Introduction
In death investigations, the cause, mechanism, and manner of death are determined through postmortem examinations. Autopsy findings provide valuable clues regarding how and why a person died. This article specifically focuses on the manner of death.
Understanding the Cause and Mechanism of Death
Before establishing the manner of death, it is essential to comprehend the cause and mechanism of death. The cause of death refers to a disease or injury that initiates the events leading to death, while the mechanism of death is a physical abnormality produced by the cause of death that is incompatible with life.
For example, consider the scenario:
“Michael set David’s house on fire. David stabs him in the chest. Michael dies on the way to the hospital.”
In this case, the cause of death is a stab wound to the chest, and the mechanism of death is excessive blood loss.
Manner of Death
The manner of death is the underlying circumstance that sets in motion a physiological process culminating in a person’s death. If a person dies solely due to a natural disease, such as diabetes, the manner of death would be “natural.” However, if the physiological process leading to death is a result of circumstances that cause injury, the manner of death is no longer considered natural. It may be classified as an accident, homicide, or suicide.
For instance, consider an incident where a pedestrian was struck by a vehicle from behind. If it was unintentional, caused by the driver trying to avoid a pothole, the manner of death would be “accident.” On the other hand, if the driver purposely ran into the pedestrian after a dispute, the manner of death would be “homicide” since the driver intended to cause harm using the car as a weapon.
Categories of Manner of Death
According to the Guidelines for the Determination of Manner of Death by the Illinois Coroners and Medical Examiners Association, the manner of death is categorized into five standardized categories:
- Natural: Death due to interruption or failure of body functions from aging or disease (e.g., ischemic heart disease, pneumonia).
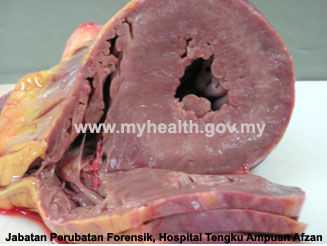
Natural Death: Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease - Accidental: Death following events where there was no intent to cause harm or death (e.g., road traffic collisions, occupational-related deaths)..
Accidental Death: Motor vehicle accident -
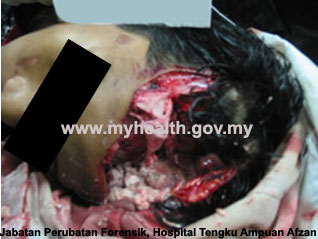
Homicidal: Death of one person caused by another person with a motive behind the killing (e.g., slash wounds, multiple stab wounds, manual strangulation).

Homicidal Death: Murder -
Suicidal: The act of killing oneself (e.g., hanging, jumping from high places, poisoning).

Suicidal Death: Carbon Monoxide Poisoning - Undetermined: When the cause of death cannot be established as natural, accidental, suicidal, or homicidal (e.g., decomposed bodies where the cause of death cannot be ascertained).
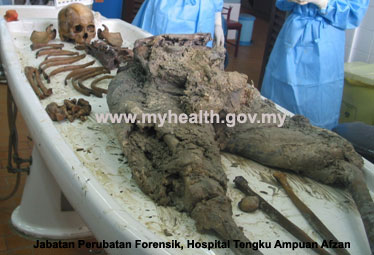
Undetermined Death: skeletal remains
Significance of Manner of Death
Establishing the manner of death is crucial for various parties involved in a death investigation, including:
- Family/Relatives: Answers to questions regarding the manner of death can alleviate grief and distress. It also impacts insurance claims and the stigma attached to suicide.
- Suspects: The manner of death helps determine whether to charge or discharge a suspect based on the intent behind the death.
- Police Force: The manner of death guides the level of investigation required.
- Court of Law: Criminal charges are specific to the manner of death, affecting the penalties upon conviction.
- Organizations: In occupational or industrial deaths, the manner of death may prompt investigations to assess contributing factors.
Conclusion
Determining the manner of death is essential for the well-being of the deceased individual’s family and relatives and to serve justice in the legal system. It ensures the protection of the deceased’s rights and provides closure to those affected by the death.
References
-
Photographs courtesy of the Department of Forensic Medicine, Hospital Tengku Ampuan Afzan, Kuantan, Pahang.
-
Cox WA. Cause, mechanism, and manner of death. Dalam: Forensic Medicine with Dr. Cox. 2009. forensicmd.wordpress.com
-
Departments of Forensic Medicine and Psychiatry & Mental Health. National Suicide Registry Malaysia Preliminary report: July – December 2007. Kuala Lumpur: Suicide Registry Unit, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, 2008.
-
DiMaio VJ, DiMaio D. Forensic pathology, edisi ke-2. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2001.
-
Illinois Coroners and Medical Examiners Association. Guidelines for the Determination of Manner of Death. 2007.
| Last Reviewed | : | February 2024 |
| Writer | : | Suhailey bt. Md Noor |
| Reviewer | : | ChM. Dr. Khairul Adli bin Nikman |







