally, the affected teeth may change colour to a greyish hue or dark yellow. This usually does not cause any problems to the child. All the same, if the child experiences dental pain, or if there is an abcess in the gum, the child would need to see a dentist.
- Subluxation
- The impact onto the tooth has resulted in tooth mobility. There will be some bleeding around the gums, but the tooth is not displaced from its original position.
- The impact onto the tooth has resulted in tooth mobility. There will be some bleeding around the gums, but the tooth is not displaced from its original position.
- Luxation
- The tooth has been displaced during injury
- The tooth has been displaced during injury
- Avulsion
- The tooth has been completely knocked out of its socket.
- The tooth has been completely knocked out of its socket.
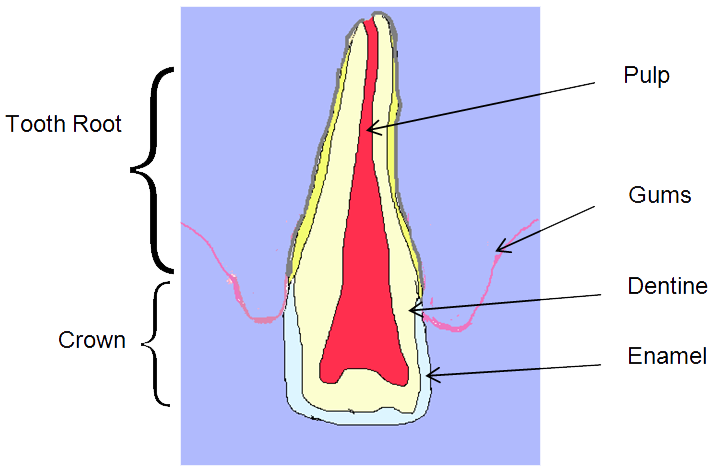
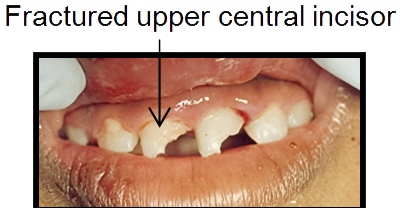
- Crown fracture
- Root fracture
- The tooth is fractured at or below the level of the gums. The tooth may be loose and there may be some bleeding of the gums as well.
Management of Injured Milk Teeth
Injuries to the milk teeth may result in trauma to the permanent tooth germs which are developing close to the roots of the milk teeth.
Therefore, parents are advised to seek dental consultation when the child sustains trauma to the milk teeth as well as if the child has delayed development of the permanent teeth.
Mobile or displaced teeth (Subluxation and Luxation)
Treatment would depend on the severity of the injury. If the injured tooth is very mobile, then it is best to extract it. If the tooth is slightly displaced and does not affect function, then it may be observed and extracted only when symptomatic.
In this situation, the milk tooth has to be extracted as it will affect function (eating, speech).
Milk teeth need not be repositioned and splinted as is done for the permanent teeth.
An avulsed primary tooth should not be replaced into its socket. The tooth should be found. If unable to find or locate the tooth, the child would need to be examined to ascertain if there is a possibility that the child may have swallowed the tooth, or inhaled the avulsed tooth.
The treatment would depend on the severity of the fracture. If the fracture involves the dental pulp, it may be better to have -the tooth removed. If appropriate, and the child is co-operative, root canal treatment may be carried out. Your dentist will be able to advise appropriate treatment after conduction a thorough examination.
Reference
- U Glendor, Epidemiology of traumatic dental injuries – a 12 year review of the literature. Dental Traumatology 2008; 24:603-611
| Last Reviewed | : | 11 May 2015 |
| Writer | : | Dr. Yogeswari a/p Sivapragasam |
| Accreditor | : | Dr. Laila bt. Abd. Jalil |