Modified Terminal Digit Failing System (MTDFS)
Introduction
Medical Records Management efficiently in a hospital is emphasized in order to reduce the waiting time to keep track of patient records, facilitate the process of preparation of medical reports, can track the location of the Medical Record Patient, ensure continuity of care, isolation record inactive for disposal easier to perform also had misfile record medical deductible.
According to a letter from the Medical Development Division Bil.KKM 87 / P1 / 11/1 (90) dated February 9, 2007 issued by the Ministry of Health has ordered the management of Patient Medical Record using MTDFS (Modified Terminal Digit Filing system) implemented in all hospitals / institutions of the Ministry of Health over the term of the 9th Malaysia Plan (2006 – 2010).
Concept Of Ministry Of Health
One Patient One Folder ‘or’ Single Folder’ in accordance with the Circular of the Director General Health Bill. 3/2005 Guidelines on Medical Records For Hospitals Ministry of Health Medical Records means all about the care and treatment of patients is stored and recorded in a folder even if the treatment is given by a multidisciplinary include inpatient and outpatient records. Outpatient Records is a record of professional clinics, not including patient records outside of the Outpatient Department and the Emergency Department.
National Registration Identity Card (NRIC)
MTDFS concept allows folders filed evenly into the compartment where NRIC read from right to left as shown below:

i. Arrangement File Inside The MTDFS RCC
Or
ii. Arrangment File Inside Pegion Hole
Arrangement From Right To Left

Or
Arrangement From Left To Right
Color Code To Be Used For Medical Record Folder
10 color codes of the numbers 0 through 9 has been selected by the Ministry of Health as follows:
Example Label File


Work Process Towards Applying Records Management MTDFS
A. Transfer Existing Patient Records
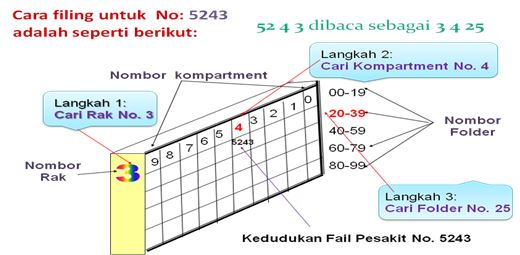
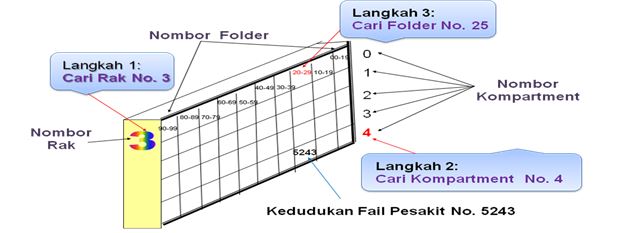
- Identifying rack for primary digit (the last digit number K / P) for example No. 3 in NRIC / P 680701-07-5243. Number 3 is named the number Shelf.
- Identify parcels for secondary-digit (digit 11 numbers K / P) for example No. 4 in NRIC / P 680701-07-5243. No. 4 is named Compartment numbers.
- Identify parcels for secondary-digit (digit 11 numbers K / P) for example No. 4 in NRIC / P 680701-07-5243. No. 4 is named Compartment numbers.
- Identify the folder for tertiary digit (digit to numbers 9 and 10 K / P) for example No. 52 in NRIC / P 680701-07-5243. Read from right to left, the number 25 is called Folder numbers.
- Label the rack with the rack number, compartment number and the number of folders that have been identified.
- Separate medical records by numbers shelf, compartment number and the folder number.
- Separate medical records that are not active for the purpose of disposal.
- Citing medical records, medical records were found by the concept of ‘one patient in one record.
- File a medical record by MTDFS methods, as described in para 4.
- The composition of the file in the pigeon hole shelf is as shown in the fifth.
B. The Filing Of A New Patient Record
- Look for the earlier entry in the computer through SMRP program for each hospital discharge.
- Track medical records long if not a new field and collate the medical records of patients in the new folder as shown in the seventh.
- For the first time the medical record is created, providing a new patient folder as shown in the 7
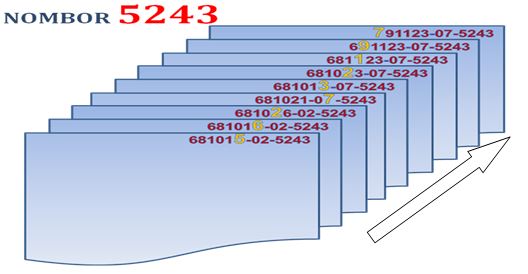
- Paste color label to the patient’s folder:-
-
- color-coded racks (the right side of the folder first)
- color-coded compartment (second box)
- The color code of (the last).
* Please refer to the 6 to the color code.
-
- Color Code Year (according to the figures of the last year, for example in 2008, the color code 8) will be changed to the color of the current year for the next year if they have the medical records of the following year.
- Originally filed medical records in accordance with the method MTDFS as shown in para 4.
- The composition of the file in the pigeon hole shelf is as shown in the 5.
Advantanges MTDFS
- Easy to trace
- Safe keeping space
- Consistent filing
Disadvantages MTDFS
- Cost very high
- Need skill person to trace medical record
- Suitable for place that have big space
Conclusion
Quality of medical records management requires the cooperation of all parties. Medical Records Unit at the hospital was given the mandate and the responsibility to ensure the success of Medical Records Management and Filing in accordance with the ‘Modified Terminal Digit Filing System’ (MTDFS). Members of the Medical Records Unit needs the support and approval of the Director of the Hospital of the financial allocation in the purchase of the patient folder, label and color code the payment of overtime, including the cooperation of specialist clinics in the success of this program.
References
- Garispanduan Pengendalian dan Pengurusan Rekod Perubatan Pesakit Bagi Hospital – hospital dan Institut Perubatan Bil 17/2010.
- Surat Bahagian Perkembangan Perubatan bil.KKM 87/P1/11/1(90) bertarikh 9 Februari 2007
- A modified terminal digit filing system enabling the use of double colour coding: Hersey AT Med Rec Health Care Inf J. 1979 Feb.
- Best Practices for Terminal Digit Filing By Chris Dimick on Nov 18, 2009
| Last Reviewed | : | 11 August 2017 |
| Writer | : | Pn. Hasnah Binti Ismail |
| Translator | : | Pn. Hasnah Binti Ismail |
| Accreditor | : | Pn. Siti Ajar Binti Baharim |







