Introduction
Intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) involves injecting a single sperm directly into an ovum under a microscope with manipulator in order to fertilise the egg and transferred to the woman’s womb.
Indication
Procedure ICSI is the best choice for fertilization if the male partner has low number of sperm, poor morphology and motility, and failure in IVF attempts.
For those with no sperm in ejaculation or had problems in obtaining an erection and ejaculation, sperm will be collected from the testicles
History
Technique of injecting a single sperm into an ovum, were first develop in early 1980s. In 1987, the world’s first micro injection technique into the zona pellucida (the outer layer of the egg) were demonstrated using ovum and sperm of mice.
However subzonal microinjection was low success in human compare to intracytoplasmic injection. The first live birth resulting from the procedure occurred in 1992 by a group of Belgian scientist. Revolution of the intracytoplasmic technique related to male factor infertility.
Procedure
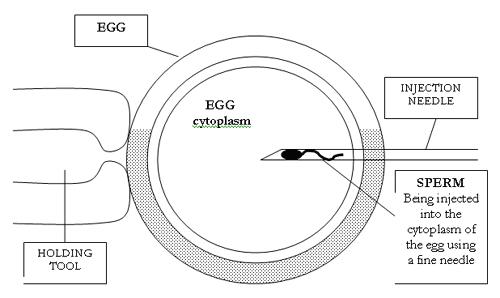
ICSI procedure is done under a microscope with micromanipulation setting. A holding pipette stabilizes the mature oocyte with gentle suction applied by a microinjector. From the opposite side, a hollow glass micropipette is used to collect a single sperm, having immobilised it by scratch its tail with the point of the micropipette. The oocyte is pierced through the oolemma and directed to the inner part of the oocyte (cytoplasm). The sperm is then released into the oocyte. In the picture, oocyte with an extruded polar body at about 12 o’clock indicating its maturity. The polar body is positioned at the 12 or 6 o’clock position, to ensure that the inserted micropipette does not disrupt the spindle inside the egg. After the procedure, the oocyte will be placed into cell culture media and checked on the following day for signs of fertilization.
ICSI usually performed as the same procedure as IVF started from the stimulation of ovaries until the oocyte retrieval.
Success rate
High fertilization rate in ICSI technique when compared to IVF due to natural fertilization sperm compete in IVF. However the pregnancy rate and live birth of both ICSI and IVF is more less the same with maternal age related.
Complication
ICSI is consider safe and effective therapy for male factor infertility, but may carry an icreased risk for the transmission of selected genetic abnormalities to offspring. There is also not enough evidence to say that ICSI procedures are safe in females with hepatitis B in regard to vertical transmission to the offspring. Since the puncture of the oocyte can potentially avail for vertical transmission to the offspring.
Religious objectio ns
In the past there were incidences where embryos have been mixed up. Human fertilization and embryology authority (HFEA) suggested a double witness system to keep the chances of this mix up to a minimum.
Many arguments about how IVF work against natural conception. Many religions believed that infertility is God’s will and to go against it is wrong. There also further objection on the number of embryos involved in IVF or ICSI. To give a couple the best chances for a pregnancy multiple embryos are produced and with many discarded if they aren’t good in quality. For some religious groups for instance, each embryo represents a life, so the disposal of embryos is considered in the same light as abortion.
However, the arguments are lighten up as we have social and religious convictions as well as beliefs about the basis of the reproductive desire and needs of humans.
| Last Reviewed | : | 22 October 2014 |
| Writer / Translator | : | Siti Norfaizah bt. Wagiman |
| Accreditor | : | Krishnan a/l Kanniah |