Introduction
Medicines are chemicals used to treat or prevent diseases. Certain disorders or health problems can also be controlled with medicines. There are various delivery routes of medicines; taken orally, applied as local application, as injection, inhaled or administered into body orifices.
Several types of pharmaceutical dosage form available for oral medicines are as follow:
|
Pharmaceutical dosage
|
Features
|
Shape
|
|---|---|---|
| Tablet |
Consists of various shapes Scored tablet can be cut into halves |
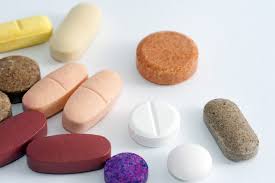 |
| Pil |
Spherical shape Cannot be cut |
 |
| Capsule |
Consists of body and cap Cannot be cut |
 |
| Soft gelatin capsule (softgel) |
Consists of oval shell filled with liquid Cannot be cut |
 |
| Syrup |
Liquid form Need to be measured with measuring device before taken orally |
 |
|
Suspension liquid |
Should be shaken well before taken. Need to be measured with measuring device before taken orally |
 |
| Powder or granule |
Powder, granules or crystal form. Should be diluted with water or fruit juice before taken
|
 |
Certain medicines specifically should be taken before or after food.
How foods influence the efficacy of medicines
Food can influence medicines efficacy through several ways:
- Food stimulates production of gastric acid.
Stomach will produce acid to enhance food digestion.Certain medicines such as erythromycin, isoniazid and azithromycin will compromise when exposed to acidic condition. Acidic environment will cause the medicine to degrade. Consequently, medicine absorption will reduce and less medicine will be absorbed into body. As a result, the medicine will become less effective. Hence, such medicine should be taken during empty stomach.
However, there are also medicines which require acidic environment to optimize absorption such as ketoconazole and itraconazole. Such medicines should be taken after food.
- Food can remove active ingredients of medicine through chelation process
Certain food contain mineral such as calcium and ferum. Certain medicines such as biphosphonates and ciprofloxacin will react and bind themselves to the minerals. This process is called chelation process and will cause the medicines to deactivat. Thus, such medicines should be taken before food.
- Absorption of certain medicines enhanced by bile secretion
Bile secretion enhances absorption of certain medicines such as tacrolimus, carbamazepine and griseofulvin, thus such medicines are suitable to be taken after food.
- Rate of gastric emptying
Fatty food will reduce rate of gastric emptying. Reduction in rate of gastric emptying will reduce absorption rate of the drug.
- Physical adsorption
Certain medicines such as digoxin are easily adsorbed on high-fiber foods. Thus, such medicines should not be taken with high-fiber foods.
- Food effects on central nervous system
Food and beverages containing alcohol will cause depression on central nervous system. Certain medicines such as chlorpheniramine, hydroxyzine, dexchlorpheniramine and triprolidine can cause sleepiness and drowsiness. Thus, such medicines should not be taken with alcoholic foods or beverages. Alcohol will potentiate the effects of the medicines.
Medicines properties and how to take the medicines
Properties of the medicines will affect whether the medicine are suitable to be taken before or after food:
- Nausea and vomiting induced by the drugs
Certain medicines such as allopurinol, bromocriptine and combination of levodopa + benserazide can induce nausea and vomiting. Such medicines are suitable to be taken after food to reduce the side effects.
- Irritation, difficulties in digestion, gastric ulcer induced by the drugs
Certain medicines can irritate the stomach. Thus, such medicines are suitable to be taken after food. For example: acetylsalicylic acid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as diclofenac and ibuprofen and corticosteroid such as prednisolone and dexamethasone.
- Medicines used to treat gastric acid reflux and digestion problems
Antacid is a medicine used to treat gastric acid reflux and digestion problem which happens due to secretion of gastric acid after food entering the stomach. Thus, antacid should be taken immediately after food.
- To avoid medicines removed by foods.
Medicines used to treat oral thrush such as nystatin syrup and miconazole gel should be used after food. Food will remove the medicines which subsequently reduce the effectiveness of the medicine.
- Food improves drug absorption
Medicines such as ritonavir, saquinavir, and nelfinavir are more easily absorbed with the presence of food such as medicines which are suitable to be taken after food.
- Diabetic medicines
Diabetic medicines such as metformin and gliclazide should be ideally taken with not too long after or before food. This is to avoid hypoglycaemia and at the same time to ensure glucose blood level is not too high after food.
How to know whether the medicine should be taken before or after food?
Instruction on how to take medicine is usually printed in the product leaflet. If you are not supplied with such leaflet, you may obtain the information from pharmacists.
Consumption of medicine before or after food will influence the medicine bioavailability of the medicine in our body. Low bioavailability will reduce the effectiveness of the medicine. Hence, it is important to take the medicine in the right order.
References
- McLahlan A & Ramzan I (2006) Meals and medicines. Australian Prescribers, 29, 40-42.
- NHS (2015) Why must some medicines be taken with or after food? Retrieved Mac 10, 2016, from http://www.nhs.uk/chq/Pages/866.aspx?CategoryID=73
| Last Reviewed | : | 27 October 2017 |
| Writer/Translator | : | Khairul Naim bin Zainal Abidin |
| Accreditor | : | Munira bt. Muhammad |







